Updated July 6, 2023
Meaning of Autarky
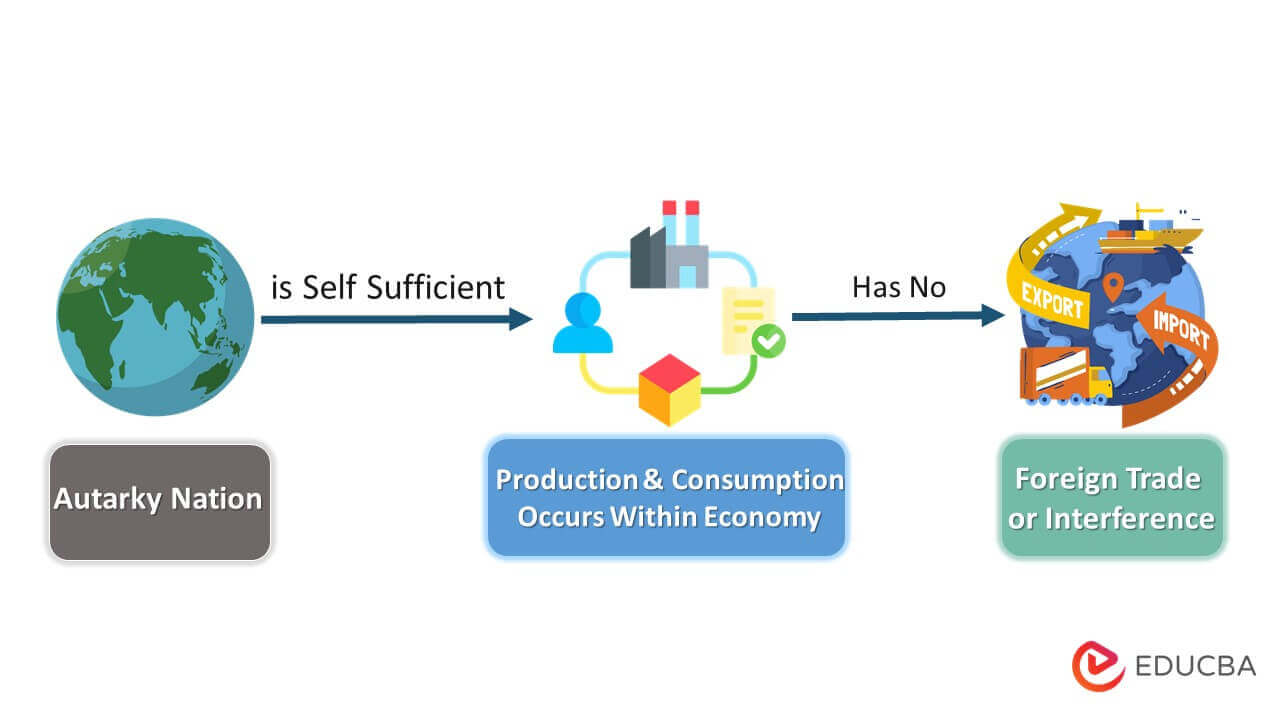
Autarky is an economic system where the nation is self-dependent, i.e., producing all goods/services within the country and not allowing foreign trade (export & import). For Example, North Korea is an autarkic nation that refrains from foreign trade and is self-sufficient in every economic aspect.
A total autarky or closed economy is when no money flows or trades with other countries. When a nation adopts autarky, it must fulfill its requirements by itself, as it does not export or import its goods/services. The production is for domestic use.
Key Highlights
- Autarkies are closed economies that are self-sufficient without any foreign influence.
- The autarkic nations produce and consume their products without the help of any external sources.
- The Ricardian Model equilibrium represents a barter system where products are exchanged not in lieu of money but for other products.
- This economy achieves financial freedom by cultivating, producing, and trading its goods domestically, allowing no international trade.
History
- Modern autarky mainly dates back to German economist Friedrich List‘s publication of “The National System of Political Economy” (1841).
- List gathered knowledge from Friedrich Wilhelm and Joseph Schelling and kept on attempting to improvise and modernize the economic philosophies of Alexander Hamilton.
- In his book, List argued that national interests should always come first, but his views ran directly against the principles of free commerce and national autonomy in international relations.
- Hegelian philosophy, at its foundation, focused on the interdependence of political and economic forces with the nation-state. It stated that doing business outside constituted treason since it endangered the state’s long-term survival and development.
- This idea faded away until its rebirth during the 1929 stock market disaster. The government believed that enacting laws like the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act, which imposed high duties on imports, would rescue the nation from the deep economic slump.
Examples
#1: Germany
Nazi Germany (1933–1945) considers having adopted autarky. The Nazis tried to gain power, consolidating control by expansion in the surrounding countries, to maximize trade within their economic blocs and stop the same with outsiders.
#2: North Korea
North Korea is also considered an example of autarky in today’s modern economy. This is because the country adopts the government ideology of “Juche” (self-reliance), which is concerned with maintaining its domestic economy in the face of isolation.
North Korea is not entirely a closed economic state. They conduct trade with other allied nations like China and Russia.
#3: Rojava
Rojava in Northern Syria is self-sufficient and does not engage in much foreign trade, adhering to Murray Bookchin’s theory of autarky. Here, individuals work with the available resources, and there is no private ownership.
Present World Examples
With the two new omicron variants, China might return to being an autarkic nation, shutting down all international trade and facing a lockdown (2022-2023).
Autarky Price
- The autarkic price of an item is its production cost and the selling price in an autarkic economy.
- In a closed economy, the cost of production is the price charged for the good.
- If the price is higher compared to other countries for the same item, then it is a failure of the economy as an autarky.
Opponents of Autarky
- One of the leading critics of this system is Adam Smith, the founder of modern economics.
- Smith advocated for free trade and opined that the nations should manufacture only the things with a clear competitive edge and exchange the others.
- Some countries might have no absolute advantage if they overproduce any product in an economy.
- Given the country’s resources, they have a comparative advantage or a more optimal opportunity cost of producing fewer goods than others.
- Producing these and trading the other would also add to the overall benefit of all the nations.
Demerits
- Very few nations successfully achieve self-sufficiency; in most cases, it is practically impossible.
- To fulfill the demands and desires of the consumers, an autarkic nation has to produce a wide range of goods that might not have a mass appeal.
- International trade can only suffice the demand for goods not produced in the domestic market.
- A group of producers cannot have expertise in every field—so low-efficiency results in high prices.
- Lack of proper economic resources (or production variables) might be challenging.
- It brings about isolation from international relations that might adversely affect national emergencies.
Characteristics
- In such a closed economic system, the business advantage depends on the comparative edge of any article.
- Since there is zero foreign influence, it is the ultimate form of protectionism.
- Productivities within the same industry vary among nations, indicating that trade and specializations are partly dependent on technological disparities.
- It makes way for a barter system that helps to maintain a balance between producers and consumers.
Ricardian Model – Autarky: Equilibrium
The Ricardian model is a representation of the barter system. Therefore, instead of using currencies, people can use goods to purchase other goods or products. It can help maintain autarky within independent industries.
Example
Suppose Adam and Mia work at a cheese factory. They receive their salary in the form of cheese and not in terms of money. They can then exchange some portion of the cheese with other products sold in the market. Thus, any person can follow this method and satisfy all their needs, keeping the currency mode out of the picture.
Final Thoughts
Autarky has appeared multiple times throughout economic history, yet this system has repeatedly failed. Most economists disagree with it, and it sometimes results in resource underutilization. It does not help in economic growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is autarky?
Answer: Autarky is a system of national self-sufficiency and limited trade in an economy. Such economies are independent and in no way affected by any foreign interference.
Q2. Is autarky beneficial?
Answer: Autarky benefits economically strong countries with zero foreign influence on their economies, helping them grow stronger.
Q3. What is the motivation for adopting autarky?
Answer: Securing the supply of essential goods and a desire to lessen overall dependency on other countries are typically the driving forces behind an autarky strategy. Reduced dependence on other countries minimizes the scope of political and economic rivalry, depending on the type of political organization in a nation.
Q4. Which countries are autarky?
Answer: Nazi Germany and North Korea are two nations that have an autarkic economy with no foreign influence. Also, Rojava, in Northern Syria, is an Autarkic nation.
Recommended Articles
This is an EDUCBA guide to the concept of autarky. For further information, please refer to EDUCBA’s recommended articles.