Updated July 19, 2023
What is Equity?
Equity represents ownership in a company and typically takes the form of stocks or shares. It is the money a company gathers from the investment from the owner or the public through the allotment of shares. In accounting, it is also the total amount of funds left with the company after selling and paying all its assets and liabilities, respectively.
Equities help determine a company’s net worth, that is, what it owns after it settles all its debts and liabilities. Gaining funds through the allotment of shares fuels the company’s operations. It also enables the investors to be a part of the company.
For example, Company ABC allotted 50,000 shares of 100 each to investors, resulting in gaining $5 Million in funds. Economists call this amount Equity. The owner gathered this amount from various investors and, in return, will provide them with attractive returns when the business makes a profit.
Key Highlights
- Equity is the value that would be restored to a company’s shareholders after selling all of its assets and settling all of its debts.
- Economists calculate it by subtracting the total liabilities from the total assets, where total assets are what the company owns, and total Liabilities are what the company owes.
- Businesses prefer raising capital from this method rather than debt to lower the risk.
How Does Equity Work?
A business can gather money to fund operations and projects by offering shares. When any individual purchases shares of a company, that person becomes the shareholder and gains some control over the company’s assets. When the company performs well and makes a profit, the investors gain a return on their investment and vice versa.
However, such investments are always a bit riskier than other financial instruments, as the investors have no control over the workings of a company. One wrong decision by the board of directors can result in the company losing millions of dollars and the investors losing all their invested money.
Formula for Equity
The formula to calculate it is as follows,
Where,
- Total Liabilities are all the debts a company owes to the debtors. It includes borrowings, accounts payable, etc.
- Total Assets are all company investments that will provide them with returns. It includes inventories, accounts receivable, etc.
Examples of Equity
#1 Walt Disney Company
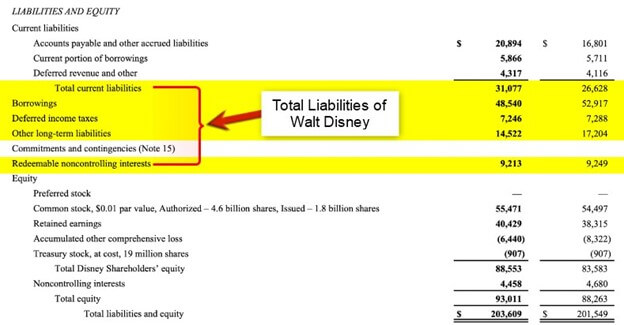
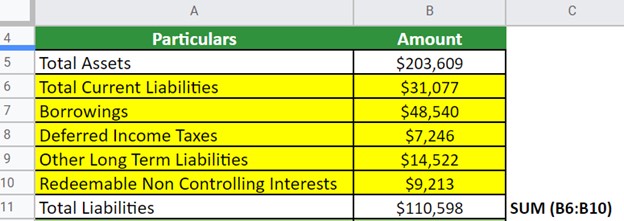
According to the 2021 Balance Sheet of Walt Disney, we have the following data. Calculate Walt Disney’s Equity for 2021.
Given,
(Image Source: Walt Disney Company Annual Report 2021)
Solution:
First, let’s calculate the Total Liabilities,
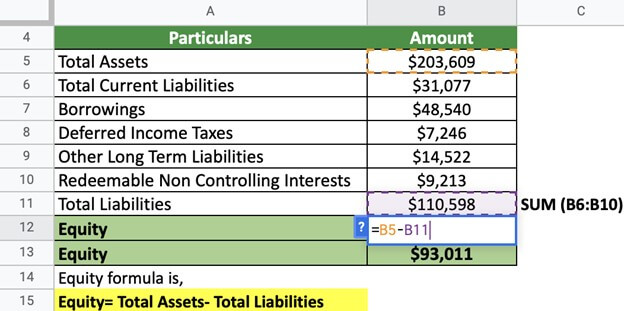
Now, we calculate the Equity,
The Equity of Walt Disney is $93,011. This is a healthy number where assets outweigh liabilities.
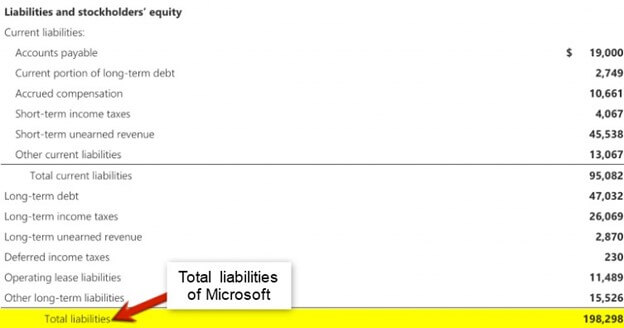
#2 Microsoft
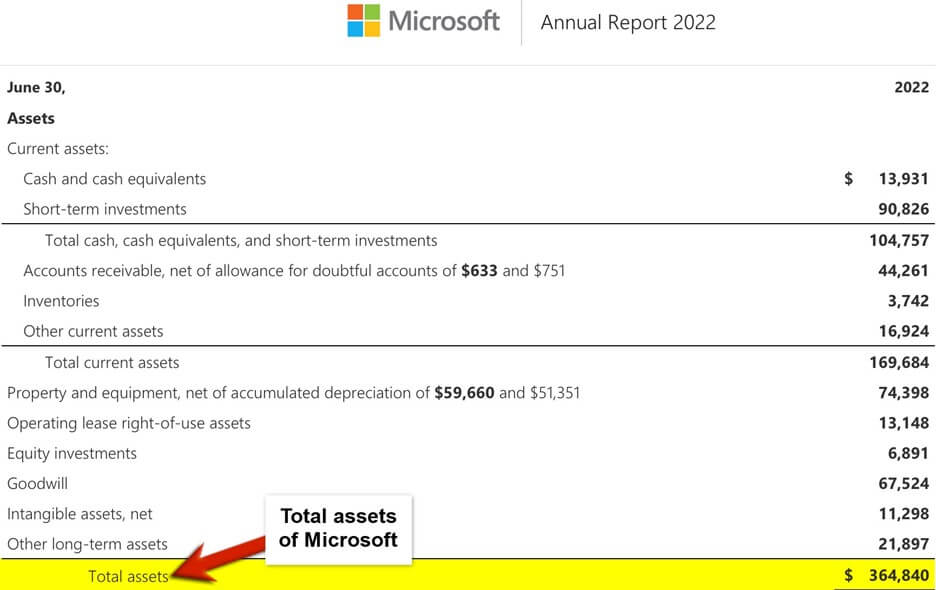
According to the 2022 Balance Sheet of Microsoft, we have the following data. Calculate Microsoft’s Equity for 2022.
Given,
(Image Source: Microsoft Annual Report 2022)
Solution:
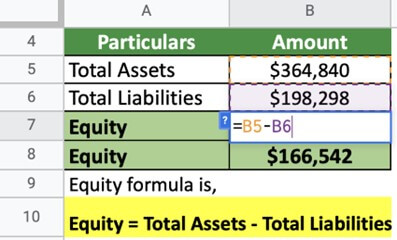
Lets calculate Microsoft’s equity for 2022,
Equity for Microsoft is $166,542. This is an excellent sign of the business being self-sufficient.
Types of Equity
#1 Owner’s Equity
Accountants deduct total liabilities from the company’s total assets to determine the value left with the owner. It includes money brought in by the business owner and the profits made by the business.
#2 Stockholders Equity
Stockholders Equity is of the following types:
- Common stock is the basic stock that represents an investor’s ownership of a company. If a company allotted ten stocks to the public, one stock would mean 10% ownership over the company.
- Preferred stock is a type of stock that generally has a higher claim on assets and earnings than common stock but does not come with voting rights. However, holders of preferred stock may receive a fixed dividend.
- Retained earnings represent the part of a company’s profits that the companies keep rather than distributing it as dividends. The company often reinvests these earnings to help fund growth.
- Employee stock ownership plan (ESOP) is a type of employee benefit plan which intends to encourage employees to acquire shares in the company.
- Treasury Stocks are the stocks a company buys back from its investors.
- Additional Paid-in Capital is the amount a shareholder accepts to pay above the basic value of a common or preferred stock.
Equity Features
- Entitlement to a share of profits: Shareholders are entitled to a share of the company’s earnings in the form of dividends.
- Claim on assets and earnings: Shareholders claim the company’s assets and earnings. If the company is liquidated or bankrupt, it will pay out all shareholders after settling all their debts and liabilities.
- Voting rights: Common stockholders usually have the right to vote at shareholder meetings, giving them a say in important company decisions such as board members’ appointments and approval of significant transactions.
- No fixed return: The return on this investment is not fixed and can fluctuate depending on the company’s financial performance and the stock market’s overall performance.
- Unlimited upside potential: The value of this investment can increase significantly if the company is successful, allowing investors to potentially earn a significant return on their investment.
- Risk: Economists consider this investment riskier than debt, as the company is not obligated to pay dividends, and the value of the investment can fluctuate greatly.
- Liquidity: Economists consider equities liquid assets, which means they can be easily bought and sold on the stock market.
- Ownership: Shareholders are considered company owners and have the right to participate in the company’s management.
- Tax advantage: Dividends paid to shareholders are usually taxed lower than the interest paid to debt holders.
Debt vs. Equity
| Debt | Equity |
| It is the borrowed money that a company must repay with interest. | It represents ownership in a company and entitlement to a share of profits made by the company. |
| Companies don’t need to pay interest to creditors. | Companies don’t need to provide interest payments to investors regularly. |
| There is a risk of default, which means the company won’t be able to fulfill the necessary debt obligations to its creditors. | There is no risk of default, as the company doesn’t have an obligation to pay dividends or return to shareholders. |
| Creditors have no impact on ownership and control. | Investors have an impact on ownership and control. |
| A few examples include loans, bonds, etc. | Examples include Common stock, Preferred stock, Retained earnings, etc. |
Importance of Equity
- It is an essential component of any business model because it fuels a company’s operations, intending to generate profits.
- Companies prefer gathering capital through this method over debt because it is much safer as they are under no obligation to pay the investors/lenders back, as in the case of debt.
- A company that raises capital from the general public in this way is much more transparent about its operations, as it keeps the public updated on its financials by publishing annual financial statements.
- It showcases a business’s net worth and self-sufficiency.
- Companies publicly traded on the stock exchange make it easier for investors to make investment decisions based on the company’s performance and policies.
Equity Calculator
You can use the following Equity Calculator.
| Total Assets | |
| Total Liabilities | |
| Equity = | |
| Equity = | (Total Assets - Total Liabilities) |
| = | (0 - 0 ) = 0 |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is called Equity?
Answer. Equity refers to the total funds a company is left with after it sells all its assets and pays all its liabilities. It is the value of each company’s share multiplied by the total number of shares offered. It is what the company owner brings into the company, either on his own or by offering shares.
Q2. What is an Equity example?
Answer. Any company offering shares to the public to gain funds is an example of Equity. A well-respected digital payment platform company like Visa released its IPO in 2008 for the public to invest in.
Q3. Why is it called Equity?
Answer. Economists call shares of a company Equity because they represent an individual’s ownership over the company. They allow the investors to gain benefits when the company performs well. The total amount of shares multiplied by their price determines the company’s Equity.
Q4. How is Equity calculated?
Answer. Economists calculate Equity by subtracting Total Liabilities from Total Assets. Total Assets are what a company owns, and Total Liabilities are what a company owes. Any individual can find the Total Assets and Total Liabilities of a company on the Balance Sheet of the company. The formula to calculate it is,
Q5. What is the difference between equity and shares?
Answer: Equity represents the overall ownership stakes in a company. On the other hand, shares are the division of equity that computes an individual’s or a business’s ownership in a company.
Recommended Articles
This was an EDUCBA comprehensive guide to Equities. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information,