Updated November 21, 2025
Meaning of Transportation
Transportation refers to the movement of people and goods from one location to another. It is crucial to a country’s economy and the growth and development of its society. Transportation can be long-distance or short-distance, each serving distinct and various purposes.
Some of the essential uses of transportation include transferring commercial goods, daily travel for workers, and emergency services such as ambulances. Transportation can be either by road, water, air, or rail, each having its own advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Transportation
Let’s look at some of the advantages and disadvantages of transportation below:
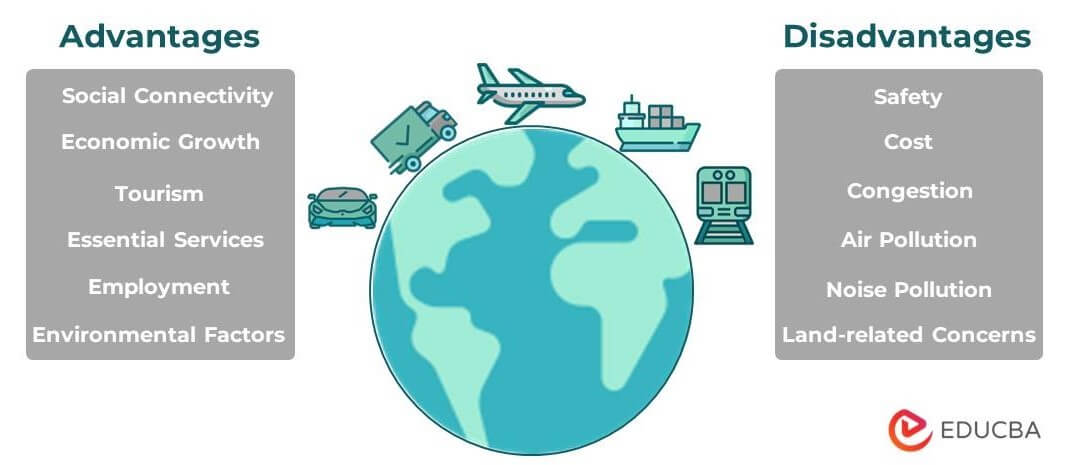
Advantages of Transportation
1. Essential Services: Transportation facilitates essential services such as water supply, ambulances, fire brigades, school buses, and commuting to workplaces, among others.
2. Economic Growth: Transportation plays a critical role in the economic development of a nation by enabling the transfer of raw materials to factories and the delivery of finished goods to markets. Improved transportation systems increase efficiency and productivity, contributing to economic growth.
3. Employment: The transportation industry provides many job opportunities, including truck, bus, and cab drivers, pilots, locomotive engineers, and others.
4. Social Connectivity: Transportation helps people stay connected with friends and family, bridging the distance between people living far apart.
5. Tourism: Transportation has significantly boosted the tourism industry, making it easy and quick to travel to previously hard-to-reach or unknown locations.
6. Environmental Factors: Eco-friendly transportation, such as electric vehicles, can help with environmental conservation by reducing air pollution and carbon emissions. Enhanced public transportation systems can also reduce the number of private vehicles on the road, which can help reduce air and noise pollution.
Disadvantages of Transportation
1. Air Pollution: Transportation is a major contributor to air pollution. Cars, trucks, buses, planes, and ships emit greenhouse gasses, which are the leading cause of global warming. Vehicles also emit other pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, and particulate matter, which can cause smog, acid rain, etc.
2. Noise Pollution: Transportation traffic significantly contributes to noise pollution. Prolonged exposure to noise pollution can lead to hearing loss and other health problems.
3. Congestion: Traffic congestion is a common problem in cities and densely populated areas. Congestion causes commuter delays, reduces transportation system efficiency, and increases air and noise pollution.
4. Safety: Safety is a significant concern in transportation due to the potential for accidents. Vehicles can crash into each other, pedestrians, and property. Passengers can also be injured or killed in air, rail, or sea accidents.
5. Cost: Transportation can be expensive due to fuel prices, regular maintenance of vehicles, and infrastructure. For businesses, tracking logistic spend has become increasingly important, helping them monitor rising costs and optimise overall budget management.
6. Land-related Concerns: Building transportation systems may require the acquisition of lands that can often be ethically problematic. For example, building roads may often require lands with large people settlements. Likewise, building railways or metros may require cutting down many trees, causing environmental problems.
Transportation Case Study – Konkan Railway, India
The Konkan Railway was one of India’s most incredible transportation projects in recent history. Its construction began in 1990, and the entire track between Mumbai and Mangalore, covering a distance of approximately 760 kilometers, was laid by 1998. The Konkan Railway is an important link connecting several cities, including remote villages that were previously only accessible via time-consuming roads.
|
Konkan Railway |
|
| Year of Construction | 1990 – 1998 |
| Route | Mumbai to Mangalore |
| Distance Covered | Approximately 760 kilometers |
| Importance | Connects several cities and remote villages previously accessible only via time-consuming roads |
| Travel Time | Total distance now covered within 14 hours |
| Challenges | Construction through difficult mountainous regions and numerous rivers |
| Number of Tunnels | More than 90 tunnels |
| Number of Bridges | More than 2000 bridges |
The project created many employment opportunities in the Konkan region and facilitated economic progress. Furthermore, rail connectivity has boosted tourism in the region as well. Konkan Railway is a significant mode of transportation for thousands of people across three states of India and has contributed to the nation’s development in multiple ways.
Role of Transportation Infrastructure in Various Modes of Travel
Infrastructure plays a crucial role in transportation, as each mode of transportation requires different types of architecture.
- For example, roads necessitate well-built concrete infrastructure. Road transport infrastructure typically has fewer constraints, with multiple roads leading to a destination or multiple lanes on a single road, making repair work less challenging. However, for roads that serve as the sole route to a destination, any repair work could cause severe difficulties for commuters.
- Maintaining railway systems is particularly essential, as any minor impediments on the route could break down the entire schedule on that route. Railway systems require frequent and extensive maintenance, which can be particularly challenging, especially as some rail routes traverse remote areas.
- Air and sea transportation require airports and ports, respectively. Although there is nothing to maintain on air and water routes, ports and airports do require immense maintenance. For example, runway maintenance in airports, a thorough examination of planes and ships, ensuring proper working of the navigation system, maintaining tight security, and so on.
Safety in Transportation
The administration must undertake several safety measures to ensure effective transportation. Some of them are:
- Providing training to drivers to follow safety protocols and granting licenses only to those who meet the requirements.
- Establishing checkpoints to prevent suspicious activities such as drunk driving or transporting illegal materials without causing unnecessary delays or hassles for commuters.
- Implementing extensive security measures at airports and ports for various reasons, such as preventing unauthorized entry or exit, preventing the smuggling of illegal goods, and ensuring passenger safety.
- Ensuring effective emergency response in the event of accidents by providing hospitals, police stations, ambulance services, and telephone facilities at regular intervals. Large-scale safety measures are crucial when it comes to incidents of airline crashes, ship sinking, or train derailments.
- Ensure vehicles come with safety equipment and air and sound pollution is minimal.
- Enforcing these rules and guidelines effectively and penalizing violators accordingly while ensuring that penalties are appropriate and proportionate. Education and awareness campaigns can also be effective in promoting safe behavior without relying solely on punitive measures.
Transportation Planning and Policy
There are various measures that governments can undertake to improve the transportation industry:
- Infrastructure Development: Funds should be allocated for developing transportation infrastructure, such as constructing new roads and bridges or upgrading existing ones. Additionally, airports, railway stations, and ports should be built wherever necessary, in addition to revamping the old ones.
- Safety: The government must ensure people follow the guidelines pertaining to driving and commuting. Not only should penalties be imposed for violations, but awareness programs must also be undertaken to inform citizens of the rules and regulations. However, the penalties should be appropriate and proportionate to avert the possibility of corruption.
- Legal Measures: The process of licensing should be simple and transparent. The terms and conditions pertaining to licensing various facets of transportation, such as tourism, cab-sharing, or personal transport, must be clear and accessible. Only after due checks and diligence should licenses be allotted to individuals appropriately.
- Toll Tax: The government determines the toll amount for certain roads and highways. The amount helps generate revenue that can be utilized for constructing new transport infrastructure or revamping existing ones.
- Sustainable and Environmentally-friendly Transportation: The government can promote alternatives like electric or hybrid vehicles. It can also encourage carpooling, public transportation, and setting emissions standards for vehicles to keep pollution levels minimal.
Future Technology
The transportation domain is witnessing innovations that are quite different from past transportation and are altering the domain completely. For example:
Autonomous Vehicles: They are one of the most innovative transportation technologies, as every form of vehicle requires a driver hitherto. These vehicles utilize sensors, cameras, and other technologies to detect their surroundings and make decisions based on that data.
Electric Vehicles: Electric vehicles operate on electricity instead of gasoline or diesel, resulting in fewer emissions than conventional vehicles. As a result, they are gaining popularity, and their range and charging infrastructure are improving. As the usage of electric vehicles increases, they could play a crucial role in reducing emissions and improving air quality.
Hyperloop Trains: Hyperloop is a high-speed transportation model currently in testing. It is a sealed tube or system of tubes through which a pod may travel free of air resistance or friction, transporting people or objects at high speed. The vehicle is estimated to travel at a speed of 760 miles per hour (1,200 kilometers per hour).
Future Outlook
The transportation industry is currently at a crucial point with the emergence of several innovative technologies having the potential to revolutionize it. Conventional train systems will likely be gradually replaced by advanced transport systems such as metros, bullet trains, maglev, and Hyperloop.
Furthermore, with the introduction of electric and autonomous vehicles, road transportation is predicted to transform significantly. Although the arrival of electric cars represents a positive development in terms of environmental conservation, the impact of autonomous driving technology is yet to be fully observed.
Thus, the transportation landscape is anticipated to be completely transformed in the next decade or two.
Final Thoughts
Transportation has both advantages and disadvantages. It allows people to travel quickly and conveniently, providing access to places that would otherwise be difficult to reach. Further, it plays a vital role in facilitating trade and commerce, contributing to a nation’s economy.
On the other hand, transportation can also have negative environmental impacts, such as creating noise and air pollution, which can contribute to global warming. It can be expensive to operate and may require significant public investments.
Safety is also a crucial concern in transportation, requiring proper measures to be taken. The industry is at a critical juncture, with the latest innovations expected to completely alter the transportation landscape. Therefore, it is essential to carefully consider the advantages and disadvantages of transportation in creating a sustainable future.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Advantages and Disadvantages of Transportation” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information,