Updated October 13, 2023
Revenue Meaning
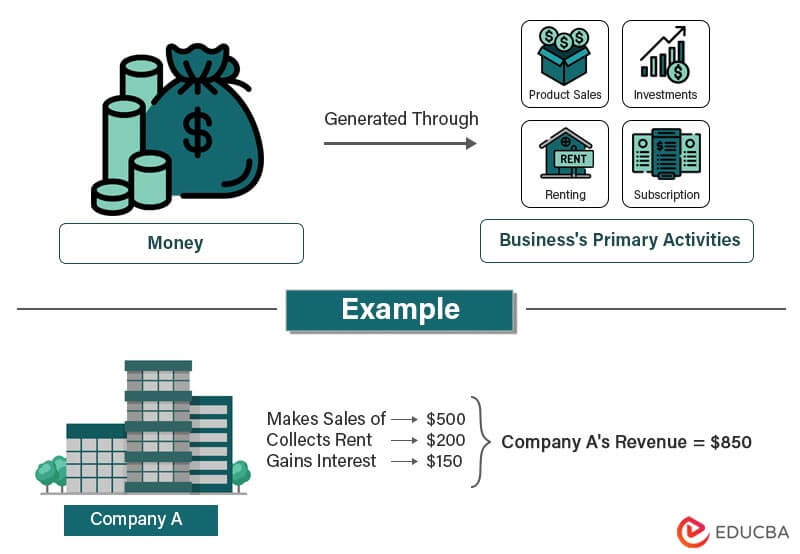
Revenue is the total amount a business or organization generates from its primary activities, such as product sales, services, rentals, subscriptions, etc.
For instance, an FMCG company may generate revenue through product sales in stores or online, distribution deals with retailers, and brand licensing.
It is a crucial indicator of a company’s financial performance and is typically reported on the income statement. By analyzing the figures from each stream, companies can determine which products or services are most profitable and make strategic investment decisions.
Key Highlights
- Revenue is the total amount of money a company makes from its normal operations and core activities.
- It is a critical indicator of a company’s financial health, closely monitored by investors, analysts, and stakeholders.
- Its various sources include product sales, subscription fees, advertising, and investment income.
- Companies use their forecasting to predict future trends and make informed business decisions.
How Does Revenue Work?
To illustrate the process, let’s consider ABC Corporation, which manufactures and sells Sunglasses. Here are the steps that ABC Corporation would take to earn income from the sale of Sunglasses:
1. Production of Sunglasses
ABC Corporation produces Sunglasses by sourcing raw materials, manufacturing, and packaging.
2. Sale of Sunglasses
The company then sells Sunglasses to consumers or retailers. Let’s assume the company sells Sunglasses to consumers for $20 each.
3. Recognition
One can calculate the revenue from selling sunglasses when a customer receives the order, even if there is a delay in the payment
Revenue Formula
The formula for calculation is,
- Sales Volume refers to the number of goods or services a company sells.
- The price of Goods or Services is the amount the company charges for each good or service.
How to Calculate it?
Step 1: Determine Sales Volume and Price of Goods or Services
Primarily, we need to know the sales volume and the price of goods or services sold.
Let’s consider a company that sells T-shirts. If this company sells 500 T-shirts at $20 per T-shirt, the sales volume would be 500, and the price of goods or services would be $20.
Step 2: Multiply Sales Volume by the Price of Goods or Services
The next step is multiplying the sales volume by the price of goods or services. In our example, we can calculate the income earned by the company as follows:
Revenue = Sales Volume * Price of Goods or Services = 500 * $20 = $10,000
So, the company’s total revenue from selling 500 T-shirts at $20 per T-shirt is $10,000.
Step 3: Deduct Any Discounts or Returns
If the company offers discounts or accepts returns, we have to deduct these from the earnings.
For example, if the company offered a 10% discount to customers who bought more than three T-shirts and three customers took advantage of the offer, the discount would be:
= 10% * 3 * $20
= $6.
It would reduce the total revenue to $9,994.
Step 4: Calculate Net Revenue
We must deduct any costs or expenses associated with producing and selling the T-shirts.
For instance, if the cost of producing 500 T-shirts is $6,000, we can calculate as follows:
Net Revenue = Revenue – Costs and Expenses
= $9,994 – $6,000
= $3,994
So, the net revenues earned by the company after deducting the cost of producing the T-shirts is $3,994.
Examples
#1: Retail Sales
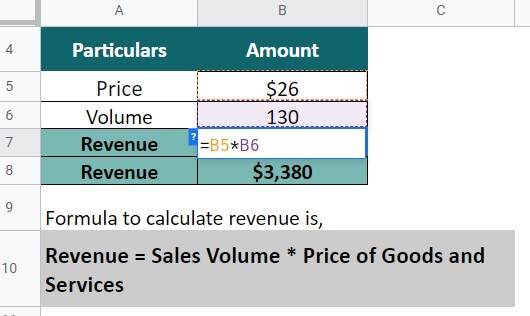
A retail textile store, John and sons, sells clothes. The price for the men’s shirts is $26. In January 2023, they sold a total of 130 shirts. Calculate the total money incoming in the store.
Given,
Solution:
As per the formula,
Revenue = Sales volume * Price of goods and services
= 130 * $26 = $3,380
Thus, the total yield of the John & Sons is $3,380.
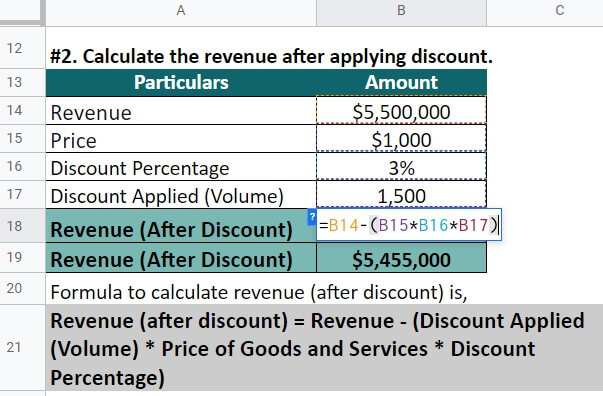
#2: Tech Developer
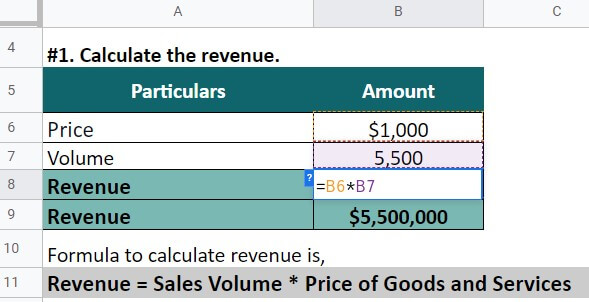
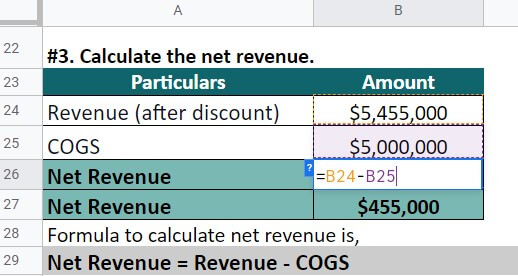
A technology company, TechnoSolutions, sells 5,500 laptops in 2022. Each laptop costs $1,000. Its COGS for the production of goods is $5,000,000. Moreover, the company offered 3% off for all bulk purchases; the discount was given to selling 1,550 laptops. Calculate the net revenue.
Solution:
Step #1: Calculate the revenue,
Revenue = Sales volume * Price of goods and services
= 5,500 * $1,000 = $5,500,000
Step #2: After excluding discount costs, the income is,
Value After discount = Revenue -(Discount * No. Of. Units * Product Price)
= $5,500,000 – (3% * 1,550 * $1000) = $5,455,000
Step #3: The net revenue will be,
Net Revenue = Revenue – COGS
= $5,455,000 – $5,000,000 = $455,000
TechnoSolutions had net earnings of $455,000 in 2022.
Types of Revenue Streams
It is of two main types: operating and non-operating.
Operating:
It is the capital a company generates through its core business operations, such as selling goods or services. Examples include:
1. Sales: The money generated from selling goods or services to customers.
Example: Apple earns from selling iPhones and other devices.
2. Service: The capital generated from providing services to customers.
Example: Amazon generates income by providing cloud computing services through Amazon Web Services (AWS).
3. Rental: It is generated from renting out property or equipment.
Example: A car rental company generates income by renting out cars to customers.
4. Subscription: Income generated from subscriptions to a product or service.
Example: Netflix earns through subscription fees from its customers.
5. Advertising: Earnings from selling advertising space or time.
Example: Facebook generates capital from displaying ads on its platform.
6. Commission: It is generated from earning a commission on sales made by others.
Example: A real estate agent generates money by earning a commission on the sale of a property.
Non-Operating:
It refers to the money a company earns from sources other than its core business operations. Examples include:
1. Investment income: The income generated from investments in stocks, bonds, or other financial instruments.
Example: Berkshire Hathaway generates non-operating capital by investing in stocks, bonds, and other financial instruments.
2. Gain on the sale of assets: It is the money from selling assets such as land, buildings, or equipment.
Example: General Electric generated non-operating earnings by selling its stake in NBC Universal for $16.7 billion.
3. Rental income: The earnings generated from renting out the property are not part of the company’s core operations.
Example: McDonald’s generates income by leasing its real estate to franchisees.
4. Interest income: The capital generated from earning interest on loans or other financial instruments.
Example: Citigroup generates non-operating capital by earning interest on loans it has issued to customers.
Recognition of Revenue
Here are the steps to recognize revenue,
Step 1: Identify the Contract with the Customer
The good/service provider binds a contract with the customer.
Example: A software company contracts a customer to provide software services for a year.
Step 2: Determine the Performance Obligations
Both parties should determine the required obligations of the contract.
Example: The software company promises to provide access to the software service, maintain the software, and provide customer support.
Step 3: Determine the Transaction Price
The customer and the provider discuss and establish the price of the product/service.
Example: The software company agrees to provide the service for $100,000 annually.
Step 4: Allocate the Transaction Price to Performance Obligations
The service provider assigns the decided price to functions and tasks.
Example: The software company allocates the transaction price of $100,000 for access to the software service, maintenance, and customer support based on their relative value.
Step 5: Recognize Revenue when Performance Obligations Satisfied
When the customer is content with the performance of the service or product, the service provider recognizes the income.
Example: The software company recognizes monthly yield when it provides access to the software service, maintains it, and provides customer support.
Recognition Methods
Here are the various methods to recognize revenue,
Sales-basis Method:
This method recognizes the direct incoming earnings. It is when the customer pays for the product/service upfront and within a short period. For instance, a customer purchasing medicine pays when they get the product. Therefore, the delivery of the product triggers recognition.
Completed-contract Method:
We use it for contract-based transactions. In this method, recognition occurs when one fulfills all the contractual obligations. However, the recognition will reflect inconsistently on the financials for long-term contracts. Thus, it is beneficial only for contracts with shorter periods.
Installment Method:
Businesses use this method for high-value purchases such as purchasing houses, renting machines, etc. The company receives the payment in installments over the months or years. Thus one can recognize the income after receiving each payment.
Cost-recoverability Method:
It is similar to the installment method. However, businesses use this method only when they need help estimating the cost of the goods. The recognition occurs only when the final company receives the final amount after completing the contract and all obligations.
Percentage of Completion Method:
This method of recognition works for long-term contracts. The companies track their incoming payments and recognize the yield through milestones or other progress methods. Herein, the agreement includes a detailed description of all such milestones. It helps firms portray a consistent income stream on their financials.
Revenue Vs. Profit
| Particulars | Revenue | Profit |
| Definition | It is the money businesses earn from their operations and other sources | It is the amount of money a company retains after deducting all expenses |
| Calculation | Price of good/service * Volume of Sales | Total Income – Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) – Operating expenses
|
| Placement on Income Statement | It is the top line of a company’s income statement | Profit is the bottom line of a company’s income statement |
| Consideration of Expenses | It does not take expenses into account | Profit takes into account all expenses, including taxes, salaries, and cost of goods sold |
| Significance | It is a measure of a company’s ability to generate income | Profit is a measure of a company’s financial performance and overall success |
| Importance for Growth | It is essential for growth and expansion | Profit is vital for sustainability and long-term success |
Revenue Calculator
Use the following calculator to calculate revenue.
| Sales Volume | |
| Price of goods or services | |
| Revenue = | |
| Revenue = | (Sales Volume * Price of goods or services) |
| = | (0 * 0 ) = 0 |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between revenue and sales?
Revenue and sales are terms often used interchangeably but have different meanings. Sales refer to the money a company earns from selling its products or services. For example, if a company sells 100 units of a product for $10 each, its sales would be $1,000.
On the other hand, revenue refers to the total amount of money a company earns from sales and other sources such as investments, rentals, and commissions. For example, if the same company from the previous model made $500 additionally from renting out equipment, its revenue would be $1,500.
Is revenue the same as income?
Revenue and income are related concepts but are not the same thing. Revenue is the total amount of money a company earns from its operations or other sources, while income refers to the profits or earnings after deducting all expenses.
For example, a small business owner runs a bakery and earns $100,000 annually. However, the owner also incurred expenses such as rent, utilities, wages, and cost of ingredients totaling $75,000. In this case, the bakery’s income would be $25,000 ($100,000 revenue minus $75,000 expenses).
What is the difference between gross and net revenue?
Gross income is the total amount of money a business earns from selling goods or services before deducting any expenses. On the other hand, net income is the amount of money remaining after subtracting all costs and fees, including the cost of goods sold and operating expenses.
Example: If a company earns $1 million from selling its products but incurs $400,000 in expenses (including the cost of goods sold, salaries, rent, and utilities), its gross revenue would be $1 million, and its net income would be $600,000.
What factors can impact a company’s revenue?
Several factors can impact a company’s income, including changes in consumer demand, prices of goods or services, competition, and economic conditions. Companies must consider these factors and adjust their strategies to ensure continued income growth.
Recommended Article
We hope that this EDUCBA information on Revenue was beneficial to you. For further guidance, EDUCBA recommends these articles: