Table of Contents
What are Plant Assets?
Plant assets are physical resources that companies own for more than a year and use to create & sell goods/services to generate income. These are fixed assets such as land, buildings, factories, machinery, and vehicles.
Types & Examples of Plant Assets
We can divide plant assets into different categories depending on their size, purpose, useful time period, etc. The following are the four subdivisions for plant assets:
1. Land & Land Improvements
The land is a business area where a company establishes its factory or office to manufacture goods or provide services. On the other hand, land improvements include additional things like a parking lot, fence for security, or roads to access the facility.
2. Buildings
Buildings are structures like factories, offices, warehouses, and other places where businesses produce goods or provide services.
3. Furniture
Furniture refers to movable items like desks, chairs, shelving, lighting, and artwork for day-to-day operation.
4. Machinery and Equipment
Machinery refers to the hardware technology that helps a company to produce goods and provide services. In comparison, equipment includes pipes, wiring, and other systems that provide essential utilities like water, electricity, manufacturing equipment, computers, trucks, and communication services.
Characteristics of Plant Assets
- One characteristic of plant assets is that they are replaceable. Businesses can sell or replace them when they are no longer needed or useful.
- They need regular maintenance to work properly for a long period.
- Depreciation is unavoidable because they become old or worn out.
- Businesses require huge capital for purchasing or upgrading these assets.
- The introduction of new technologies can replace traditional plant assets.
- They do not last forever, and their value goes down over time.
Plant Assets Accounting
In accounting of plant assets, we will see where a company records the purchase of an asset, depreciation as well as disposal.
Purchase
When a company buys a new plant asset, it records the cost of the asset in its balance sheet. Specifically, it comes under the “Property, Plant, and Equipment” category. This cost includes everything the company spent to get the asset, like purchase price, transportation expenses, installation costs, and any other directly attributable costs.
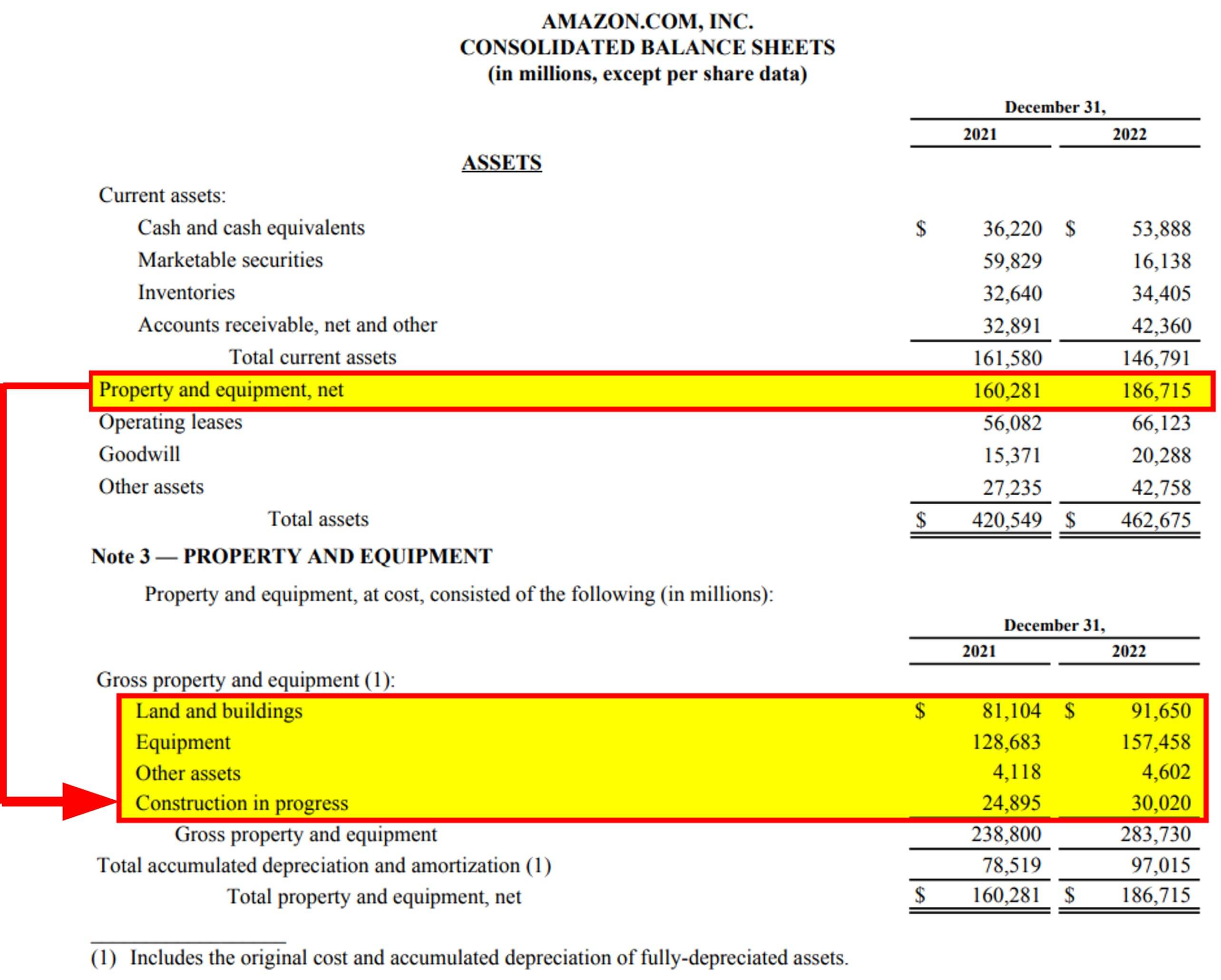
Let’s examine Amazon’s plant assets for 2022, which consist of land and buildings, equipment, and other assets. We can find the plant assets on the balance sheet, clubbed as property, plant, and equipment. The segregation of this property, plant, and equipment is present in the notes as shown below:
(Source: Amazon Annual Report 2022)
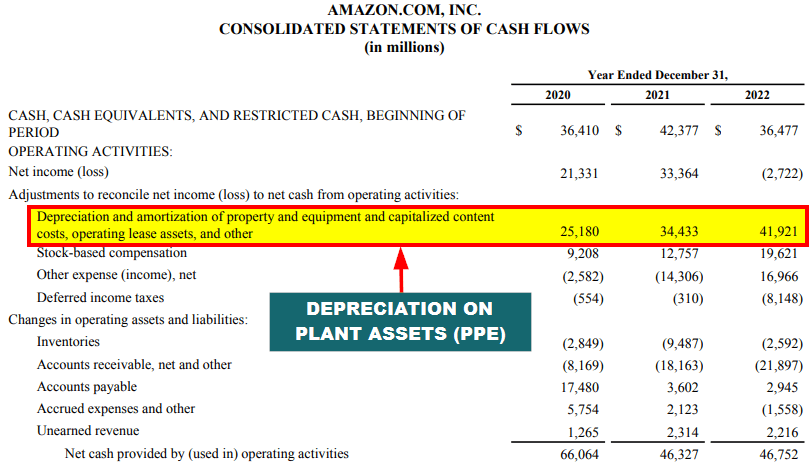
Depreciation
Over time, plant assets lose value, and this decline refers to depreciation. Companies depreciate an asset by dividing its purchase cost throughout its useful life, i.e., until the asset benefits the company. Depreciation helps to accurately show the asset’s reduced value and plan for its replacement when the value becomes zero.
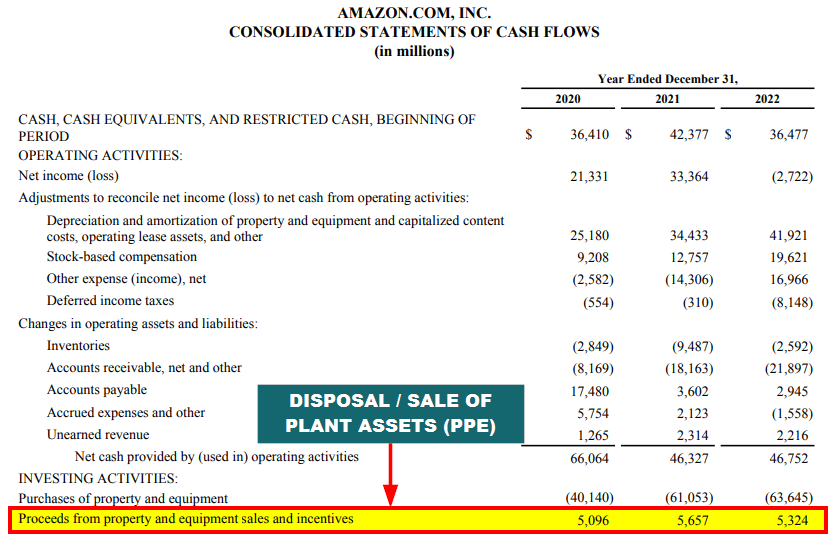
Disposal
When an asset depreciates, the company either sells or replaces it, known as the disposal of the asset, which can either result in a gain or loss. Such disposal changes the asset’s ownership, reduces unnecessary damages, and ensures proper analysis of the company’s financial position.
Methods of Depreciation
Depreciation Methods are ways to divide the cost of an asset every year. There are different methods for different situations:
- Straight-Line Method: It first divides the cost of the asset equally each year according to its useful life and then subtracts the depreciation expense from the cost.
- Written-Down Value Method: It calculates a fixed rate of depreciation every year on the cost of an asset after subtracting the depreciation of the previous year.
- Sum-of-the-Years’ Digits Method: It focuses on the remaining useful life of the asset every year and reduces a higher amount of depreciation at the early stage.
- Units of Production Method: This method calculates depreciation based on the number of units produced by that particular asset. It means comparing the number of units produced with the total production capacity of the asset.
Example – Plant Assets Depreciation
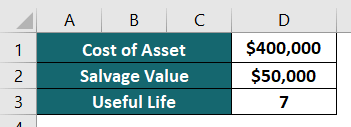
Imagine GreenTech Manufacturing owns various plant assets. One among them is a machine they purchased at $400,000. The expected useful life of the machine is 7 years, and the salvage (scrap) value after 7 years will be $50,000.
Calculate depreciation for the machine for the useful life of 7 years.
Given,
Solution:
Here we will use all 4 methods to calculate the machine’s depreciation.
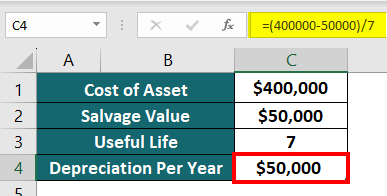
Method #1: Straight-Line Method (SLM)
Let us use the below formula:
Depreciation = (Cost of Asset – Salvage Value) / Useful Life
=($400,000 – $50,000)/7 = $50,000
Look at the below image to understand the calculation.
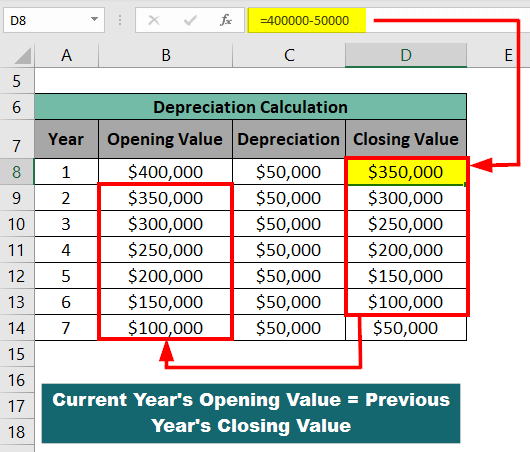
The Straight-Line method depreciates an equal amount of $50,000 from the opening value each year for 7 years until the asset’s value reaches the salvage value of $50,000. The image below shows the opening, depreciation, and closing values for 7 years.
Method 2: Written Down Value Method (WDV)
The formula for this method is as follows:
Depreciation for Year 1 = Current Book Value x Depreciation Rate
Current Book Value (Year 2) = Current Book Value (Year 1) – Depreciation (Year 1)
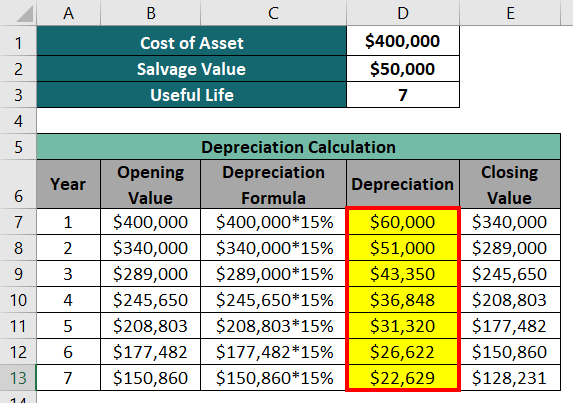
The following image shows proper depreciation calculation using WDV Method:
Here, WDV Method takes 15% of the opening value and then subtracts it from the opening value to get the closing value for the next year.
In this example, the closing value for the 7th year ($128,231) does not equal the predicted salvage value of $50,000. It is because the Written Down Value Method does not consider the salvage (scrap) value.
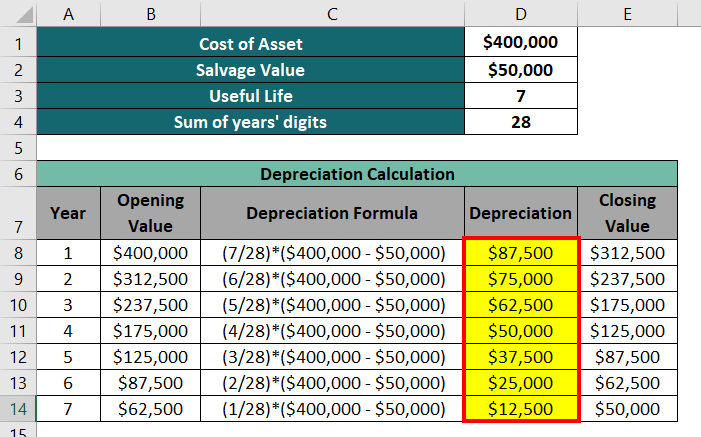
Method 3: Sum Of Years’ Digits Method
The formula for depreciation is as follows:
Depreciation = (Remaining useful life / Sum of the years’ digits) x (Cost – Salvage value)
Sum of years’ digits = 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 = 28
The depreciation amount for each year will be as follows:
The Sum of Years’ Digits depreciation method divided the depreciation expenses every year by a fraction based on the number of remaining years.
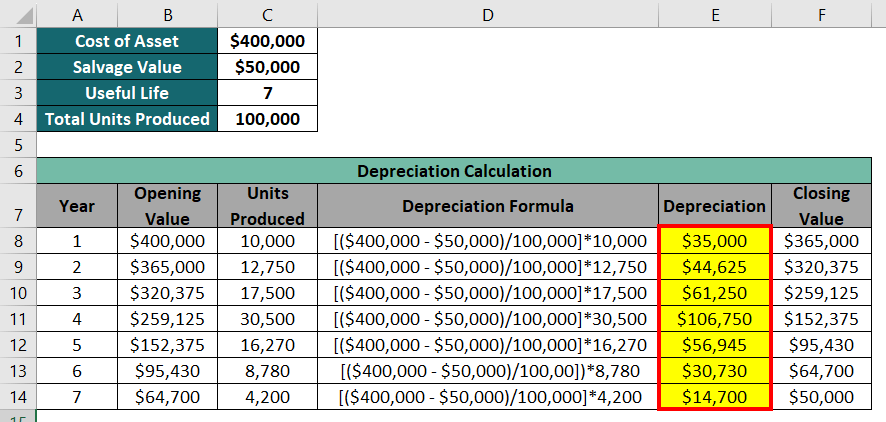
Method 4: Units of Production Method
To use the units of production method, we need to know the units produced by the machine each year of its useful life. Thus, let’s assume GreenTech Manufacturing produced a total of 1,00,000 eco-friendly products in 7 years as follows:
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | Year 6 | Year 7 | Total |
| 10,000 | 12,750 | 17,500 | 30,500 | 16,270 | 8,780 | 4,200 | 100,000 |
The Units of Production Method has the following formula:
Depreciation = [(Asset cost – Salvage value) / Estimated units for entire useful life] x Actual units made that year
The below image explains the calculation of depreciation for each year:
Here, the units of production method subtracted the salvage value from the initial cost of the asset, divided it by the total units to get the depreciation per unit, and then multiplied it by the units produced in each year. The process continued until the asset’s value reached the salvage value of $50,000.
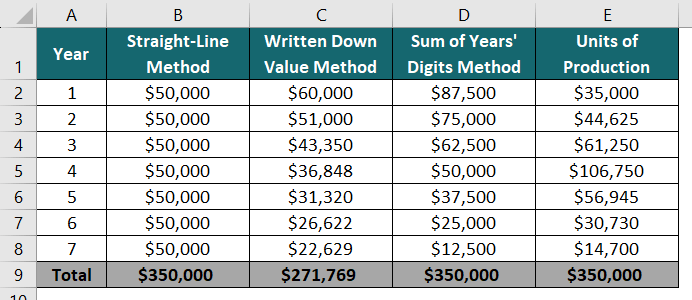
Analysis of Different Depreciation Methods
Now we will analyze the difference in the depreciation amounts for all the methods.
The below table shows the different depreciation calculations over 7 years of useful life using four different methods.
Different methods can result in varying depreciation expenses due to their unique approach as follows:
- Straight-Line Method: Equal amount of depreciation year.
- Written Down Value Method: High amount of depreciation in the beginning which decreases gradually.
- The sum of Years’ Digits Method: Unequal rate of depreciation with a large depreciation amount in the beginning.
- Units of Production Method: Depreciation based on number of units produced by the plant asset.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is Plant Assets Management?
Answer: Plant Asset Management refers to the systematic and effective arrangement, analysis, and organization of plant assets owned by a company. The company has to check and improve the assets’ maintenance, operations, and performance. It ensures the quality and reliability of a plant asset. Efficient plant asset management involves team efforts in engineering, production, and finance for best results.
Q2. Is a plant asset a fixed asset?
Answer: Yes, a plant asset is a fixed asset. A fixed asset includes buildings and equipment owned by a company for more than 1 year. As plant assets have a useful life of more than 1 year, they come under fixed assets.
Q3. Is inventory a plant asset?
Answer: Inventory is not a plant asset. Plant assets include long-lasting buildings, machinery, equipment, etc. On the other hand, inventory refers to the goods or products that a plant asset produces to sell to customers. It is not a long-lasting asset as a company has to sell goods quickly and generate main revenue for the business.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Plant Assets. Here we discuss the meaning, accounting procedure, depreciation methods, and an example. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –