Updated August 4, 2023
Table of Contents
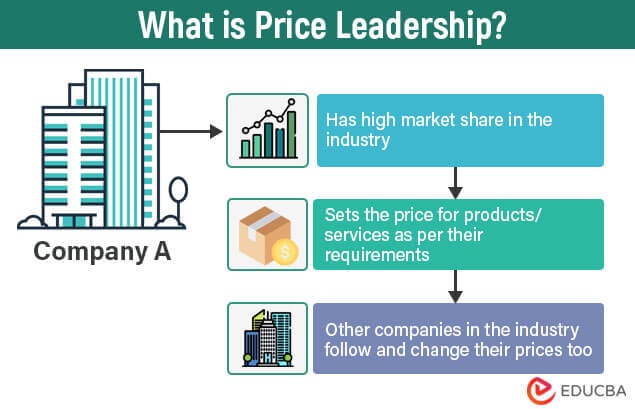
What is Price Leadership?
When a company has a majority of market share in an industry, it can decide the prices for products and services, while other companies have to follow it. This is known as price leadership.
Being a price leader in the market can be advantageous for a company because it allows them to have a significant influence on market conditions and competitors’ behavior. However, there can only be one price leader in a given industry; only some businesses have the choice to be the price leader.
Price Leadership in Oligopoly
The concept of price leadership is very common in oligopolistic markets. It is because, in such markets, there are very few large-scale, dominant companies whose actions influence other companies’ pricing decisions. Here are some key reasons why it exists in oligopoly markets:
- Fewer Competitors: As only a few firms in the market have high market power, their actions can easily influence market dynamics.
- Mutual Dependence: As all firms know their competitors’ actions and reactions, a price change by one firm will likely lead to reactions from other firms.
- Higher Barriers to Entry: As existing companies have stable market positions, there are high entry barriers, making it difficult for new competitors to enter the market.
Examples
Let’s discuss some real-world examples of price leadership.
#1 Delta Air Lines
Delta Airlines, an American airline, has the second highest market share of 17.2% in the air travel market as of 2023. Using its strong market position, it employs its leadership strategy to its advantage.
During peak travel seasons like summer, the airline raises ticket prices, maximizing revenue and profit margins from customers prioritizing convenience and reliability over cost. Conversely, during periods of lower demand, Delta strategically sets lower maximum prices to attract price-sensitive customers, keeping its planes filled and outsmarting competitors.
#2 Apple
Apple’s price leadership significantly impacts the entire consumer electronics industry. When Apple releases a new product with premium pricing, it often sets a benchmark for competitors. As a result, other companies in the market have to adopt similar pricing strategies for their products.
Price Leadership Model
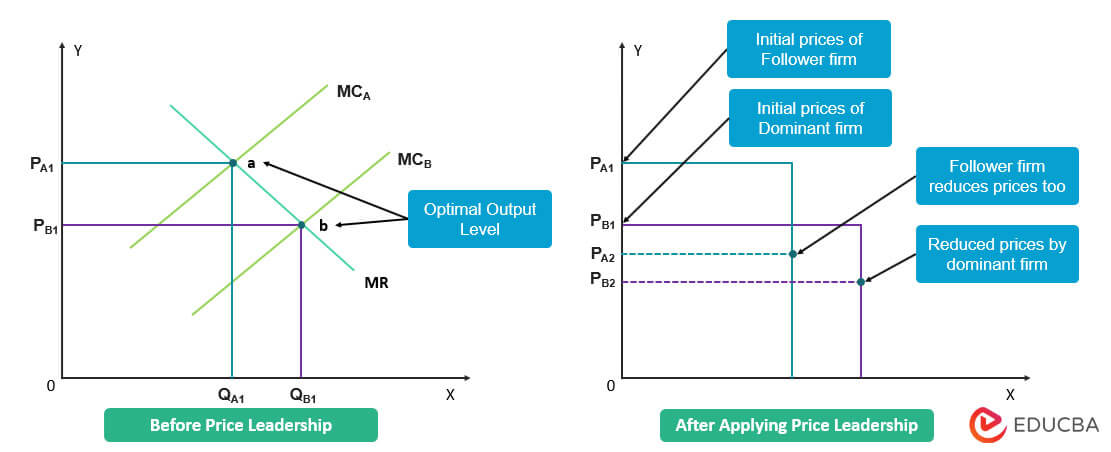
The price leadership graph shows the best production level for each firm, where their marginal cost and marginal revenue intersect. This level ensures good profits for the firms. The dominant firm’s optimal output level is typically lower than the follower firm’s. It means they are able to generate more profits even by making products at a lower price. However, note that sometimes the dominant firm’s output level can be higher than the follower firm’s, depending on factors like production capacities, cost structures, and demand levels.
Thus, when the dominant firm reduces product prices, the follower firm must also lower prices, even if it means going below their optimal level of production.
Example
Let us take an example of an airline company to understand this model.
Imagine the airline industry has two significant players, Horizon Airways and Velocity Airways. Horizon Airways, known for its excellent service, is a major player in the airline industry, as it has a significant market share. On the other hand, Velocity Airways is a smaller competitor in the same region, offering competitive services.
During an economic downturn, Horizon Airways predicted reduced demand and offered reduced ticket prices across all routes to create demand. In response to Horizon’s price reduction, Velocity Airways decided to follow the leadership and reduce ticket prices.
If we observe the graph, we find that Velocity Airways’ optimal output is at point a, while Horizon Airways’ optimal output is at point b, which is lower than a. This shows that Velocity Airways can be profitable only by selling tickets at higher prices. However, when Horizon Airways reduces prices using price leadership, Velocity Airways must also lower prices below its optimal output level to stay competitive.
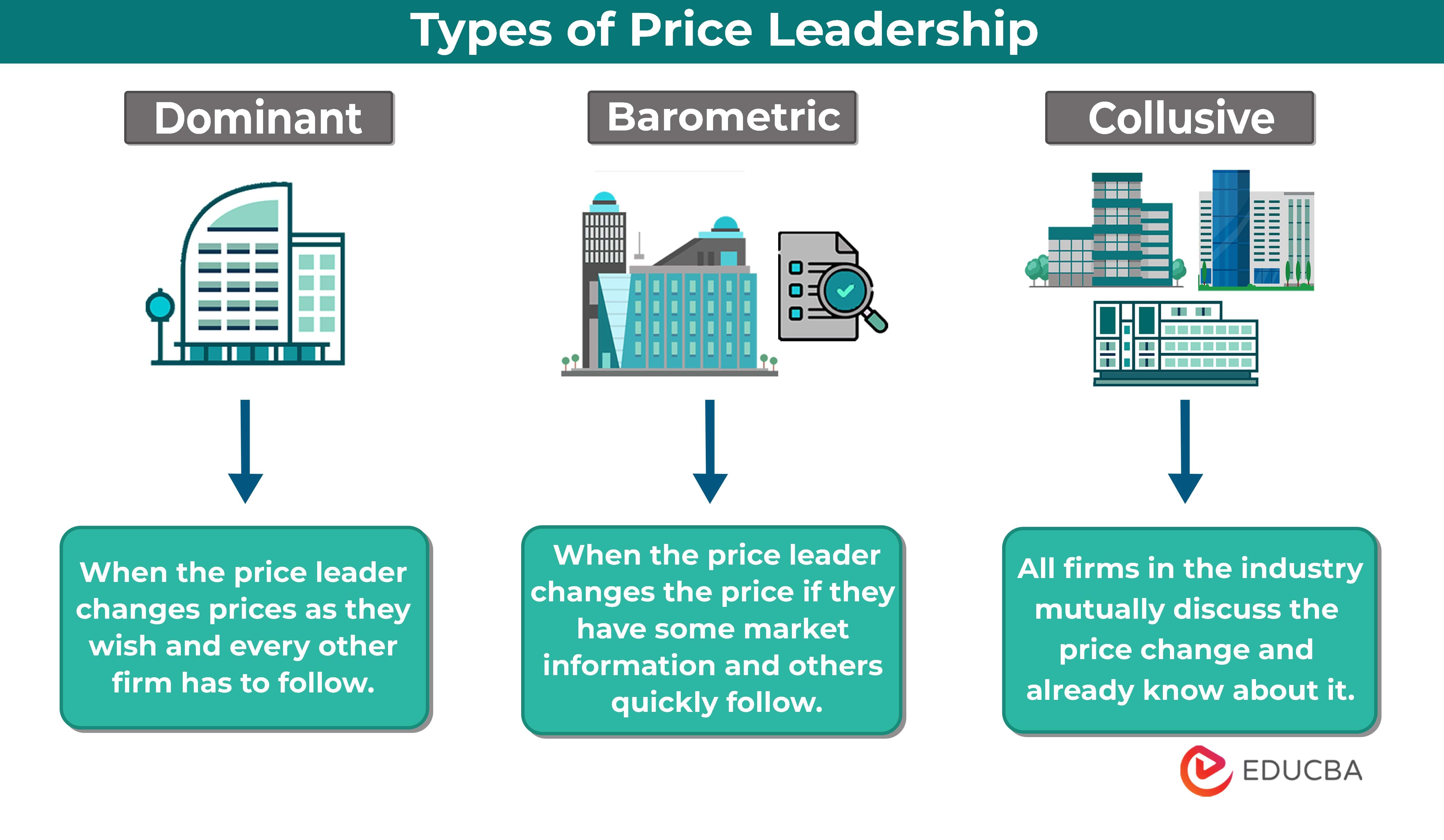
Types
Below are the three types of price leadership:
#1 Dominant
- It occurs when an industry has a clear and powerful market leader. This leading company sets the price, and other companies usually follow it.
- The dominant company’s position and market influence makes it easier for them to control the pricing in the industry.
#2 Barometric
- It happens when the price leader changes the price of its products or services when they have some insider or new information about the market.
- Other companies in the same sector notice this change and quickly adjust their prices to match the changed price.
- It is very unplanned and can change frequently, depending on market conditions and the actions of the leading company.
#3 Collusive
- It happens when competing companies mutually collaborate and work together to determine the prices of their products or services.
- It’s similar to making a hidden agreement to avoid price competition and instead set their prices at a similar level to maximize their profits.
Advantages and Disadvantages
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| It benefits companies by demanding them to compete in the market with a good strategy. | A price leader may lose market share if it loses to influence the other competitors. |
| Smaller companies can profit more if they follow the low market price set by the price leader. | High prices set by price leaders may also lead small businesses to bankruptcy. |
| High profits will help industries make more quality products and services. | Many small firms may not compete with the price leader’s price, limiting consumer options. |
| It prevents price wars if the price leader fixes the market price that every firm follows. | It may result in a lack of innovation as the price leaders focus more on maintaining their status. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What’s the difference between cost leadership and price leadership?
Answer: Though these two words are used together, their meaning differs. Price leadership focuses on offering the lowest prices among competitors, while cost leadership aims to have the lowest operating costs. Thus, the cost leader is more profitable than the price leader despite both offering low prices.
Q2. What are the characteristics of Price Leadership?
Answer: The main characteristic of price leadership is that a company, known as the price leader, sets the price for its products or services in the market. Other companies in the same industry follow the price leader’s pricing decisions rather than determining their own prices.
- Price Setter: The leading company sets the price for its products or services.
- Follower Trend: Other companies in the industry follow the leader’s price changes quickly.
- Market Control: The leading company has a significant market share and influence over competitors.
- Limited Price Competition: Price leaders reduce high price competition among firms in the industry.
- Adaptability: This leadership can change with time as market conditions and leading companies evolve.
Q3. What is aggressive price leadership?
Answer: Aggressive price leadership occurs when a big and well-established company takes the lead by setting very competitive and low prices. Other companies in the industry must follow their pricing decisions. The aggressive price leader influences the market by pushing others to match its pricing strategies.
Recommended Articles
This article is a guide to price leadership, where we discussed its meaning, features, and real-world examples. You may have a look at some similar articles below: