What is Financial Management?
Financial management is the way a business manages its money. It includes cash flow management, handling risks, taxation, forecasting, investing strategies, and plans regarding assets & liabilities.
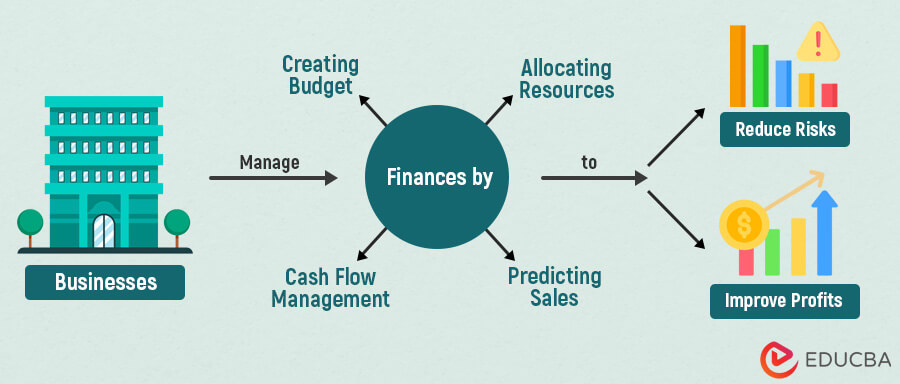
Table of Contents
Key Highlights
- Financial management is how businesses manage monetary funds.
- Fund allocation, managing assets & liabilities, creating budgets, and forecasting are integral parts of finance management.
- It maximizes the business’s profits and per-share earnings by identifying capital resources and determining investment strategies.
How Does it Work?
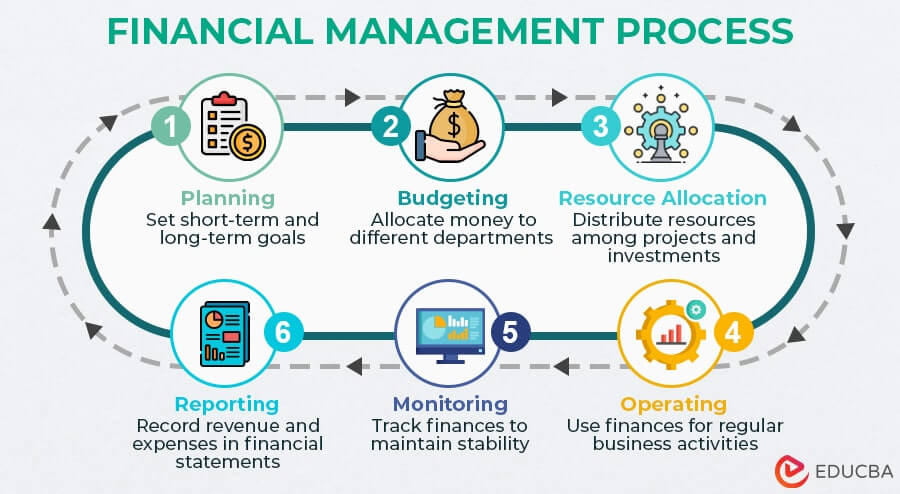
Companies follow a cyclic financial management process that they repeat each financial year. The process includes the following steps:
- Planning: Businesses start by developing proper financial short-term and long-term goals.
- Budgeting: They then allocate money into various departments to control money flow in business.
- Resource Allocation: Companies then distribute the financial resources among different projects, departments, or investments.
- Operating: After clear resource allocation, firms continue their regular financial activities, like employing, investing, marketing, etc.
- Monitoring: Businesses keep analyzing and monitoring their economic actions to maintain consistent financial stability.
- Reporting: Finally, this process includes maintaining financial statements by recording revenue collection and expenditure and planning a new budget for the next financial year.
Examples
Let us see a few examples to understand how financial management works.
Example #1
Imagine a company that wants to launch a new smartphone. To achieve this, it will follow these steps:
- The company will make a detailed budget plan to allocate money to areas like research and development, hiring skilled engineers, and manufacturing processes.
- After that, it will use financial analysis to predict future sales and revenue from the new smartphones.
- Finally, it will track its cash inflows and outflows for better cash flow management.
Example #2
Suppose you are a boutique owner and want to open a new store in a new city. Your financial management process can include:
- You should develop financial goals, such as setting a certain income goal for the first quarter.
- Then, create a budget and allocate funds to different operational departments.
- You can plan where to purchase raw materials, how much to spend on one batch, and determine funding sources to invest in your company.
- You must keep tracking your expenses to manage your finances efficiently.
- Finally, maintain records of each transaction, create financial statements, and review the financial performance of new stores.
- You can also forecast the next financial year’s budget based on current performance.
Types & Functions
There are 3 common types of financial management: capital budget management, capital structure management, and working capital management. We can further divide these types into essential functions.
A) Capital Budget Management
1. Financial Planning and Forecasting
- It includes developing a clear financial plan regarding the company’s short-term and long-term goals.
- It also contains budgeting strategies as well as forecasting the business’s future performance.
2. Calculating Capital Expenses
- Companies must compute how much expenses they may incur in the financial year.
- It can include production and marketing costs, fixed and current asset expenses, investment capital requirements, etc.
B) Capital Structure Management
1. Creating a Capital Structure
- A capital structure explains what percentage of the company’s capital will be from equity and debt.
- Designing an effective capital structure helps determine the growth rate and efficiency of the company’s operations.
2. Finding Capital Sources
- After deciding on the capital structure, businesses should choose the appropriate fund sources for their financing.
- They must check several factors before choosing any sources. For instance, in the case of debt, they can check the interest rates.
3. Collecting Necessary Funds
- Once the firm finalizes its fund sources, it can start the process to collect those funds.
- For example, transferring the equity, providing collateral for a debt, and receiving capital in return.
C) Working Capital Management
1. Cash Flow Forecasting
- Financial management lets firms easily forecast their future cash flows, including sales, expenses, returns, etc.
- This helps the company understand its profit levels and if it will have enough available capital in the future.
2. Cash Management
- It ensures the firm has enough funds to cover necessary expenses and daily operations smoothly.
- It also includes decisions regarding how the company must distribute the cash. For instance, deciding how much cash flow should go into investments and repaying debts.
3. Making Investments
- It simplifies the process of allocating and investing resources into profitable ventures to generate maximum returns.
- It consists of calculating risks and making an effective investment strategy to help businesses grow their profits.
4. Disposal of Surplus Profits
- Finally, businesses decide how to use the additional or surplus profits.
- They can provide dividends to the shareholders or reinvest the money in the business, etc.
Role of Financial Management
Financial management plays the following crucial roles for businesses:
- Resource Management: Financial management allows businesses to use available financial resources effectively, such as prioritizing profitable projects or investments to maximize income.
- Risk Mitigation: It helps identify, assess, and reduce potential risks by assisting firms in developing strategies that protect the organization’s assets and resources.
- Financial Reporting: It assists firms in preparing accurate financial statements representing their true financial position and performance.
- Tax Planning: Managing finances lets companies identify ways to minimize their taxes using available tax laws and regulations.
- Specialist Consultation: Engaging a Microsoft Dynamics Finance and Operations Consultant can further optimize financial management by providing deep insights into effective resource allocation, risk mitigation, and strategic financial planning.
Job Roles, Responsibilities, and Salary
The hierarchy of financial management job roles varies from one organization to another. However, here is a standard hierarchy structure from the lowest to the highest:
Financial Assistant → Finance Analyst → Finance Manager → Finance Director → Treasurer → Chief Financial Officer.
The below table describes the responsibilities and salary range for each job role.
| Role | Responsibilities | Average Annual Salary |
| Finance Assistant | Assist in maintaining financial records, updating day-to-day financial operations, and more. | $40,775 |
| Financial Analyst | Responsible for analyzing financial data, creating financial models, assessing performance, etc. | $86,399 |
| Finance Manager | Overseeing financial functions, including planning, managing, and executing budgets and supervising other finance teams. | $118,500 |
| Finance Director | Developing long-term financial strategies and working with senior executives to ensure the company’s financial stability. | $160,758 |
| Treasurer | Managing cash flow, investments, and financial risk, ensuring liquidity and financial stability. | $243,588 |
| Chief Financial Officer | Supervising the overall financial operations of an organization, approving financial reports, and analyzing every monetary detail. | $270,553 |
Salary source: Comparably
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the scope of financial management?
Answer: Financial management can be useful in various fields other than just the finance and accounting domains. It can help businesses based in production management, marketing, HR, accounting, etc. This practice can help companies with profit management, investment & financing decisions, dividend distribution, and more.
Q2. Why is managing finances important?
Answer: The importance of financial management is as follows:
- It helps a business acquire sufficient funds to meet short-term and long-term future goals.
- It assists in efficiently allocating, managing, and acquiring funds, which helps increase profitability and improve economic performance.
- Assist in making informed financial decisions to enhance the company’s performance and safeguard the company against the financial crisis.
Q3. What are the various risks in financial management?
Answer: Some financial risks are as follows:
- Credit risk: Unable to repay a loan or other debt.
- Operational risk: Loss due to errors or inadequate data in operational procedures.
- Liquidity risk: Not having enough cash on hand to meet short-term obligations.
- Fraud risk: Someone taking advantage of the company’s resources for personal gain.
Recommended Articles
It is an EDUCBA guide to Financial Management. Please refer to EDUCBA’s Recommended Articles to learn more about finance-related topics.