Updated September 29, 2023
What is Predatory Pricing?
Predatory pricing is when businesses intentionally set their prices much lower than their competitors to gain market share and drive the competitors out of business.
The idea is to set the price so low that no one can compete with it. Thus, businesses with lesser financial resources cannot compete with this price and start losing market share. It helps the predatory company establish a monopoly or near-monopoly in the market. After achieving this, the predatory company can increase its prices and reduce quality, knowing consumers have no other options.
Table of Contents
- What is Predatory Pricing?
- How Does it Work?
- Examples
- Diagram
- Effects
- Predatory vs. Limit Pricing
- The Legality
- Advantages and Disadvantages
Key Highlights
- Predatory pricing is a pricing strategy that large companies use to run small companies out of business by setting unreasonably low prices.
- This strategy can help the predatory company form a monopoly.
- This strategy involves two phases – predation and recoupment.
- The major difference between predatory and limit pricing is that while predatory pricing intends to eliminate all competition, limit pricing only aims to keep new entrants away from the market.
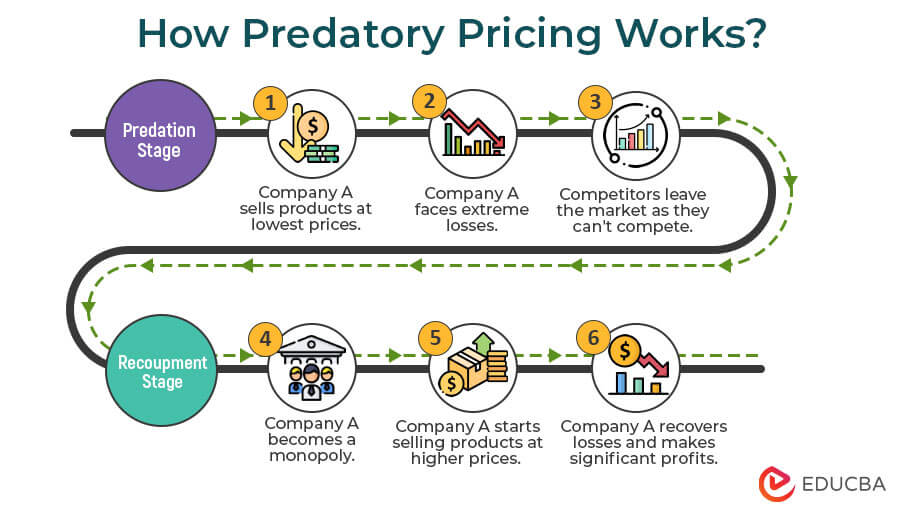
How Does It Work?
In predatory pricing, companies set prices very low, which means they have to face losses. Therefore, it is only a short-term tactic because a business can only handle facing loss for a short time. Thus, after a period, the company has to increase its prices, and once they do, new competitors start entering the market.
There are usually 2 stages in this strategy.
1. Predation: In this stage, the company decides to lower its prices below what’s financially sound for any other business. Before this, the predatory company sets aside a significant sum of money to continue operating, even when it’s losing money.
2. Recoupment: Once competitors successfully leave the market, the predatory company raises its prices again. This ensures that the company recovers the losses of the predation phase from the profits of the recoupment phase.
Real-World Examples
Although predatory pricing is hard to prove, there have been some instances where companies were guilty. Here are some of those examples.
Example #1
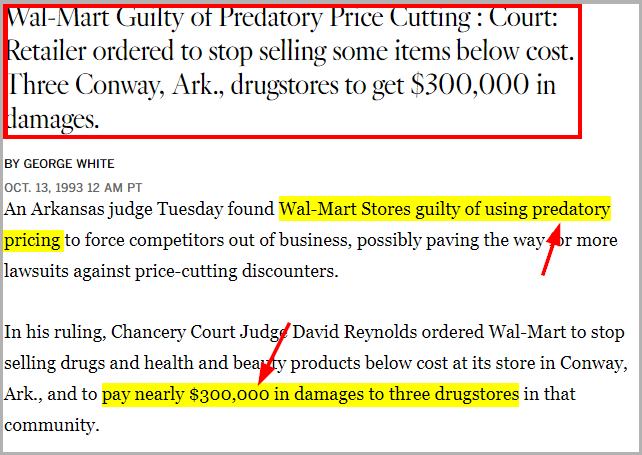
In the year 1993, Walmart faced a lawsuit from three local drugstores in Conway, Arkansas. They accused Walmart of deliberately selling drugs and other products at a loss to drive the local drugstores out of business.
In a landmark decision, an Arkansas judge found Walmart guilty of the practice. The judge then ordered the company to stop selling their drugs, health, and beauty products below cost and to pay damages of around $300,000 to the three drugstores.
Source: Los Angeles Times
Example #2
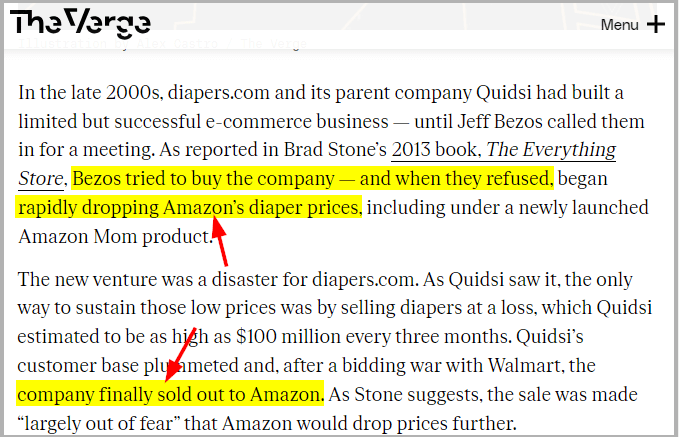
Various companies accuse Amazon of using an illegal pricing strategy to force its competitors to either leave the market or merge with Amazon. As per the news, Amazon wanted to buy Quidsi, the parent company of diapers.com. However, Quidsi disagreed; thus, Amazon soon started selling its diapers at a very low price. In the end, Quidsi ended up offering its company to Amazon. However, even though numerous businesses believe that Amazon uses predatory pricing, companies have no solid proof to prove it.
Source: The Verge
Diagram
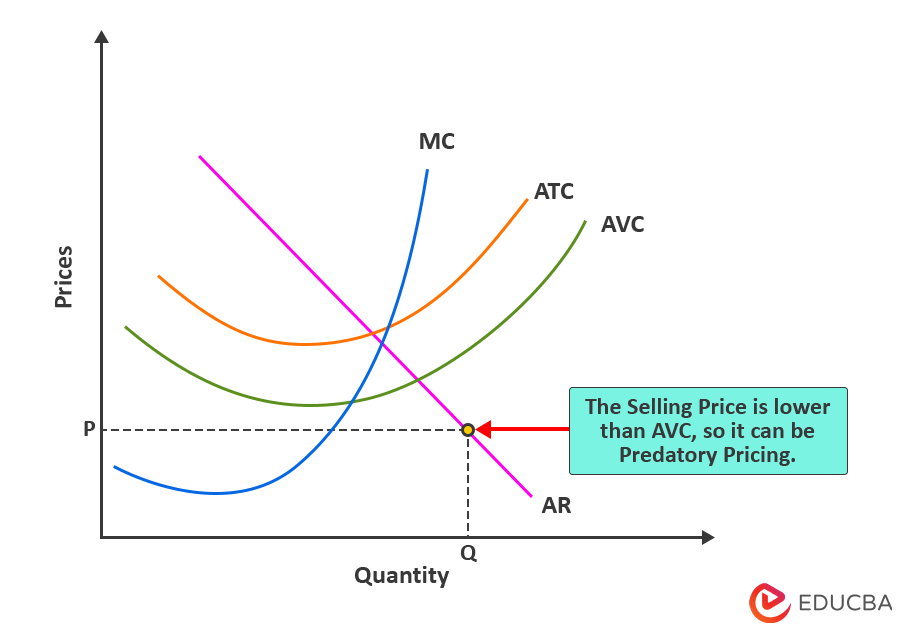
The predatory pricing diagram shows how companies lower prices to kick out rivals from the market. It’s like a simple supply and demand chart where we see how businesses set their prices and costs for their products.
Graph:
Where,
- X-axis: It shows the output level of the economy.
- Y-axis: It shows the prices of the product.
Key curves on the graph:
- AR (Average Revenue) Curve: This curve represents the demand for the product in the market. Generally, it is a downward-sloping curve, indicating that as prices drop, demand for the product increases as more people are willing to buy it.
- MC (Marginal Cost) Curve: The MC curve shows how much it costs to produce one more unit of the product. It typically slopes upward because producing more units of a product can become increasingly expensive.
- ATC (Average Total Cost) Curve: This curve shows the total cost of producing a product. It is generally a U-shaped curve, showing that costs might be high initially but then fall to the lowest possible costs and then start rising again as production increases.
- AVC (Average Variable Cost) Curve: This curve represents the costs that vary depending on the number of units, such as raw materials, labor, etc. This curve generally has a U shape, similar as well as parallel to ATC.
How to Interpret the Diagram?
To understand the graph, you can look at the curves on it. This will help you see how a company prices its products. If prices are much lower than the AVC line, it might mean that the company is engaging in predatory pricing, where it is temporarily lowering prices to drive competitors out of the market.
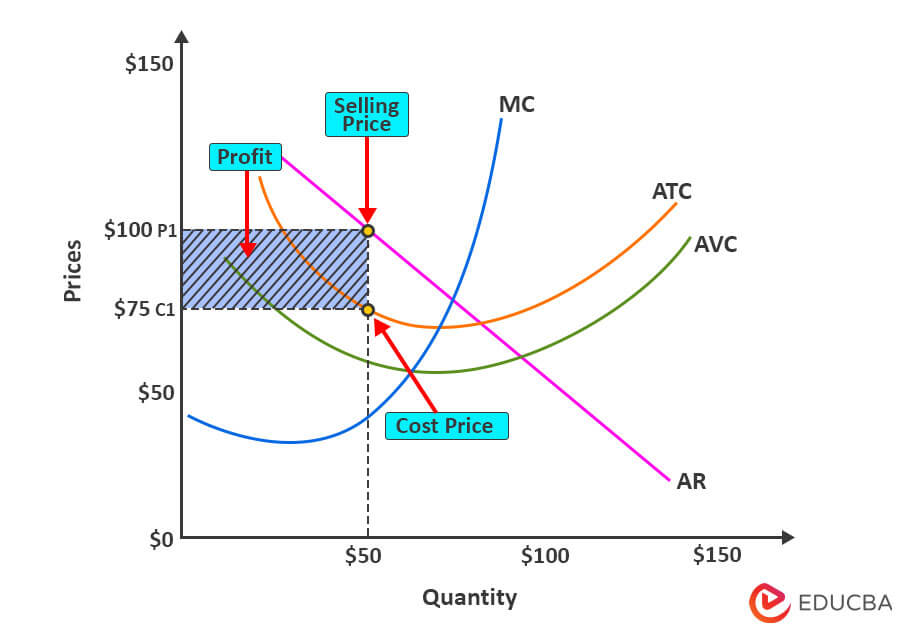
To understand the diagram, let us now take an example of a hypothetical company, ABC, that practices predatory pricing.
1. The company has the following data before predatory pricing:
| Quantity | 50 |
| Cost Price | $75 |
| Selling Price | $100 |
| Profit | $25 ($100 – $75) |
As we can see in the graph, the company ABC is selling the products at $100, which is more than what it costs ($75) for the company to produce the product. This means the company is making a profit of $25.
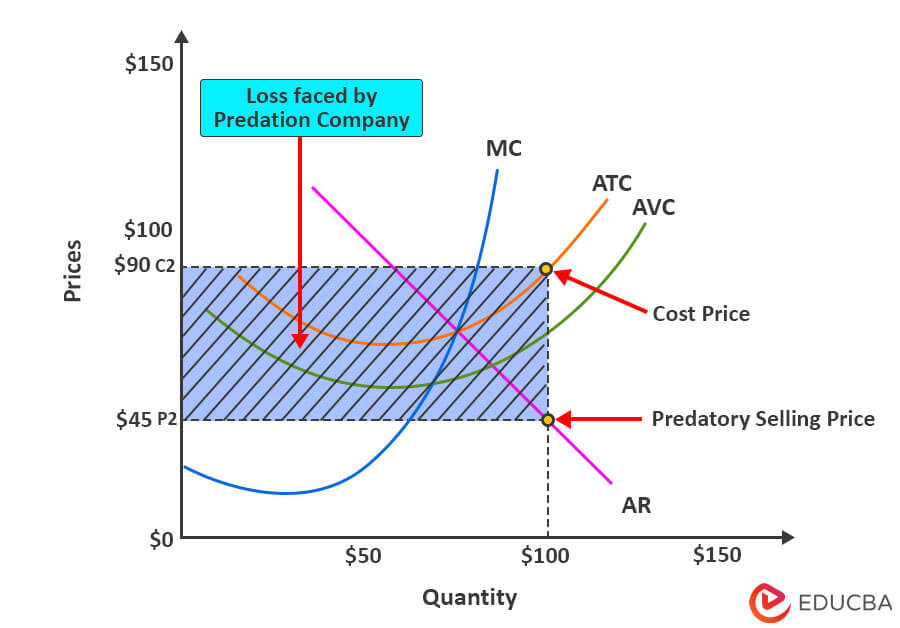
2. The company has the following data during predatory pricing:
| Quantity | 100 |
| Cost Price | $90 |
| Selling Price | $45 |
| Loss | $-45 ($45-$90) |
Now, as per the above graph, the company has set its selling price at $45, which is way below its costs ($90). This indicates that the company is facing a loss of $45. The important thing to note is that the selling price is below the AVC curve, meaning that the price is predatory, and the company ABC might be using a predatory pricing strategy.
Effects
Predatory pricing has the following effects on the market, the predatory firms, and consumers.
Effects on the Market:
- It helps businesses remove competitors from the market.
- It also creates new barriers so that new companies cannot enter the market.
- Moreover, fewer companies in the market can cause supply and demand inefficiency.
- Reduced competition also reduces innovation.
Effects on Predatory Business:
- The predatory business gets a higher market share.
- The business may also have to face legal scrutiny, as it can be considered anti-competitive.
Effects on Customers:
- Consumers get the chance to buy products at the lowest prices for a while.
- However, in the long run, they lose the option to choose from different companies as there is only one dominating company.
Predatory Pricing vs. Limit Pricing
Here are the main differences between the limit and predatory pricing strategies.
| Aspects | Predatory Pricing | Limit Pricing |
| Intention | The company wants to form a monopoly or near-monopoly and drive all the competition out. | The company wants to maintain its market share by making sure no new players enter the market. |
| Strategy | The set price is lower than the cost to make it impossible for any business to compete at the same price point. | The price is set low enough to make it unattractive for new entrants. |
| Time horizon | It is a short-term strategy. | It is a long-term strategy. |
| Legality | It is illegal in most countries in the world, as authorities view it as an anti-competitive behavior. | It is legal as authorities see it as a legitimate pricing strategy to protect the firm’s market position. |
The Legality of Predatory Pricing
Most countries consider predatory pricing illegal because it is anti-competitive and causes harm to consumers by reducing competition, resulting in lower-quality products or services and higher prices in the long run.
The United States prohibits the use of this strategy under Section 2 of the Sherman Antitrust Act. However, to determine if a company’s pricing strategy is predatory, the courts typically look at the following factors:
- Whether the company can sustain losses for an extended period.
- Whether the company’s pricing is below its costs.
- Whether the company has a plan to recoup its losses once it has eliminated competition.
- Whether the company’s actions harm competition and consumers.
If the authorities find a company engaging in such practices, the company can face significant fines and other penalties, including paying damages to affected competitors. In addition, the court may also prohibit the defendant from engaging in similar conduct in the future.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Following are the advantages as well as disadvantages of predatory pricing.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| It can be beneficial for consumers in the short run as they can buy products at unbelievably low prices. | In the long run, consumers lose their right to choose as there are very few players in the market. |
| It helps companies undercut their competition and form a near-monopoly. | A predatory company can reduce the quality and increase the price of its products as much as it likes once it forms a monopoly. |
| The predatory company can increase its price once there’s no threat of competition, thus eventually turning profitable. | Selling a product at a loss decreases the profitability of the entire market. |
Final Thoughts
It is often hard to distinguish between predatory and competitive pricing as proving intentions is complex. This helps many businesses successfully avoid any punishments. However, companies should refrain from such practices as they are not beneficial for anyone in the long run.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is predatory pricing in the Indian Competition Act 2002?
Answer: According to Section 4 (2) (a) of the Competition Act of 2002, any company that has a higher market share cannot use predatory pricing to claim a monopoly.
Q2. How can companies defend against predatory pricing?
Answer: To avoid losing to predatory pricing, companies can innovate or differentiate their products, making them less susceptible to price competition. Additionally, companies may partner with other companies or merge with competitors to increase their bargaining power.
Q3. How does predatory pricing differ from competitive pricing?
Answer: Companies implement competitive pricing to be able to compete with other players in the market. On the other hand, companies use predatory pricing to eliminate all competition.
Q4. How does predatory pricing impact small businesses?
Answer: Large companies setting unrealistically low prices can harm small businesses as they are unable to match the price and are subsequently forced out of the market.
Q5. How do antitrust laws address predatory pricing?
Answer: Antitrust laws prohibit companies from using their market power against the competition and consumers. Companies can face fines, legal action, or other penalties if found guilty of predation.
Recommended Article
The above EDUCBA article is a guide to Predatory Pricing. If you need any further guidance on other economics-related topics, EDUCBA recommends these articles: