Updated October 7, 2023
What is a Macroeconomic Factor?
A macroeconomic factor is any geopolitical, environmental, or economic event that impacts an entire region, nation, or, in some cases, the world. It can be any condition or characteristic that has a large-scale impact affecting an entire economy rather than just a part of it.
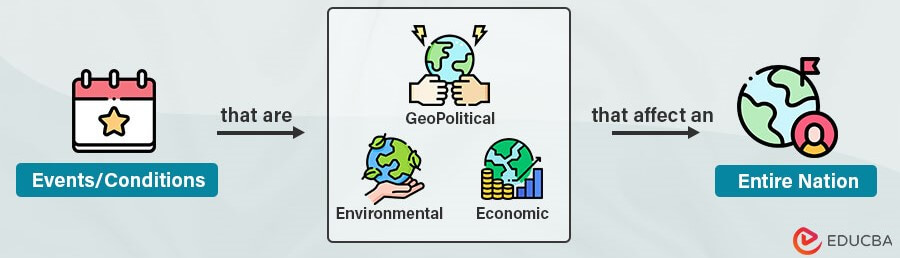
Table of Contents
Key Highlights
- A macroeconomic factor is any event or characteristic that can affect a large population, typically an entire nation.
- These factors can be either positive, negative, or neutral.
- GDP, unemployment rates, national income, and inflation are some common and important factors.
- Analyzing these factors is important to understand the current and future health of an economy, as well as deciding government policies and making investment decisions.
- The main difference between a macroeconomic and microeconomic factor is that while a microeconomic factor focuses on individual consumers, firms, and markets, the macroeconomic factor focuses on the entire economy as a whole.
Macroeconomic Factor Types
Economists categorize macroeconomic factor into the following 3 groups:
Positive Factors:
- Any event or factor that promotes economic stability and growth within a country or a group of countries is a positive macroeconomic factor.
- For instance, a low unemployment rate is a positive factor because it means the availability of more jobs, leading to more income, signifying the economic prosperity of a country.
Negative Factors:
- Events that may risk the domestic or global economy are called negative macroeconomic factors.
- Factors like high inflation rates are negative factors because high prices of goods and services reduce the spending power of consumers. This results in decreased demand, thus impacting the country’s GDP and overall economic health.
Neutral Factors:
- These are macroeconomic events or changes that neither benefit nor harm the economic conditions of a country.
- Usually, these changes are so minor or temporary that they don’t have any significant impact on the economy.
- For example, a small change in an otherwise stable currency exchange rate is less likely to affect the economic condition of a country.
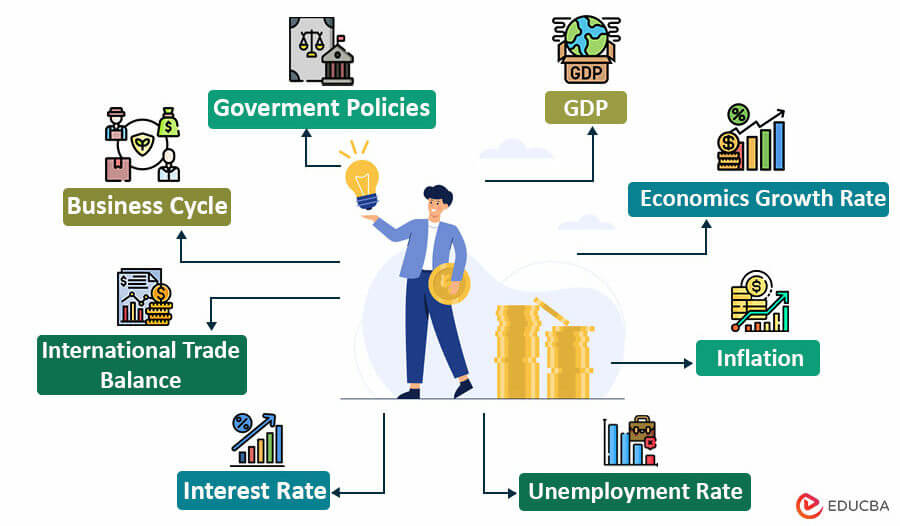
Different Macroeconomic Factors (with Examples)
Here are some of the common macroeconomic factors, along with their examples:
1. Gross Domestic Product or GDP
The total economic worth of the commodities and services that a nation produces within a specified period is known as its gross domestic product or GDP. Along with the financial impact of trade and investments within a country, GDP also tracks government and citizen spending. A rising GDP generally indicates economic growth, while a declining GDP may suggest a recession.
Formula:
where,
C = Consumption,
I = Investment,
G = Government Spending, and
NX = Net Exports
Example: Let’s take the example of a fictional country called A.
- Consumption: Now, let’s assume in the year 2023, the citizens of A spent a total of $14.44 trillion on goods and services, housing, transportation, food, healthcare, and entertainment.
- Investment: The businesses invested $3.61 trillion in equipment, machinery, buildings, and other assets.
- Government Spending: The government spent $6.55 trillion on its different programs and services.
- Net Exports: And finally, the net export value or NX was -$670 billion as the imports were more than the exports.
Therefore, the GDP of Country A for 2023 = $24.94 trillion ($14.44 trillion + $3.61 trillion + $6.55 trillion – $670 billion = $24.94 trillion)
2. Economic Growth Rate
The cost of the output of goods and services in a nation over a given period, as compared to that same period in the previous year, is known as the economic growth rate. A higher economic growth rate means higher demand for goods and services, leading to higher business profits.
Formula:
where,
GDP2 = the GDP of the current year
GDP 1 = the GDP of the previous year
Example: The GDP of Country A in the year 2013 was $1.211 trillion, and its GDP in 2023 was $6.087 trillion. So, the economic growth rate of Country A from 2013 to 2023 will be,
=($6.087 trillion – $1.211 trillion)/$1.211 trillion = 403.64, which is equal to 40.36%.
Therefore, Country A showed a growth rate of more than 40% from 2013 to 2023.
3. Inflation Rate
The inflation rate is when the general price level of goods and services rises, leading to a decrease in the purchasing power of money. Moderate inflation is generally considered healthy for an economy, but higher inflation can decrease the value of a currency and cause economic instability.
Formula:
where,
CPI = Consumer Price Index (the average price change over time for a basket of goods and services a typical household needs).
x = the initial year.
x+1 = the current year.
Example: Suppose in 2022, the Consumer Price Index for country A was $2,000. In 2023, the Consumer Price Index grew to $2,500. So, the inflation rate in 2023 = (2,500-2,000) / 2,000 = 0.25. Multiplying it by 100, we get 25%. Thus, the inflation rate is 25%.
4. Unemployment Rate
The unemployment rate refers to the percentage of a country’s population that is jobless despite actively looking for a job. It reflects the health of the labor market and the availability of jobs. A lower unemployment rate indicates a healthier job market, while a higher rate suggests economic challenges, such as joblessness and reduced consumer spending.
Example: In August 2023, the unemployment rate in the US increased to 3.8% from July’s 3.5%. The total number of unemployed people (people who are actively looking for jobs but not finding them) is $6.36 million as of August 2023.
5. Interest Rates
Interest rates (set by a country’s central bank) influence borrowing costs for businesses and consumers. Changes in interest rates can impact spending and investment decisions. When central banks raise interest rates, borrowing becomes more expensive, potentially slowing down economic growth to control inflation. Conversely, lower interest rates can increase borrowing and spending, boosting economic activity.
Example: The central banks of every country set their interest rates based on the current economic activity in the region. Currently, Japan has the lowest interest rate at just -0.10%, while Turkey has the highest interest rate at 30%.
6. International Trade Balance
The balance of trade is the difference between a nation’s imports and exports in a particular period. It impacts a nation’s economic health since it shows how valuable its currency is and how much global demand there is. When a country exports more than it imports, it has a surplus, which makes its currency more valuable due to higher demand for its exports.
Formula:
Example: In July 2023, the US exported goods worth $251.7 billion while the total imports were worth $316.7 billion. This means the balance of trade for July 2023 was – $65 billion. In other words, the US is suffering a trade deficit of $65 billion as its imports exceed its exports.
7. Business Cycle
A business cycle is when an economy experiences constant expansion (periods of growth) and contraction (periods of decline) over time. During expansion, the economy has more jobs, an increase in money supply as well as spending. On the other hand, during contraction, people choose to spend less as they are earning less, too.
Example: Before the great depression of 1929, the economy was doing extremely well. It had a high GDP and very low unemployment. However, once the contraction hit, the economy fell into the great depression, where the GDP fell to its lowest.
8. Government Policies
Government’s policies and regulations can influence the other economy as well as other macroeconomic factors. These policies can be fiscal (government spending, taxation, etc.), monetary (money supply, interest rates, etc.), and trade (Tariffs, trade agreements, etc.).
Example: Suppose a country is facing financial problems, and to solve those, the country’s government introduces monetary policy by reducing interest rates. This, in turn, increases borrowing, spending, and, eventually, economic growth.
Importance of Macroeconomic Factor
Here are the reasons why macroeconomic factor is important for governments, businesses and economists:
Government:
- Government bodies analyze factors like GDP, inflation, growth rate, etc., to create fiscal and monetary policies.
- A central bank, for instance, might choose to supply more money into the financial market if a country is going through a recession.
- On the other hand, it can restrict the supply of money to reduce the spending power of consumers during inflation.
Businesses & Investors:
- A business’s capability to borrow from banks depends on factors like interest rates, general price level, and national income.
- Domestic and foreign investors also need to evaluate the country’s macroeconomic factor before making any investment decisions.
Economists:
- Economists use the macroeconomic factor to understand how an economy is performing.
- They also use past and current data about various macroeconomic factors to forecast the economic future of a region, country, or the world.
Microeconomic vs. Macroeconomic Factor
Following are the major differences between microeconomic and macroeconomic factor:
| Aspects | Macroeconomic Factor | Microeconomic Factors |
| Meaning | These are the factors that impact a larger population. | These factors impact a smaller population. |
| Scope | Deals with an entire economy like a country or a region. | Deals with factors impacting individual consumers, firms, and markets. |
| Goals | To understand how a nation allocates its resources and maintains the overall economic health and stability. | To understand how producers and consumers allocate their scarce resources to obtain maximum benefits. |
| Factors |
|
|
| Uses | Government bodies use these factors to formulate monetary and fiscal policies. | Businesses use these factors to decide their production and pricing level. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are macroeconomic methods?
Answer: Macroeconomic methods are tools and techniques that economists and policymakers use to analyze, measure, and influence economic trends. These methods help understand the broader economic picture, make informed decisions, and formulate effective economic policies. These methods include national income accounting, input-output analysis, international trade analysis, policy-impact analysis, business cycle analysis, and so on.
Q2. What macroeconomic factor affect businesses?
Answer: Some of the key macroeconomic factors that affect businesses are economic growth rate, inflation rate, interest rate, unemployment rate, and currency exchange rate.