Updated October 30, 2023
Economic Stimulus Package Meaning
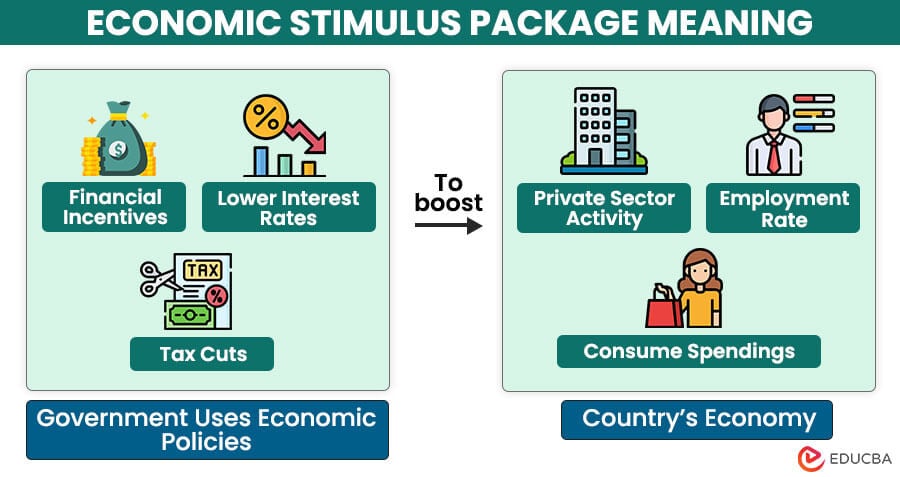
An economic stimulus package, or a stimulus package, is a set of measures and policies that the government uses to boost a country’s economy during an economic downturn or recession.
The main aim is to promote private-sector activity to boost economic growth, create jobs to reverse recession and stabilize financial markets. These packages typically include monetary and fiscal policy measures depending on the economic circumstances and the government priorities. For instance, they can include tax cuts, lowering interest rates, increasing government spending, subsidies, and other financial incentives.
Table of Contents
Types
The following are the different types of economic stimulus packages that the government implements.
- Fiscal Policy: It is when the government uses its revenue and expenditure to influence the economy. It includes tax reduction to increase consumer’s spending capacity, which helps increase demand, leading to businesses hiring more workers. It also includes increasing government spending on infrastructure development, like hospitals, highways, etc., to create employment.
- Monetary Policy: These are measures the central bank takes to control the money supply. It includes lowering the interest rates so that businesses and individuals will spend or invest more, stimulating economic activity.
- Quantitative Easing: Quantitative easing is a type of monetary policy where central banks purchase government bonds or other financial assets to increase the money supply in the economy.
Real World Examples
Example #1: Aatma Nirbhar Bharat Abhiyan 2020
In 2020, India’s Prime Minister Narendra Modi launched a comprehensive economic stimulus package, “Aatma Nirbhar Bharat Abhiyan,” worth INR 20 lakh crore ($275 Bn). The government introduced this package to tackle the severe financial challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic. The primary objective of this package is to make the country self-sufficient in significant sectors, create employment opportunities, and promote economic growth.
Example #2: CARES Act 2020
After the U.S. Congress passed the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act on March 25, 2020, President Donald Trump signed it into law on March 27, 2020. This economic relief package worth $2.2 trillion was to recover from the COVID-19 pandemic’s economic impact.
It provided financial assistance to individuals, businesses, industry sectors, and healthcare systems affected by the pandemic. Additionally, the act authorized direct payments of $1,200 per adult and $500 per child under 17.
Example #3: Recovery Act 2009
President Barack Obama signed the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act (ARRA) in February 2009. This act was a significant economic stimulus package worth $787 billion. The purpose of the law was to stabilize the economy and promote recovery during the Great Recession.
The government wanted to jumpstart the economy after the Great Recession of 2008. So, the primary goal of ARRA was to create or save jobs, modernize the country’s infrastructure, and provide tax relief. It also included substantial investments in sectors such as healthcare, energy, and education.
Risks
It’s important for policymakers to carefully consider the risks of implementing stimulus packages to avoid potential negative consequences. Here are a few possible risks of using economic stimulus packages:
- Inflation: When the supply of goods and services does not align with increased demand, it can lead to a rise in product prices, thereby increasing
- Debt and Budget Deficits: To finance a stimulus package, the government increases its spending, which can sometimes lead to debt. It can also create an imbalance in the budget, creating budget deficits.
- Resources Mismanagement: Improper stimulus measures may result in the misallocation of resources. For instance, if the government invests funds in projects or industries that are not economically profitable, it can lead to low returns and a waste of resources.
- Stimulus Dependency: It can create an over-dependence on government intervention to maintain economic growth. This can weaken the ability of the private sector to grow and invest in projects organically.
- Exchange Rate Fluctuations: These measures can impact exchange rates, affecting trade balances. If a country’s currency value drops, it can boost exports but make imports expensive, reducing the demand for imported goods.
- Long-Term Economic Impact: In some cases, stimulus measures may lead to structural imbalances in the economy, leaving long-term negative effects.
Final Thoughts
In an economic stimulus package, policymakers implement a monetary and fiscal policy or a combination of both to achieve financial stability. These stimulus measures usually provide short-term relief. Thus, policymakers must consider all risks before implementing any policy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How does stimulus benefit the economy?
Answer: The economic stimulus benefits the economy in the following ways:
- Increasing government spending on infrastructure projects leads to employment opportunities in construction and related industries.
- Tax reduction measures put more money in customer’s hands, boosting their spending or purchasing capacity.
- It encourages business investment in expansion, research and development, and technology.
- It promotes long-term growth with strategic investments to maintain financial stability.
Q2. What is the root cause of the economic stimulus package?
Answer: Some of the root causes of implementing an economic stimulus package are:
- Recessions: A recession is a significant decline in economic activity characterized by reduced consumer spending and high unemployment.
- Financial Crises: These involve disruptions in the financial system, like banking crises, stock market crashes, etc.
- Natural Disasters: Natural disasters like hurricanes, earthquakes, or pandemics cause severe economic disruptions and require government intervention.
- Structural Problems: Long-term economic challenges like persistent high unemployment rates or imbalances in certain industries can also lead to the need for stimulus measures.
Recommended Articles
We hope this article providing comprehensive information on the economic stimulus package was helpful to you. For further guidance on similar topics, please refer to our recommended articles: