Updated November 30, 2023
What is a Trade War?
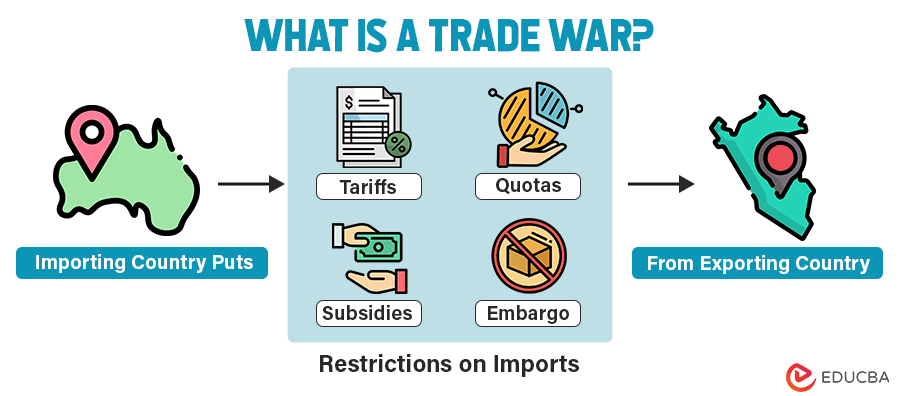
A trade war is when countries use trade barriers like tariffs, quotas, etc., to put restrictions on imports from other countries.
These have been going on for decades, but in recent years, there has been a significant increase in these wars in many parts of the world, including Europe and America.
Table of Contents
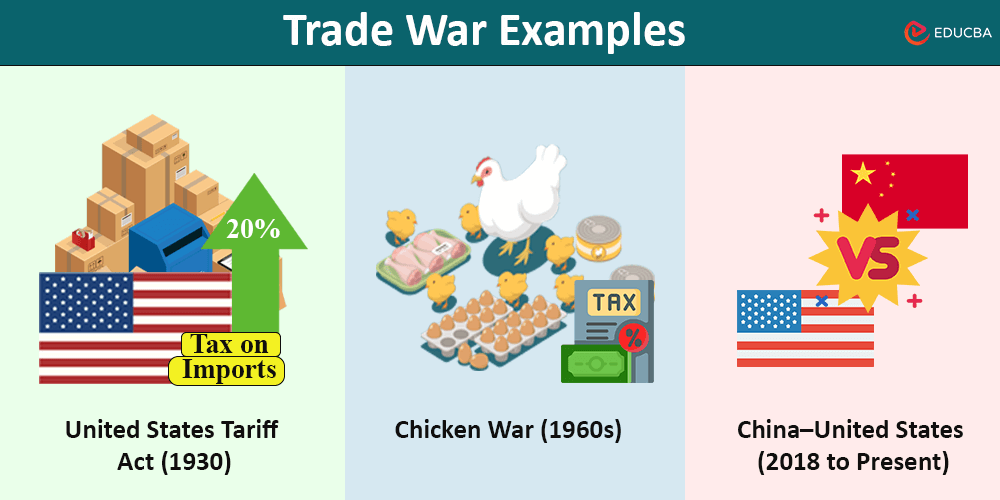
Real Trade War Examples in History
Example #1: United States Tariff Act (1930)
On June 17, 1930, US President Herbert Hoover approved a law to increase the average taxes on imported goods by almost 20%. Utah’s Senator, Reed Smoot, and Oregon’s Representative, Willis Hawley, suggested this.
The reason behind higher tariffs was the constant competition from Europe and other nations that harmed the US’s domestic agricultural economy.
However, due to these barriers, within the next two years, several other countries responded with similarly higher tariffs. As a result, imports and exports worldwide were costly and hence decreased significantly. This stalled the economic recovery from the Great Depression. Moreover, the US economy faced an approximately 66% decline in imports and exports.
Finally, after four years, in 1934, US President Franklin D. Roosevelt removed the higher tariff by signing the Reciprocal Trade Agreements Act.
Example #2: Chicken War (1960s)
In the 1960s, the Common Market, a group of European countries, raised tariffs on imported American chicken. This was to support local European chicken farmers and make the European community more self-sufficient in agriculture.
However, these tariffs made it hard for US poultry growers to sell in Europe, causing a massive decline in American chicken exports. It resulted in heavy losses for the US, but the Common Market did not agree with the amount of loss the US government declared, which led to disagreements on the financial impact.
When the US threatened to impose retaliatory tariffs, the GATT panel added an arbitration under the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT). The arbitration was that countries would set reasonable tariffs to maintain conflict-free world trade.
Eventually, when the panel ruled that the US had incurred losses of $26 million, US President Johnson imposed a 25% tax on “light trucks,” including imported Volkswagen buses, French brandy, potato starch, and dextrin. This led to the boom of pickup trucks in America.
Example #3: China–United States (2018–present)
Trade between the United States and China has grown significantly in recent decades. This trade has helped US consumers buy products at lower prices, and US companies are able to make substantial profits. On the other hand, it allowed China’s economy to boom.
However, due to these higher imports and exports, millions of Americans lost their jobs. The US also raised some concerns about national security, technology theft, etc.
So, as a response to these issues, in 2018, the US government imposed 10% tariffs on $200 billion worth of Chinese goods. Later, the United States also imposed tariffs on steel and aluminum imports. To retaliate, the Chinese government imposed retaliatory tariffs against US goods, resulting in a trade war. Both countries had been imposing tariffs on goods imported from the other country.
Recently, on 15th November, both nation’s Presidents, Xi Jinping and Joe Biden met to discuss how to settle the dispute. However, any actual actions or results are yet to be seen.
Reasons
A few causes of trade wars are:
- A country might start a trade war with another country to benefit its own economy. During trade wars, when imports decrease, the country’s internal production increases. In turn, their own people get more jobs, and their own economy grows.
- Another reason is that the country wants to keep its trade secrets or unique technology & patents hidden and safe from other nations.
- Typically, when a country has a significantly higher trade deficit, it tries to decrease imports from other nations to reduce its deficit and balance the trade differences.
- Sometimes, if one country believes that a competitor nation has unfair trading practices and is taking advantage of their trade relationship, they may start a trade war.
- Rarely are there situations where a nation uses trade wars to weaken another country’s economy. This can happen only when the other nation’s majority of income comes from imports.
How Do Countries Fight Trade Wars?
Countries use several economic factors to rage and fight trade wars, such as:
1. Increasing or Imposing Tariffs
Tariffs are when a country imposes taxes on products that they are importing. It means the businesses that are importing from other nations have to pay taxes on the goods they import. When tariffs increase, imports usually decrease.
2. Declaring a Quota on Imports
As the name suggests, it is when countries set a quota, i.e., limitation of the number of goods that one can import. This way, only a limited amount of products come from other countries, and domestic manufacturers produce the rest.
3. Declaring Subsidies Within the Nation
Subsidies are when the government provides businesses with financial benefits like tax cuts, grants, low-interest loans, etc., for manufacturing products. This way, the manufacturing costs decrease, and in turn, domestic producers can sell their products at a lower price. As a result, they can compete with international imported product prices.
4. Devaluing Their Own Currency
While it may seem drastic, countries sometimes employ monetary policies to intentionally lower the value of their currency compared to other nations. As a result, importers have to pay higher costs to import products from other countries, reducing import quantity.
5. Embargo
This is an extreme measure that counties rarely take. It is when a country bans importing products from another country. They usually stop the import of some specific items from a specific country.
Effects
Although starting a trade war aims to increase economic growth and protect domestic manufacturers, there can be adverse effects. First and foremost, it damages a country’s relationships with other nations and harms cross-cultural communication, reducing international trade.
Trade wars also lead to higher prices for goods due to tariffs, making them more expensive for consumers. Moreover, reduced imports also decrease the supply of goods. This makes it harder for people to buy what they want, lowering consumption levels. Additionally, rising prices can lead to increased inflation.
Additionally, sudden trade barriers create uncertainty, causing interest rates to rise and investments to decrease, impacting economic growth. Lastly, when one country imposes trade barriers, others may respond by raising tariffs too. This continuous battle can often result in higher prices of consumer goods, job losses, and slower economic growth.
Final Thoughts
A trade war is a controversial by-product of protectionist policies. According to supporters, it safeguards national interests and benefits domestic businesses. However, trade war opponents assert that these conflicts ultimately harm small businesses, consumers, and the economy.
Recommended Articles
We hope this detailed article on the trade war was informative for you. For more similar articles, visit the following links: