What are Out-of-Pocket Expenses?
Out-of-pocket expenses are costs you pay from your own money for goods/services or medical care. Your insurance or other benefits do not cover these costs, so you must use your funds to pay for them. You may or may not get reimbursed for these expenses.
Within an organization, these expenses refer to the costs that employees pay for work-related needs, which the company will later reimburse or pay back to the employees. These expenses may include parking charges, airplane or train tickets, office supplies, meals, lodging, and other similar costs.
In medical, these expenses refer to the healthcare costs that a patient must pay on their own, beyond their insurance coverage, which the insurance policy or company does not reimburse. These expenses may include doctor’s visit fees, prescription drugs, deductibles, copayments, etc.
Table of Contents
- What are out-of-pocket expenses?
- Medical Expenses
- Examples
- Deductible Vs.Out-of-Pocket Expenses
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
Out-of-Pocket Medical Expenses
Out-of-pocket expenses commonly apply in the field of medical and health insurance. It includes deductibles, copayments, coinsurance, and costs of health care services not covered by insurance policy. Additionally, the insurance policy does not cover ambulance fees, gloves, alternative therapies, and other miscellaneous expenses.
Therefore, it’s important to understand insurance plans covering healthcare costs to avoid unexpected medical bills. The impact of these uncovered expenses can leave patients in medical debt. Hence, many insurance plans have annual out-of-pocket maximums, the maximum amount an individual has to pay in a year.
Examples of Out-of-Pocket Costs
The following are some examples of the expenses in healthcare and organizations.
#1:Copays: Copays or copayments are a fixed amount a patient pays for a specific medical service, such as a hospital trip, doctor’s visit, or prescription bills.
#2 Deductibles: Deductibles are the initial amount an individual must pay from their own pocket before the insurance company begins covering costs. It is a predetermined cost and can vary depending on the coverage, location, severity of disease, and more.
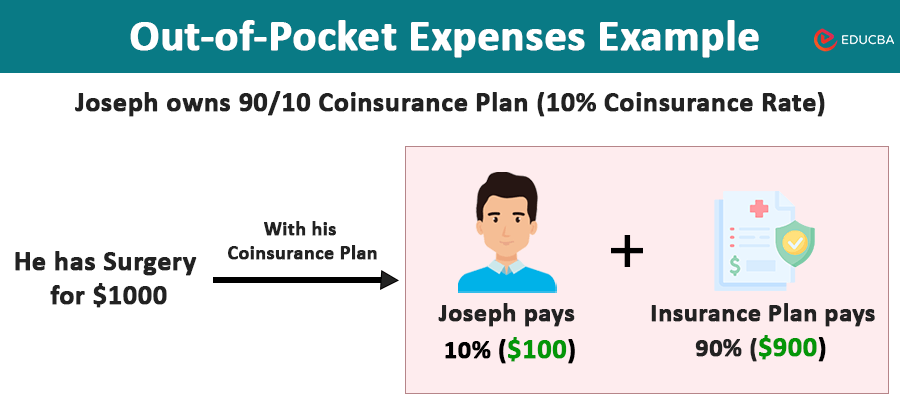
#3 Coinsurance: Coinsurance refers to the cost-sharing arrangement between an individual and their insurance company after the individual has paid their annual deductible. Simply, it decides what percentage the insurance will cover and how much an individual needs to pay for medical services or treatments.
#4 Prescription medication: Prescription medication refers to the cost individuals pay for medications their doctor prescribes. These costs vary based on the medication types, what the insurance plan covers, and whether the drug is generic or brand-name.
#5: Work-Related expenses: These expenses are what individuals spend on work-related tasks, including plane tickets, renting cars, travel fares, fuel, parking, staying at hotels, meals, etc.
Deductible Vs.Out-of-Pocket Expenses
The difference between deductible vs. out-of-pocket expenses is as follows.
| Particulars | Deductible | Out-of-Pocket Expenses |
| Definition | The initial amount an individual pays before insurance covers the expenses. | The maximum amount an individual pays directly for healthcare services not covered by insurance. |
| Amount type | Fixed amount set by insurance plan. | Variable amounts depend on expenses incurred in healthcare. |
| Coverage Application | Must be paid before insurance starts covering expenses. | Includes all costs until reaching the maximum expenditures limit. |
| Examples | Only medical expenses under the medical insurance coverage. | Deductible, copays, coinsurance, prescription drugs, etc. |
Advantages
The following are some advantages of these expenses.
- Flexibility: Individuals have the freedom to choose their healthcare services and insurance plans.
- Avoiding unnecessary treatments: Individuals are less likely to undergo unnecessary treatments or procedures, which can save money.
- Avoiding insurance restrictions: It allows individuals to choose doctors and treatments, as they are not bound by the specific treatment covered in the insurance coverage plan.
- Tax deductions: These medical expenses can sometimes be tax-deductible, providing potential tax benefits.
Disadvantages
The following are some disadvantages of these expenses.
- Financial strain: Medical expenses can cause financial strain or burden, particularly for those with low incomes or pre-existing medical conditions.
- Limited access to care: Some individuals may avoid seeking medical care or delay necessary treatments, which can worsen their health conditions.
- Unpredictable costs: These are often unpredictable and make it difficult to budget or plan for healthcare costs.
Final Thoughts
Out-of-pocket are costs individuals pay for healthcare or work-related services not covered by insurance. While these expenses offer flexibility, tax benefits, and self-awareness of healthcare costs, they can also lead to financial strain. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the impact of these expenses in managing one’s budget and healthcare needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Are there any limits on out-of-pocket expenses?
Answer: Yes, various health insurance plans have out-of-pocket maximum limits. These are the total amount individuals pay for covered healthcare services within a year. Once this limit is reached, the insurance company covers all remaining expenses for that period. In the United States, the out-of-pocket maximum from 2024 will be $9,450 for an individual and $18,900 for a family.
Q2. How to reduce out-of-pocket medical expenses?
Answer: The following are the ways by which you can reduce medical expenses
- Choose a healthcare plan with lower deductibles or copays that align with your needs.
- Prefer in-network providers, like doctors, hospitals, and facilities covered by your insurance plan.
- You can use generic medicines to cut down prescription costs.
- You can enquire about available financial assistance programs in hospitals or healthcare organizations.
- Focus on a healthy lifestyle to reduce health issues and lower medical care needs, reducing expenses.
Q3. What other kinds of expenses are categorized as out-of-pocket costs in business?
Answer: In business, out-of-pocket costs include expenses like petroleum, parking or tolls during traveling, and reward certificates or trophies for employees. In addition, it also includes depreciation, amortization, purchasing fixed assets, or other non-cash expenses.
Recommended Articles
We hope this information about “Out-of-Pocket Expenses” was beneficial and informative. To learn more, check out the following articles.