Updated December 30, 2023
What is International Finance?
International finance is a part of international economics that studies how money moves across different countries by focusing on exchange rates, global trade, foreign investments, capital flow, and currency markets.
Businesses are continuously evolving and expanding their operations in different countries. When a country does business in another country, it has to follow certain government rules and regulations, international trade policies, currency exchange rates, borrowing and lending loans in foreign currencies, etc. Hence, international finance management is important in cross-border trading and investment and helps businesses operate smoothly internationally.
Table of Contents
Examples of International Finance
Let’s understand the concept of the international finance system using the following examples.
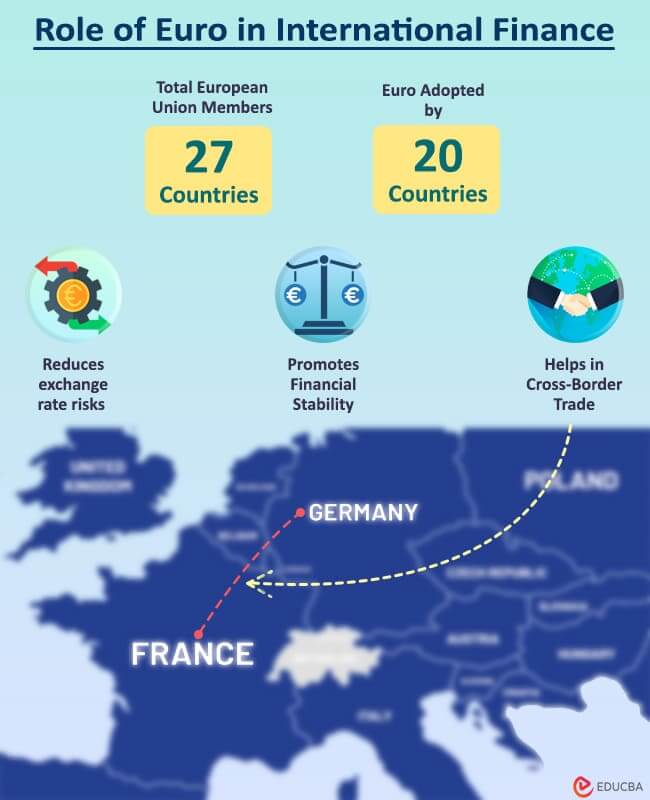
1. Euro
The European Union comprises 27 countries, and the official currency is the “Euro,” which is adopted by 20 countries. This arrangement facilitates smoother cross-border trade and financial transactions among member countries, reducing the burden of currency conversion costs and other risks.
For instance, a company in Germany can sell goods to France without worrying about exchange rate fluctuations as both countries use the Euro. Also, buyers from Ireland can easily buy products from Belgium without extra costs.
2. International Monetary Fund
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is a prominent institution that plays an important role in international exchange rates and transactions. It aims to facilitate international trade and promote financial stability, employment, and sustainable economic growth.
It also provides financial support to member countries facing financial difficulties. The IMF’s actions and policies impact the stability and functioning of the international monetary system.
Theories
The international finance system consists of theories, principles, and microeconomics models, which are as follows.
1. Mundell-Fleming Model
The Mundell-Fleming model theory explains how a country’s monetary policies can affect its economy, especially exchange rates and interest rates. This model assumes that prices of goods should remain the same or fixed. In this scenario, when a country changes its government spending or interest rate, it affects its trade with others, thereby changing its currency value.
Consider Country A and Country B trading together following the Mundell-Fleming model (buying and selling goods at the same price). Now, if Country A decides to build roads using government spending, they will also increase demand for raw materials from Country B. Here, Country B will sell more raw materials to Country A.
However, if Country B raises its interest rate, Country A will think twice before buying from them. Therefore, to facilitate trading, both countries might change their currency value. So, the Mundell-Fleming model helps us understand how changes in one country’s fiscal policies affect its trade with another country and even change the value of their currencies.
2. International Fisher Effect
This international Fisher effect theory explains how nominal interest rates in different countries affect their currency values in the future. This theory assumes that if one country’s nominal interest rates are higher than another’s, its currency value should increase over time compared to the other country’s currency. This suggests that when interest rates are higher, the currency will strengthen or increase in value.
3. Optimum Currency Area
The optimum currency area theory suggests that it would be most efficient in some specific areas or regions if they shared and used a common currency, like the euro, in European countries. This is because a common currency leads to a better economy and makes trading and investing easier and more efficient for everyone.
4. Purchasing Power Parity
This theory compares the prices of goods and services in different countries to understand the real purchasing power of each currency in other countries. Basically, this theory suggests that currency exchange rates between two countries should adjust so that a product of one country should cost the same in different countries when converted into their currency value. It helps us understand how exchange rates might change based on the prices of goods and services in other countries.
Suppose Ted buys a gadget in the United States for $20, and Maria gets that similar gadget in Germany for 18 euros. In that case, this theory suggests that the exchange rate between dollars and euros should be adjusted so that they are equal. Here, $20 is equivalent to 18 euros and vice versa.
So, if there are any changes in the price of goods in one United States, it should reflect a similar change in Germany. It helps us understand how exchange rates might change based on what goods cost in the United States and Germany.
5. Interest Rate Parity
Interest rate parity suggests that the interest rates between two countries should be equal. This equilibrium state allows investors to invest in either country as both of their country’s banks offer similar interest rates.
Features of International Finance
The following are the features of international finance:
1. Boosts International Trade
The exchange of items between countries is known as international trade. This trading practice can boost the economies of both trading partners by increasing employment and income. However, trade can also lead to risks like default, currency devaluation, economic imbalances, etc.
2. Enables Diversified Portfolio Investment
Portfolio investment is buying stocks, bonds, assets, or other securities from foreign companies. This type of investment involves investor diversification, which means investing in different sources, exposure to new markets, and the potential to profit from selling the assets at a high price.
3. Facilitates Access to Foreign Exchange Markets
The foreign exchange markets determine the currency exchange rates of different countries. It allows individuals and businesses to convert one currency into another for international trade and investment. Forex is the world’s largest foreign exchange market, which operates 24/5 to improve global currency exchanges.
4. Tracks Balance of Payments
Balance of Payments (BoP) is a comprehensive record of all financial transactions between a particular country and the rest of the world over a specific period. This BoP records transactions related to the trade of goods and services, income flows, investments, and other financial transfers. It reflects a country’s net income earned from foreign countries and its trade balance (exports minus imports). This is important for understanding economic stability.
5. Allows Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) Across Nations
Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) is when a company invests money directly in another country by setting up operations or buying businesses there. FDI can bring new jobs and capital to the host country and help the investing company enter new markets. However, FDI can also be risky, as controlling operations in a foreign country can be difficult.
6. Promotes Growth of Multinational Corporations
Multinational corporations are companies that operate in multiple countries. They conduct business activities such as production, sales, and investments across borders. MNCs play a significant role in international finance through their cross-border operational activities, capital flows, and influence on global markets.
7. Affected by Market Imperfections
International finance is also affected by market imperfections. Market imperfections, such as barriers to trading in some countries and government regulations, can affect the efficiency of global financial markets. These imperfections influence decision-making by investors, governments, and businesses in their international economic activities.
Importance of International Finance
The importance of international finance is as follows.
- It plays a crucial role in the corporate industry, as many corporations can extend their operations in new markets with a deeper understanding of all factors.
- Countries can raise capital to support infrastructure and development projects by selling bonds or stocks in international markets across different countries.
- It is useful to understand exchange and interest rates and determine other countries’ financial positions and debt levels. In this way, investors can decide where to invest for maximum profit.
- It allows investors to compare the financial statements of countries following the IFRS system.
- Some international finance institutions, such as the World Bank and the International Monetary Fund (IMF), help countries facing financial crises, contributing to their economic growth and reducing poverty.
Challenges of International Finance
The following are some of the challenges in international finance management.
- As businesses expand into new markets, they deal with different currencies. Any fluctuation in the currency exchange rate can impact the company’s profitability.
- Companies may face challenges in maintaining tax policies, government regulation, and jurisdiction of foreign countries. So, companies must be well-versed in international trade and tax policies before investing.
- Changes in geopolitical tensions, trade disputes, and political instability in different countries can also disrupt international money flows and affect business operations.
- Global economic crises like economic downturns, recessions, or financial problems in one country can affect global markets, investment decisions, and financial stability worldwide.
- Credit risks arise when a company struggles to pay back its loan. This happens if the clients fail to pay the company, suppliers stop their business, or lenders ask for their money before the deadline.
Final Thoughts
International finance is an important and complex topic. Understanding how international finance works becomes increasingly important as more businesses operate globally. It helps to ensure that companies make informed decisions regarding investments and business transactions across borders for financial success.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Mention institutes of international finance
Answer: The prominent international finance institutions are:
- International Monetary Fund (IMF)
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- World Bank Group
- Asian Development Bank (ADB)
- International Finance Corporation (IFC)
Q2. What are some common job roles in international finance?
Answer: The following are some common jobs in international finance.
- Investment Analyst
- Finance Executive
- Finance Analyst
- Credit Analyst
- International Economist
- Risk Manager
- Investment Banker
- Foreign Exchange Trader
- Trade Specialist
Recommended Articles
We hope this article on international finance was informative and helpful. To learn more, refer to our below articles.