How to Select DNS Servers? – Overview
Domain Name System (DNS) servers are simply technical translators that help your devices find the exact location of the website you are looking for. For instance, when you type a website name (like “educba.com”) into your browser, DNS steps in. It translates the address into a unique number (IP address), which is the website’s exact location, and sends your device there. Therefore, knowing how to select DNS servers that best suit your needs is really important.
You might wonder what you have to do with DNS servers, but they are a crucial part of your digital journey. Usually, your internet provider, network administrator, and operating systems have pre-configured DNS servers. However, if you wish to change to a custom DNS server, be careful which one you choose.
This blog will help you identify the factors you must check before choosing a DNS server.
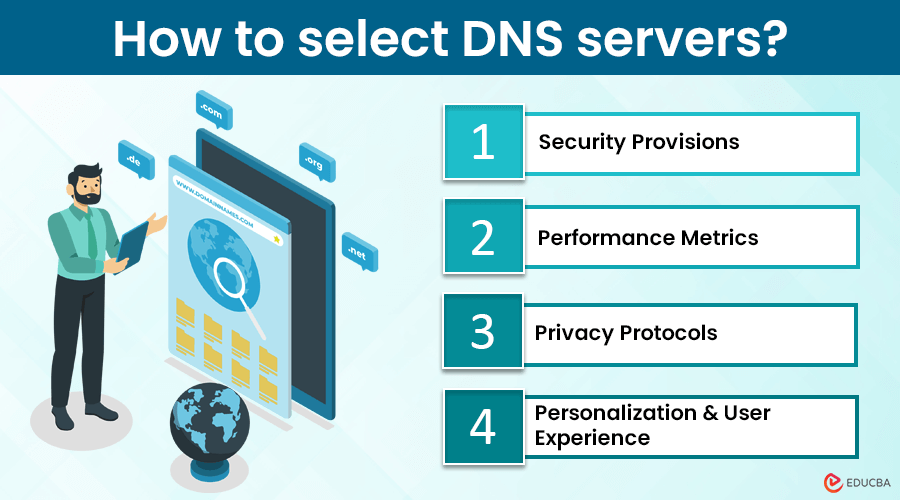
How to Select DNS Servers for Your Requirements?
➔ Security Provisions
Choose DNS services that offer strong filtering capabilities and protection against DDoS attacks. It ensures a robust defense against various online threats.
➔ Performance Metrics
Evaluate the DNS service’s response times and reliability. A fast and reliable DNS can greatly improve your internet experience.
➔ Privacy Safeguards
Ensure the DNS service has a strict privacy policy and does not log your data. It is important for maintaining your online anonymity.
➔ Personalization and User Experience
Look for DNS services that allow you to personalize settings to enhance your browsing experience.
Example:
- Parental Controls: Families can restrict access to unsuitable content.
- Gaming Optimization: Gamers should look for DNS services that reduce lag to improve their online gaming experience.
Types of DNS Services
1. Public DNS Solutions
Public DNS services like Google DNS and Cloudflare DNS are well-known for their speed, reliability, and free usage. They provide strong security features and are suitable for general users.
2. Private DNS Services
ISPs or private entities operate private DNS services. They offer customized security settings and enhanced privacy, and they are particularly useful for businesses or users with specific security needs.
3. Recursive DNS
Recursive DNS servers from ISPs or public providers like Google DNS or OpenDNS are the servers your computer or device uses to find a website’s IP address when you type in its domain name. They search through other DNS servers to get the information you need.
4. Authoritative DNS
The Authoritative DNS server holds and shares DNS records for certain domains. When you look up a website, your DNS server asks the authoritative server for that website’s info. Website owners manage these servers to control their domain’s settings.
How do DNS Queries Work?
A DNS query involves a complex yet swift process that begins the moment you enter a URL into your browser. Here’s a breakdown:
1. Query Initiation
When you enter a URL (web address) into your browser, the browser first looks into its cache to see if it has recently resolved the IP address for that URL. Caching is a key part of how DNS works, making it much faster. When a DNS server finds the IP address for a website, it saves this information for a certain amount of time, known as TTL (Time to Live). It helps websites load quicker and makes using the internet smoother.
2. Recursive DNS Query
If the browser’s cache does not have the required IP address, it sends the query to a recursive DNS server. This server acts as an intermediary and will find the IP address on behalf of the user.
3. Root Server Interaction
If the recursive DNS server does not have the IP address cached, it may query one of the root servers. These root servers are at the top of the DNS hierarchy that direct the recursive DNS server to the appropriate TLD (Top Level Domain) server based on the domain extension (such as .com, .org, .net, etc.).
4. TLD Server
The next query goes to the TLD server for the specific domain extension (e.g., the .com TLD server for a .com domain). This server knows which authoritative DNS servers are responsible for the specific domains under its TLD.
5. Final Resolution
The TLD server directs the recursive DNS server to the authoritative DNS server that holds the specific domain information for the URL in question. The authoritative DNS server then provides the necessary IP address.
6. Response Relay
The IP address comes back through the chain: from the authoritative DNS server to the TLD server (if involved), then to the recursive DNS server, and back to the browser.
Advantages of Secure DNS Services
1. Protection Against Cybersecurity Threats
DNS services go beyond just helping you navigate the internet. They play a key role in cybersecurity by ensuring secure connections to legitimate websites and blocking access to malicious ones, protecting your data and devices from digital threats.
➔ Enhances Online Privacy: Secure DNS services offer better privacy by preventing (Internet Service Providers) ISPs from tracking your browsing habits and unauthorized access to your SSID.
➔ Reduces Risks of Cyber Attack: By blocking access to known malicious sites, secure DNS services lower the risk of cyber attacks.
➔ Improves Internet Experience: Faster DNS resolution and DDoS protection lead to quicker loading times and a more reliable Internet experience.
2. Augmenting Security Through DNS Services
Secure DNS services add extra security layers by enforcing policies that direct users only to trusted sites and block harmful ones. It prevents data breaches and leaks, enhancing overall security.
➔ Blocking Malicious Sites: DNS services can filter and block malware to dangerous websites, preventing phishing attempts and intercepting malware. It forms an important defense against cyber threats.
➔ Traffic Management: DNS services help manage traffic distribution to prevent server congestion, keeping your website operational even during high traffic or DDoS attacks. It is essential for maintaining continuous and reliable service.
➔ DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC): The DNS Security Extensions add an extra layer of security. It verifies the DNS responses are accurate and unaltered, protecting against ‘man-in-the-middle’ attacks and ensuring secure connections to the intended destinations.
Step-by-Step Configuration Guide for Enhanced Security
Here are meticulous instructions to configure DNS settings on your device or router:
- Access your device’s network settings.
- Locate the DNS settings option.
- Input the DNS addresses provided by your chosen DNS service.
- Save the settings. You must try to restart the device if necessary.
➔ Best Practices for Configuration
- Regularly update your DNS settings.
- Utilize DNSSEC for additional security.
➔ Common Missteps to Avoid
- Refrain from using obsolete DNS servers.
- Consistently review and fine-tune your DNS settings for optimal security.
Advanced DNS Service Features
Modern DNS services offer advanced features to meet specific needs:
1. GeoDNS
GeoDNS allows DNS responses to be customized based on the geographical location of the DNS resolver or the end user. This feature is useful for directing users to the nearest or most appropriate server based on the location.
2. DNS Filtering
It allows administrators to block or allow access to specific websites. By controlling which sites can be accessed, it enhances security and productivity.
3. Dynamic DNS (DDNS)
It automatically updates DNS records for devices with changing IP addresses. It is useful for home networks and small businesses where devices frequently change the IP addresses.
DNS Challenges + Solutions
Despite its robust framework, DNS has vulnerabilities. Some notable threats include:
1. DNS Spoofing
Hackers can change DNS data to redirect users to fake websites.
2. DDoS Attacks
Attackers flood DNS servers with too many queries, causing service disruptions.
3. Cache Poisoning
Inserting false data into a DNS cache leads users to the wrong sites.
The Future of DNS
- Advancements in Internet Technology
With the introduction of IPv6, which offers a much larger pool of available IP addresses, DNS will remain essential for navigating the internet efficiently.
- Role in Internet Navigation
DNS plays an important role in helping users find websites and other online resources by translating domain names into IP addresses.
- Cybersecurity Adaptations
As cybersecurity threats get more advanced, DNS services must implement better security protocols and adaptive mechanisms to protect users from malicious online activities.
Final Thoughts
DNS is crucial for the internet, making it secure and easy to use. Understanding its history and future helps improve online security and experience. By choosing, setting up, and staying aware of threats, individuals and organizations can easily navigate the online world confidently. Reliable and secure DNS is important as we depend more on digital connections. To stay safe online, review your DNS setup, consider available features, and make smart decisions.
Recommended Articles
We hope you found the article on how to select DNS servers helpful. To refer and learn more about DNS, visit our below recommended list.