What are the Types of E-commerce Models?
E-commerce businesses that thrive often credit their success to selecting from the types of e-commerce models, yet this process can be intimidating with so many choices available. Making sound decisions requires patience but can result in long-term success for both yourself and your customers. This comprehensive guide covers all the types of ecommerce business models to increase sales and give an edge against rivals.
11 Types of E-commerce Models
A. Business Models
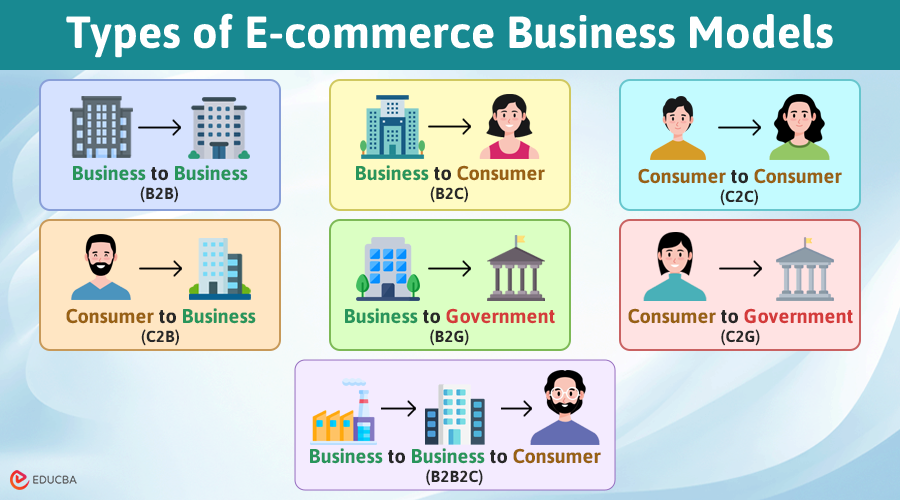
1. B2B: Business-to-Business
The business-to-business (B2B) model involves selling products or services directly to other businesses. This strategy often deals with larger orders at higher price points, increasing revenue and profit per sale while simultaneously lengthening sales cycles thanks to strong relationships among decision-makers.
2. B2C: Business-to-Consumer
The Business-to-Consumer (B2C) e-commerce business model is one of the best-known in e-commerce, as it involves direct selling to individual shoppers. B2C success hinges on offering an enjoyable online shopping experience via an attractive website, easy navigation, and an effortless checkout process for individual consumers. Marketing is important for driving sales; finding ways to differentiate your brand may be key to long-term success.
3. C2C: Consumer-to-Consumer
The consumer-to-consumer (C2C) model involves individuals selling products directly to other consumers using marketplaces like eBay or Etsy at reduced overhead costs associated with stocking products or shipping logistics. While this method reduces storage and shipping expenses, customer experience relies more heavily upon individual sellers for quality control and satisfaction than with traditional wholesale distribution or storefront sales models.
4. C2B: Consumer-to-Business
The consumer-to-business (C2B) model involves individuals providing value directly to businesses, often through online platforms. This model includes freelance marketplaces like Upwork or Fiverr, where consumers offer services to businesses, and content creation platforms where bloggers or influencers partner with companies for sponsored content. While this method allows businesses to access a wide range of skills and expertise without long-term commitments, the quality and reliability of services can vary greatly, depending on the individual providers.
5. B2G: Business-to-Government
The business-to-government (B2G) model encompasses businesses providing products or services to government agencies at various levels. It includes technology services from companies like IBM to local governments or construction firms building infrastructure for public use. Although this model often involves long-term contracts and can be lucrative, it typically requires navigating complex processes and strict regulatory requirements, which can be time-consuming and challenging for businesses.
6. C2G: Consumer-to-Government
The consumer-to-government (C2G) model entails individuals interacting directly with government entities, primarily for transactions such as paying taxes online or participating in electronic voting. By leveraging online portals, consumers can conveniently access public services and fulfill civic duties without the need for physical paperwork. However, the effectiveness of this model depends on the robustness and user-friendliness of the government’s digital infrastructure, which can vary significantly across regions and agencies.
7. B2B2C: Business-to-Business-to-Consumer
The business-to-business-to-consumer (B2B2C) model involves a business selling goods or services to another business, which then provides these offerings to the end consumer. Examples include a wholesaler supplying products to an online retailer like Amazon, which then sells them to consumers, or a software company providing a platform that businesses customize and offer to their customers. This model allows for greater scalability and reach but requires seamless integration between the businesses involved to ensure high standards of quality and service.
B. Revenue Models
1. Subscription-Based Model
Subscription-based businesses have grown increasingly popular. In this model, customers pay recurring fees on an ongoing basis to access products or services. It creates predictable recurring revenue that often has greater customer lifetime value than one-off purchases. Success requires offering products or services that satisfy customer needs consistently over time.
2. Dropshipping Model
Dropshipping is an attractive e-commerce business model for beginners. Customers place orders directly with third-party suppliers, who then ship directly. Without needing upfront inventory investments or investments in infrastructure costs, dropshipping presents minimal risk and cost to start. However, profit margins may be slim, so finding reliable suppliers is key to its success. One effective approach is to dropship from Amazon to Shopify. This allows you to leverage Amazon’s extensive product range and fulfillment capabilities while managing your online store through Shopify. By integrating these platforms, you can automate product imports, inventory updates, and order fulfillment, offering a seamless and efficient way to run your e-commerce business without maintaining inventory.
3. White Label Model
White labeling involves selling products manufactured by others under your own label to market quickly without having to develop something from scratch. However, having more control over product quality would provide additional assurance.
5. Private Label Model
Private labeling, similar to white labeling, allows greater control of product quality, ingredients, packaging and branding for your brand. Although private labeling requires higher upfront investments and longer lead times than white labeling does, you can leverage private labeling as a strategy for differentiation and customer retention.
How to Select an Effective E-commerce Business Model?
Selecting an effective e-commerce business model is vital to the success of any online store.
Consider these factors when researching your target market:
- Research Your Market
- Analyze Your Skill Set
- Take into Account Startup Costs
- Determine Profit Margin
- Establish Inventory Management Needs.
Final Thoughts
Knowledge of various types of e-commerce models will help you select the best for your company. Selecting an effective e-commerce business model is essential to the success of any enterprise. So, be flexible and responsive to market changes, use appropriate tools and strategies in order to thrive in the e-commerce landscape.
Recommended Articles
We hope this article helps you choose the ideal type of e-commerce model for your business. Here are some other articles on e-commerce you can read.



