Differences Between Java and Java EE
Java is a programming language and also a computing platform. A platform is the hardware or software environment in which programs run. Java was developed by Sun Microsystems, which James Gosling led.
Java has two components Java Virtual Machine and Application Programming Interface. Java is now available as free software under the terms of GNU General Public License.
Installing Java on your system
As Java SE is freely available on Oracle’s website can be easily downloaded and installed on a machine. To check if Java is installed or not, run the following command on Command Prompt.
Java –version
It gives the version and other details of installed JDK software. Once Java is installed, the next step is to set Environment Variables. We need to provide the path where JDK is installed on our machine. This can be done in two ways.
- Right-click on MyComputer and select
- Click on Advanced System Settings.
- Click on new, add PATH as a variable name, and give a physical path of the bin folder, which is inside the installed JDK folder.
OR
- Open a command prompt.
- Type command set PATH = %PATH;%<Give Path of bin folder which is inside the installed JDK folder.
Java Program Structure
Some important point to note about Java Programs
- You have to keep in mind that Java code is case sensitive.
- To write a Java program, you must have to define class first.
- The name of the class in Java (which holds the main method) is the Java program’s name, and the same name will be given in the filename. As mentioned above in the sample program; The name of the class is “Hello”, in which the main method is, then this file will be named “Hello.Java”.
A sample Hello Java program.
//Name of this file will be “Hello.java.”
public class Hello
{
/* Author: www.w3schools.in
Date: 2018-04-28
Description:
Writes the words "Hello Java" on the screen */
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Hello Java");
}
}
Program Output: Hello Java
Above program consists of
- public class Hello
This creates a class called Hello. All class names must start with a capital letter. The public word means that it is accessible from any other class.
- /* Comments */
The compiler ignores the comment block. Comment can be used anywhere in the program to add info about the program or code block, which will help developers understand the existing code in the future easily.
- public static void main
When the main method is declared public, it means that it can also be used by code outside of its class, due to which the main method is declared public. The word static used when we want to access a method without creating its object, as we call the main method, before creating any class objects. The word void indicates that a method does not return a value. main () is declared as void because it does not return a value. main is a method; this is a starting point of a Java program.
- String[] args
It is an array where each element of it is a string, which has been named as “args”. If your Java program is run through the console, you can pass the input parameter, and the main () method takes it as input.
- out.println();
This statement is used to print text on the screen as output, where a system is a predefined class, and out is an object of the PrintWriter class defined in the system. The method println prints the text on the screen with a new line. You can also use the print () method instead of the println() method. All Java statement ends with a semicolon.
- public class Hello
This creates a class called Hello. All class names must start with a capital letter. The public word means that it is accessible from any other class.
- /* Comments */
The compiler ignores the comment block. Comment can be used anywhere in the program to add info about the program or code block, which will help developers understand the existing code in the future easily.
- public static void main
When the main method is declared public, it means that it can also be used by code outside of its class, due to which the main method is declared public. The word static used when we want to access a method without creating its object, as we call the main method, before creating any class objects. The word void indicates that a method does not return a value. main () is declared as void because it does not return a value. main is a method; this is a starting point of a Java program.
- String[] args
It is an array where each element of it is a string, which has been named as “args”. If your Java program is run through the console, you can pass the input parameter, and the main () method takes it as input.
- System.out.println();
This statement is used to print text on the screen as output, where a system is a predefined class, and out is an object of the PrintWriter class defined in the system. The method println prints the text on the screen with a new line. You can also use the print () method instead of the println() method. All Java statement ends with a semicolon.
Head to Head Comparison Between Java and Java EE
Below Is The Top 6 Comparison Between Java vs Java EE
Key Differences Between Java and Java EE
Below is the list of points describing the difference between Java and Java EE
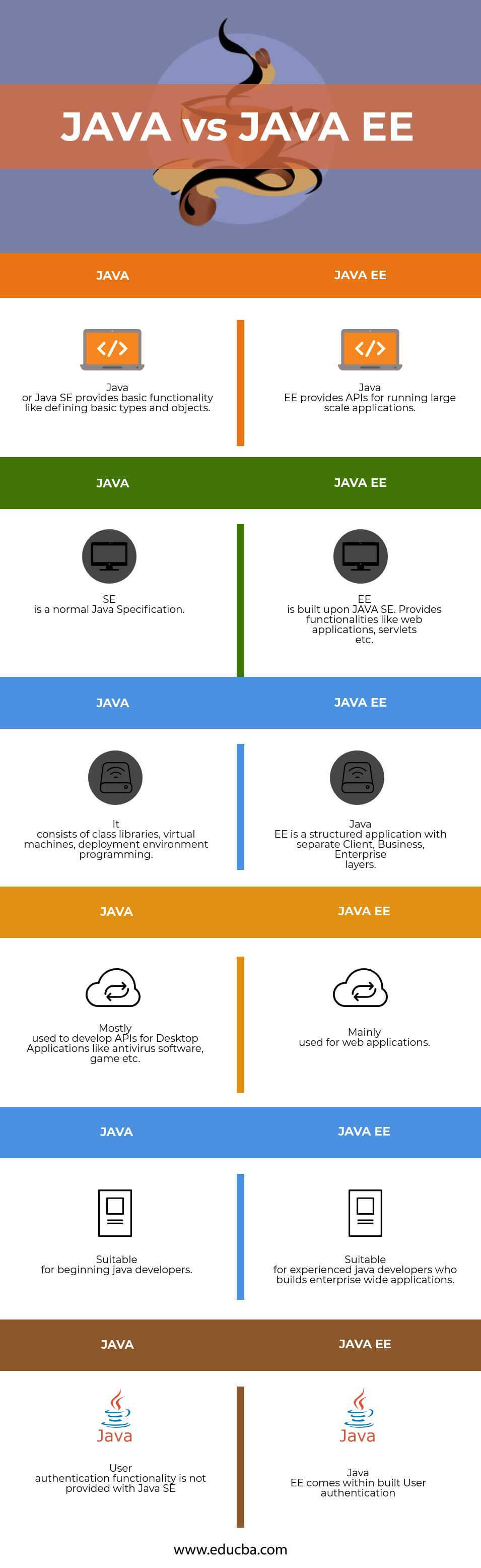
- Java SE is the core Java programming language. The Java EE platform is built on top of the SE platform, used especially for large-scale applications.
- SE defines everything from the basic types and objects of the Java programming language, hence provides all core functionalities. The Java EE platform provides an API and runtime environment for developing and running large-scale applications.
- Java SE platform consists of a virtual machine, development tools, deployment technologies, and other libraries commonly used in Java. Java EE consists of Enterprise JavaBeans, Java Server Pages, Servlets.
- SE has no code separate into different layers, while EE is a multi-tier application; this helps the application be more robust and more secure. Typical Java EE application has the following layers:
1. The Client Tier
The client tier is where user interaction happens. Applications in this tier access Java Server, which is usually located on a different machine. A client sends a request, the server processes this request and sends a response back to the client.
2. The Web Tier
This layer handles the interaction between the client and the business tier.
3. The Business Tier
This tier consists of business logic and all core functionalities.
Java vs Java EE Comparison Table
Following is the Comparison Table Between Java vs Java EE
| JAVA | JAVA EE |
| Java or Java SE provides basic functionality like defining basic types and objects. | Java EE provides APIs for running large-scale applications. |
| SE is a normal Java Specification. | EE is built upon JAVA SE. Provides functionalities like web applications, servlets etc |
| It consists of class libraries, virtual machines, deployment environment programming. | Java EE is a structured application with separate Client, Business, Enterprise layers. |
| Mostly used to develop APIs for Desktop Applications like antivirus software, game etc. | Mainly used for web applications |
| Suitable for beginning Java developers | Suitable for experienced Java developers who build enterprise-wide applications. |
| User authentication functionality is not provided with Java SE | Java EE comes within the built User authentication |
Conclusion
Both Java SE vs Java EE has their own benefits. Hence, before starting with application development, one should consider the following points.
- Desktop or Web Application: Java SE is primarily used for desktop applications and EE for web applications.
- Features: Java EE has many enterprise-wide features like Servlets, EJB, etc. Using these will definitely make application development easy and enhance an application. Also, EE will have all the core features of SE as it is built on top of SE. On the other hand, developers can opt for Java SE if an application is a simple application with basic functionalities.
- Security: As Java EE applications can be multi-tiered, they provide a layer of security and reusability.
Recommended Article
This has been a useful guide to the Difference between Java and Java EE here; we have discussed their Meaning, Head to Head Comparison, Key difference, and Conclusion. You may also look at the following article to learn more –