Updated November 6, 2023
Difference Between Future vs Option
Future vs option both are the tools of a derivative segment that traders across the globe extensively use. The base price of a security (stock price/commodity price/currency price) determines the future price, and the spot price of the security is used to extract three-month forward prices. Similarly, an option is an instrument that allows the trader to trade on a particular script, and the movement of the price depends upon the price of the script in the cash market. The put option acts the opposite way, and the trader trades when they feel the stock will fall soon.
Future
- The future price is based on the base price of a security. For example, The Spot price of TATA Steel Limited in the Cash segment is trading at INR 550, and then the cost of Future prices in the current month would be 552, followed by 554 and 557 for the next two months’ future prices. This indicates that traders are bullish on TATA STEEL, and the prices have adjusted accordingly; similarly, in a Bearish situation, when the traders expect the scrip to fall, the price decreases simultaneously.
- It is important to note that the Future prices stay for that particular month only; with the expiry of that specific month, the price also abolishes. The Future price of any script will stay for three months; for example, March’s Future price of a particular hand will start from January and will stay till March end only.
- Traders can buy or sell the Future contract and hold it for three months, and they only have to pay a part (20% of the total amount), with the margin money getting adjusted after each day’s closing price. However, there are restrictions on buying a certain number, as the Trader can only trade on the multiple of a certain number of scripts as decided by the market regulator for the particular hands.
Option
- There are two kinds of options: Call Option (when the trader wants to go Long) and Put option (when a trader wants to short). For example- suppose the price of the scripts at the Cash market is INR 100/ share, and the Call option for ‘in the money for strike price 100 quotes INR 10 for the same lot as in the Future segment.
- Again, when the script is trading at INR 100, the out-of-money call (strike price 110) will be a bit less, say, suppose INR 8, and then of money call (strike price 90) would be higher at, say, 14.5 because the CMP is at 100 which is higher than 90.
- If the price decreases and tends toward INR 90, the Call option would decrease from 8 to 6 or 5. If, on the other, the price tends to increase from INR 100 to 105, the option of strike 110 would increase from 8 to 10. When the traders pay for the contract for the Call or Put option, the contract premium is paid against fees, which are the current rate of the option. The value of the premium decays when it approaches the settlement date or the expiry date.
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Future vs Option (Infographics)
Below is the top 3 difference between Future vs Option
Key Difference Between Future vs Option
Both Futures vs Options are popular choices in the market; let us discuss some of the major differences :
- The future is almost the same as the cash price, except the capital required for the trade is only 20% of the total value. One can purchase the exclusive pricing much lower than the investment made for the future. However, the price becomes sufficiently lower if an out-of-the-money option is bought.
- If flexibility is concerned, then the Stock option provides higher flexibility compared to the stock future as the Future is related to the entire price of the stock, and any strike price is absent.
- Unlike Future derivatives, options can provide an abnormal return on investment within very few days, provided the trade is made in the right direction. The premium can become multiple times when there is an abnormal stock movement. The Future derivates give a higher return, but in most cases, they cannot multiply the amount of Investment.
Head To Head Comparison Between Future vs Option
Below is the topmost comparison between the Future vs. Option
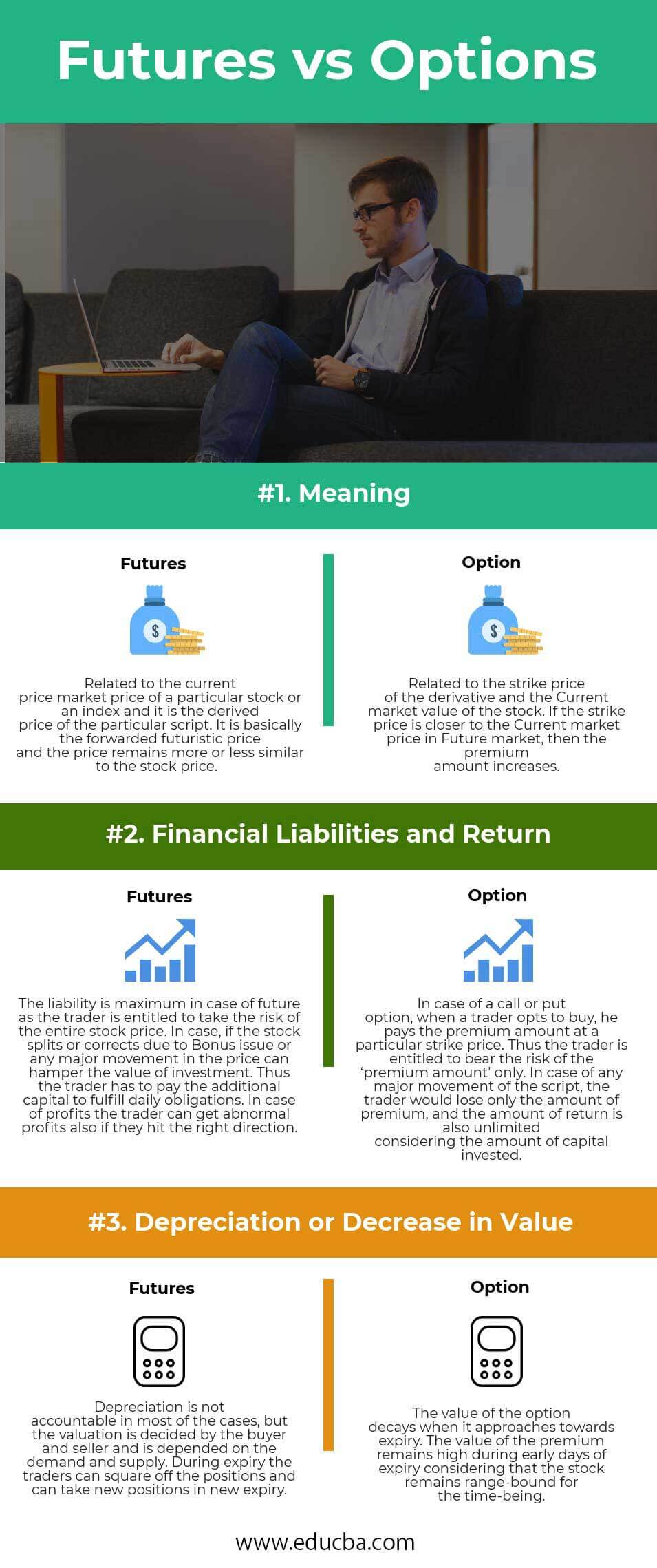
| The basis Of Comparison | Futures | Option |
| Meaning | Related to the current price, the market price of a particular stock or an index is the derived price of the particular script. It is basically the forwarded futuristic price, and the price remains more or less similar to the stock price. | Related to the strike price of the derivative and the Current market value of the stock. If the strike price is closer to the current market price in a Future market, then the premium amount increases. |
| Financial Liabilities and return | The liability is maximum in the future as the trader is entitled to take the risk of the entire stock price. If the stock splits or corrects due to a Bonus issue or any major movement in the price, it can hamper the value of an investment. Thus, the trader has to pay the additional capital to fulfill daily obligations. In the case of profits, the trader can get abnormal profits if they hit the right direction. | In the case of a call or put option, when a trader opts to buy, he pays the premium amount at a particular strike price. Thus, only the risk of the ‘premium amount’ is borne by the trader. In case of any major movement of the script, the trader would lose only the amount of premium, and the amount of return is also unlimited, considering the amount of capital invested. |
| Depreciation or Decrease in value | The buyer and seller decide the valuation, which is dependent on demand and supply, and depreciation is not accountable in most cases. During expiry, the traders can square off the positions and can take new positions in new expiry. | The value of the option decays when it approaches expiry. The value of the premium remains high during the early days of expiry, considering that the stock remains range-bound for the time being. |
Conclusion
Future vs. option is both forms of trading tools that traders frequently use for short-term gains. The prime focus is to catch the trend at which the stock would likely move in a specified time frame. Thus, the risk, ROI, and total capital amount determine which path to follow. In the case of hedging, both Futures vs. option tools can be implemented; for example- In a long trade, the trader can buy the future and control the low risk. One could buy a put option with limited capital. If the market tanks, the return from the put option can be multiplied.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top difference between Future vs Option. Here, we discuss the Future vs Option key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles –