Updated June 27, 2023

Difference Between Absolute Advantage vs Comparative Advantage
Absolute Advantage is the country’s inherent ability that allows that country to produce specific goods efficiently and effectively at a relatively lower marginal cost. A country has an absolute advantage in producing a good if it can produce that good at a lower marginal cost, lesser workforce, lesser time, and lesser cost without compromising the quality. Comparative Advantage refers to the country’s capability to produce a specific good at a lower marginal cost and opportunity cost than other countries. In absolute advantage, where the emphasis is only on marginal cost, comparative advantage considers both marginal and opportunity cost.
Example of Absolute Advantage
Let’s take the example of two countries (Country 1 and Country 2), which are manufacturing cars. However, assume County 1 produces 3 cars per hour with 10 employees and Country 2 produces 5 cars with 10 employees.
| Countries | Production of Cars/Hour | No of Employees |
| Country 1 |
3 |
10 |
| Country 2 |
5 |
10 |
Therefore, in this case, Country 2 has an absolute advantage over Country 1 as Country 2 can produce several cars per hour than Country 1 with the same number of employees.
Example of Comparative Advantage
Let’s take the example of Country 1 and Country 2. Country 1 can produce either 10 cars or 20 computers, whereas Country 2 can produce 22 cars or 30 computers with available resources.
| Product |
Country 1 |
Country 2 |
| Computers |
20 |
30 |
| Cars |
10 |
22 |
Opportunity Cost of Production
| Product | Country 1 | Country 2 |
| 1 Unit of Computer |
0.5 Unit of Car |
0.73 Unit of Car |
| 1 Unit of Car |
2 Units of Computer |
1.36 Unit of Computer |
- The opportunity cost of producing 1 unit of a computer is higher for Country 2 than Country 1, and the opportunity cost for producing 1 unit of a car is lower for Country 1 than a country
- However, According to the comparative advantage concept, Country 1 should produce computers, and Country 2 should produce cars to optimize cost.
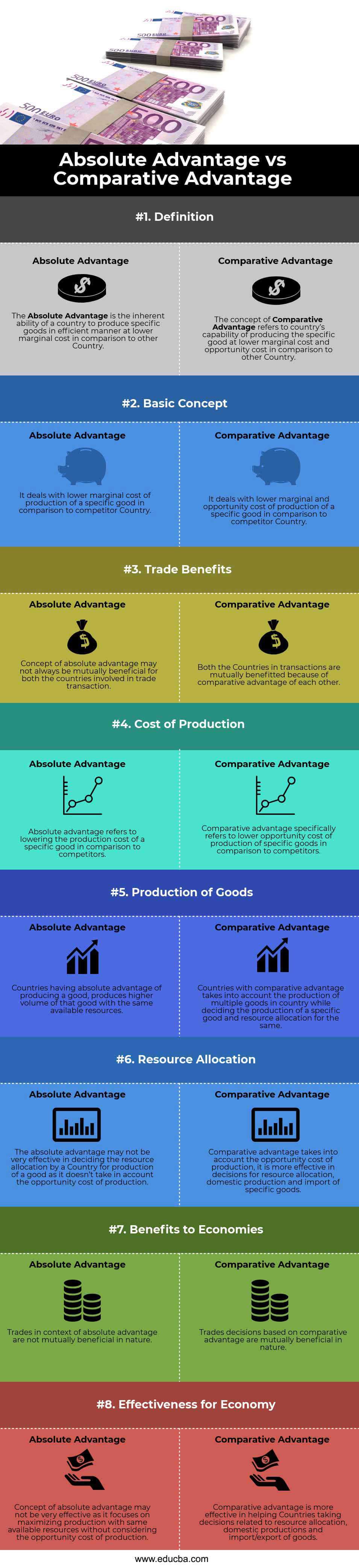
Absolute Advantage vs Comparative Advantage (Infographics)
Below is the top 8 difference between Absolute Advantage vs Comparative Advantage
Key Differences Between Absolute Advantage vs Comparative Advantage
Both Absolute Advantages vs Comparative Advantages are popular choices in the market; let us discuss some of the major Differences
- Both Absolute advantages and Comparative advantages are important concepts of international trade that help countries decide on the domestic production of goods, resource allocation, import, export, etc.
- The Absolute Advantage is the country’s inherent ability to produce specific goods efficiently and effectively at a relatively lower marginal cost. However, Comparative Advantage refers to the country’s capability to produce a specific good at lower marginal and opportunity costs.
- The absolute advantage concept is based on a lower marginal cost of production of a specific good. However, comparative advantage deals with the lower opportunity cost of production of a specific good compared to competitor Countries.
- Countries with an absolute advantage of producing a good focus on maximizing production with the same available resources. However, Countries with comparative advantage consider the production of multiple goods in the country while deciding the production of a specific good and resource allocation.
- The comparative advantage concept is more effective in helping countries decide resource allocation, production, and trade than an absolute advantage.
- Trade transactions between countries having the absolute advantage are not mutually beneficial. Thus, trade decisions based on comparative advantage are mutually beneficial.
- Absolute advantage may not be very effective and beneficial for the economy as it focuses on maximizing production without considering the opportunity cost. However, comparative advantage is more effective in helping Countries make decisions related to resource allocation, domestic production, and import/export of goods.
Absolute Advantage vs Comparative Advantage Comparison Table
Below is the topmost comparison between Absolute Advantage vs Comparative Advantage
| The Basis Of Comparison |
Absolute Advantage |
Comparative Advantage |
| Definition | The Absolute Advantage is the country’s inherent ability to produce specific goods efficiently at a lower marginal cost than other countries. | Comparative Advantage refers to the country’s capability to produce a specific good at a lower marginal cost and opportunity cost than other countries. |
| Basic Concept | It deals with the lower marginal cost of production of a specific good compared to competitor Countries. | It deals with lower marginal and opportunity costs of production of a specific good compared to competitor Countries. |
| Trade Benefits | The concept of absolute advantage may not always be mutually beneficial for both the countries involved in the trade transaction. | Both the Countries in transactions mutually benefitted because of the comparative advantage of each other. |
| Cost of Production | Absolute advantage refers to lowering the production cost of a specific good in comparison to competitors. | Comparative advantage specifically refers to the lower opportunity cost of production of specific goods compared to competitors. |
| Production of Goods | Countries with the absolute advantage of producing a good produce a higher volume of that good with the same available resources. | Countries with comparative advantage consider the production of multiple goods in a country while deciding the production of a specific good and resource allocation. |
| Resource allocation | An absolute advantage may not be very effective in deciding the resource allocation by a Country for the production of a good as it doesn’t consider the opportunity cost of production. | Comparative advantage considers the opportunity cost of production; it is also more effective in decisions for resource allocation, domestic production, and import of specific goods. |
| Benefits to Economies | Trades in the context of absolute advantage are not mutually beneficial. | Trade decisions based on comparative advantage are mutually beneficial. |
| Effectiveness for Economy | The concept of absolute advantage may not be very effective as it focuses on maximizing production with the same available resources without considering the opportunity cost of production. | Comparative advantage is more effective in helping Countries make decisions related to resource allocation, domestic production, and import/export of goods. |
Conclusion
The concept of Absolute Advantage vs Comparative Advantage is related to economics and trade, which helps countries make logical decisions on resource allocation for the production of specific goods, import, and export of goods while considering the marginal cost and opportunity cost of producing goods. Absolute advantage focuses on the marginal cost of producing a good, whereas comparative advantage specifically focuses on the opportunity cost of production. Trade decisions based on comparative advantage between countries are always mutually beneficial. However, Comparative advantage helps in more effective decision-making for countries for resource allocation and production; hence more beneficial for economies than an absolute advantage.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top difference between Absolute Advantage vs Comparative Advantage. Here we also discuss the key differences between the Absolute Advantage vs Comparative Advantage with infographics and the comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more.