Updated July 13, 2023
Definition of Accounting Profit
Accounting profit can be defined as the net income earned during a particular accounting period which is reported on the financial statements of the company based on the principles of generally accepted accounting principles, derived by deducting all explicit revenue expenses and costs incurred from the total revenue accrued during that particular accounting period.
Explanation
The organization generates accounting profit after deducting all relevant costs incurred or accrued during that period from the total revenue. This profit figure is mentioned in the bottom line of the financial statement and is generally used to evaluate business performance. Companies derive net profits using various generally accepted accounting principles per applicability. By following these mandate principles, the accrual basis of accounting is implemented in deriving accounting profits. In simple terms, accounting profit can be described as a situation where the business’s total revenue is more than its total explicit cost, the balance remaining in the accounting profit. In contrast, if the total explicit cost exceeds the total revenues, it will be termed an accounting loss.
Explicit costs are the business’s expenses that can be identified and measured, like labor, wages, rent material cost, etc. Accounting profits are also known as book profits and are limited to a particular period, like a quarter or a year.
The Formula of Accounting Profit
The formula of Accounting Profit is given below:
Total revenue – Total income generated by an organization recognized in books of accounts per GAAP principles. It is the top line item of the financial statement and is the total income earned by the sale of goods/ services.
Explicit cost is an identifiable and measurable expense, including production and overhead costs, material costs, labor costs, transportation costs, marketing, administration, sales cost, etc.
How Does It Work?
Stakeholders monitor and analyze a company’s health through net profits earned. It is used in various accounting ratio calculations and trend analyses. There are various categories of net profits like before tax, after-tax, including extraordinary items, excluding extraordinary items, etc. Applicable GAAP prescribes various rules and regulations that must be followed while accounting and recording transactions. Accounting profits are based on the accrual concept, i.e., those accrued during a particular accounting period. It is also known as bookkeeping profits. It is the net income earned after deducting all dollar costs from total revenue. Thus, net profits are the surplus revenue earned over and above the cost incurred during an accounting period.
Examples of Accounting Profit
Different examples are mentioned below:
Example #1
Leamon Tree Inc, indulged in the hospitality business operating hotel business in various countries, shows in the income statement of 2019-2020 that the total revenue was $100 million with the operating expenses of $70 million salary of employees $15 million depreciation on assets $2 million advertisement and administrative expenses $4 million interest on loans $1.25 million and taxes $1 million. The company wants to know the accounting profits for the year 2019-2020.
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
| Revenue | 100 |
| Explicit Cost | |
| Operating Expenses | 70 |
| Salary Expense | 15 |
| Depreciation Expense | 2 |
| Advertisement and Administrative Expenses | 4 |
| Interest on Loan Expenses | 1.25 |
| Tax Expense | 1 |
Solution:
Given,
Revenue = $100 million
The total Explicit Cost is calculated as
- Total Explicit Cost = $70 + $15 + $2 + $4 + $1.25 + $1
- Total Explicit Cost = $93.25 Million
Accounting Profit is Calculated as
Accounting Profit = Revenue – Explicit Cost
- Accounting Profit = $100 Million – $93.25 Million
- Accounting Profit = $6.75 Million
Example #2
From the following mentioned information, calculate the accounting profit
| Sr. No. | Particulars | Amount ($) |
| 1 | Earnings per share (equity) | 10 |
| 2 | No. of equity shares | 1,00,000 |
| 3 | Preference Shares dividend | 10,00,000 |
Solution:
Here, we are required to reverse calculate accounting profit
- EPS = Earnings (Net Profit available to Eq. shareholders)/ No. of Equity Shares
- 10 = Net Profit available to Eq. shareholders/ 1,00,000
- Net Profits for Eq. shares = 1,00,000 x 10
- Net Profits for Eq. shares 10,00,000
ADD:
- Preference shares Dividend 10,00,000
- Net profits for Shareholders 20,00,000
Example #3
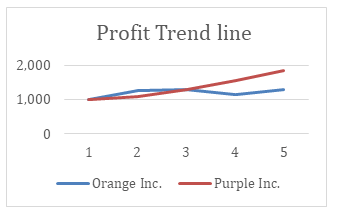
(Net Profits Analysis) Based on the below-mentioned information, comment on the company’s Net Profit trend: –
| Financial Year | Net Profits | |
| Orange Inc. | Purple Inc. | |
| 2015 | 1,000 | 1,000 |
| 2016 | 1,250 | 1,100 |
| 2017 | 1,300 | 1,350 |
| 2018 | 1,150 | 1,600 |
| 2019 | 1,280 | 1,800 |
Solution:
| Financial Year | Net Profits | Change (%) | ||
| Orange Inc. | Purple Inc. | Orange Inc. | Purple Inc. | |
| 2015 | 1,000 | 1,000 | – | – |
| 2016 | 1,250 | 1,100 | 25% | 10% |
| 2017 | 1,300 | 1,290 | 5% | 19% |
| 2018 | 1,150 | 1,540 | -15% | 25% |
| 2019 | 1,280 | 1,850 | 13% | 31% |
Change (%) is calculated as
For Orange Inc,
- Change (%) = Net Profits (2016) – Net Profits (2015) / 1000
- Change (%) = (1,250 – 1,000) / 1000
- Change (%) = 25%
Similarly, for all year
For Purple Inc,
- Change (%) = Net Profits (2016) – Net Profits (2015) / 1000
- Change (%) = (1,100 – 1,000 / 1000)
- Change (%) = 10%
Similarly, for all year
Comment: – Based on profit trend analysis, we can interpret that investing in Orange Inc. is riskier as its Accounting profit trend is not rising constantly. On the other hand, Purple Inc.’s profits are rising constantly. Therefore, an investor should invest in Purple Inc. instead of Orange Inc.
Accounting Profit Analysis
Accounting profit analysis requires dissecting the profit figures of a business to determine the real extent of its profitability. Accounting profits are used for various accounting ratios calculation, trend analysis, preparing and presenting comparative financial statements (inter and intra companies), etc. This measure is an important indicator of any business entity’s financial and operating capacity. Net profits can be used in the calculation of various ratios like-
- Net Profit Ratio (Net Profits / Sales)
- Return on Investment (Profits/ Capital employed)
- Net Profit to Gross Profit ratio (Net profit/ Gross Profit)
Comparing and analyzing net profits of two different accounting periods will help a stakeholder to understand and determine the company’s growth trend. Whether a company is growing or not. Analyzing net profit trends will help determine and develop an investment decision.
Let us understand the analysis of accounting profit by way of an example-
Apple Inc. has a financial statement for the year 2019-20. Details oF the expenses and revenue are given below (Figures in a million dollars)-
| Particulars | 2019-2020 | 2018-2019 | Change in % |
| Revenue | 1,00,000 | 80,000 | 25 |
| Explicit Cost | |||
| Raw Materials | 50,000 | 36,000 | 28 |
| Wages | 30,000 | 26,000 | 13.3 |
| Rent | 10,000 | 10,000 | 0 |
| Electricity | 2,000 | 2,000 | 0 |
| Distribution Expenses | 4,000 | 3,000 | 25 |
| Total Explicit Cost | 96,000 | 77,000 | 24.67 |
| Accounting Profit | 4,000 | 3,000 | 33.33 |
Analysis of the above figures:
In the above case of Apple Inc., the calculation of accounting profits shows an improvement in 2019-2020 over 2018-2019 by $1000 million, i.e., a 33.33% increase over the previous year. We can interpret that company has operated more efficiently during 2019-20 as with just a 25% increase in revenue; it has increased net profits by 33.33%. This indicates improvement and growth in the company’s operating efficiency. This calculation also helps in understanding the book value of the business. By this accounting profit calculation, we can evaluate the performance and efficiency of Apple Inc. It also helps analyze future business calls relating to further investments, market positions, etc.
Advantages
Some of the advantages are given below:
- It is a more useful measure than cash profit, as accounting profits can be manipulated legally in favor of a business.
- It is the mirror for the performance and financial positions of the business.
- It is an indicator that compares across industries and businesses.
- It helps the management make strong decisions regarding business expansion, performance, and investments in the business.
- It shows whether a business is profitable or not, as a profitable business attracts investors and stakeholders.
- It is an important element that measures the repaying capacity of the business.
Disadvantages
Some of the disadvantages are given below:
- It is only book profit and varies from cash profit, meaning it is not a real profit and does not include the real cash flow.
- Accounting profits may have extraordinary and exceptional transactions included.
- There are various methods of amortization and depreciation, provisions, impairments, valuations, and accruals, so it cannot be used as a proper comparison tool between businesses.
- There exist chances of data manipulation and window dressing. These can be done easily in the presentation of financial statements.
- Only profits cannot be considered for comparison as several factors indicate comparison, like financial ratios, revenue, cash flow position, etc.
Conclusion
Accounting profit can be defined as net surplus earned and accrued over and above expenses and costs incurred during an accounting period. Net profits are one of the prime indicators of an entity’s financial strength and operating efficiency. Net profits are used in financial statement analysis, like calculating accounting ratios, undergoing trend analysis, etc. Although net profits also possess certain drawbacks, they are still the most widely used financial statement analysis tool.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Accounting Profit. Here we also discuss the definition, how accounting profit works, and advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –