Updated July 18, 2023

Difference Between Accounting Profit vs Economic Profit
The accounting profit can be the profit that is earned and reported on the income statement. Economic profit is the profit the business derives over and above the opportunity costs. The accounting profit can be at the bottom line of the income statement, whereas economic profit is after determining the free cashflows.
Accounting profit can be the profit that the business earns as per the book of accounts of the business. The accounting profit is the difference between total sales by the business and the costs incurred by the business that could be accounted for explicitly. The explicit costs may comprise the cost of goods sold, operational expenses, and non-cash expenses.
The revenues or sales are generally income that the business generates while performing business activities. The economic profit, on the other hand, is the difference between revenues by the business and the sum of implicit and explicit costs by the business. The implicit costs are generally the opportunity costs the business has to bear for foregoing an opportunity by selecting an alternative through the course of business. As a business, it’s important to carefully consider all available options before committing to organizational resources. Once a decision is made, it’s difficult to backtrack as the chosen alternative was selected from a range of options. Therefore, it’s crucial to make the best possible choice from the choices at hand.
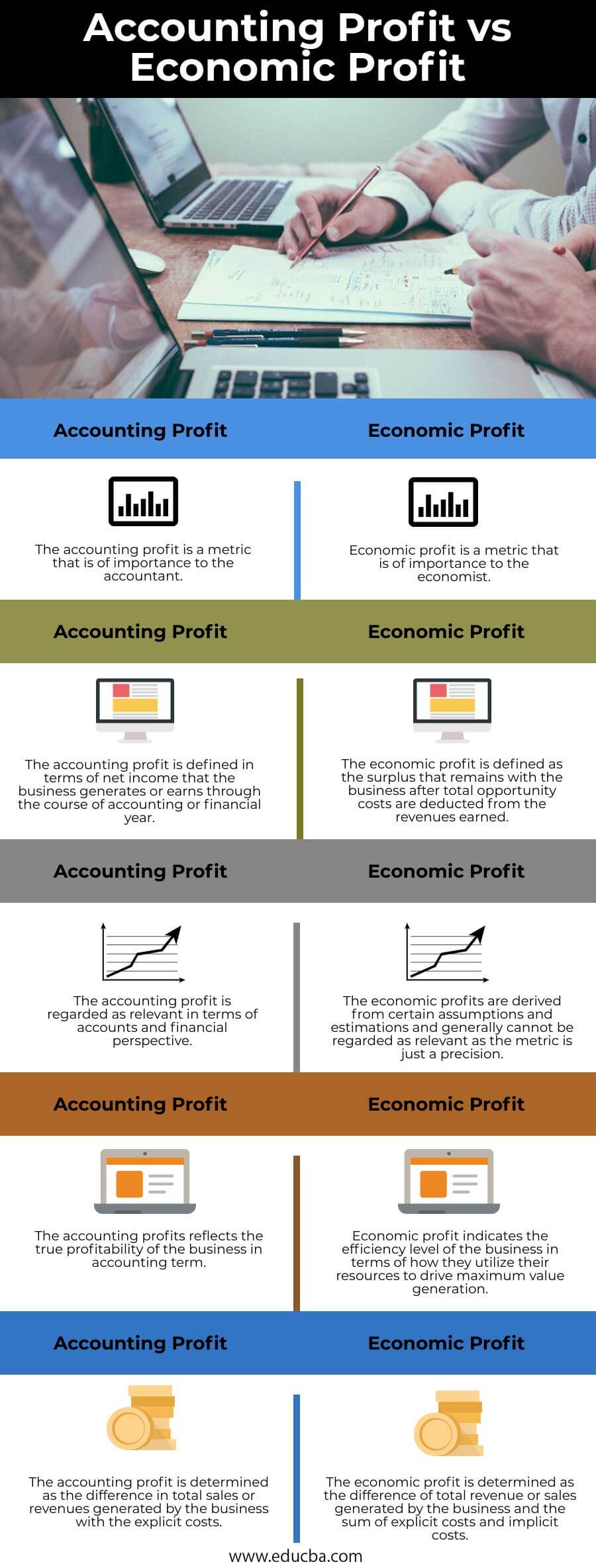
Head-to-Head Comparison between Accounting Profit vs Economic Profit (Infographics)
Below are the top 5 differences between Accounting Profit vs Economic Profit:
Key Differences Between Accounting Profit vs Economic Profit
Following are the key differences between Accounting Profit vs Economic Profit:
- The accounting profit can be termed the profit the business realizes for a given financial year. Economic profit, on the other hand, defines as the profit levels that the business earns over and above the expenses that are generally termed opportunity costs.
- The accounting profit is generally larger than the economic profit as economic profit using multiple assumptions and re-using multiple categories of income and expenses.
- The accounting profit is determined by deducting expenses arising from assets being leased, depreciation or non-cash expense, and provisions for the development costs. In contrast, economic profit may comprise opportunity costs, salvage or residual values, charges on inflation, taxation rates, and interest levied or applied on cashflows.
- The accounting profit can be the revenue post deducting all costs of economic nature. Economic profit is revenue over and above opportunity costs. The accountant generally relies on the accounting profit as it accounts for production costs and their overall impact on the earning potential.
- The economist always relies on economic profit as it tells the economist how the business utilized its resources and assessed the opportunity costs to earn a positive economic profit. The business generally incorporates a vision to earn a higher economic profit. The economic profit is generally positive when the accounting profits exceed the overall implicit costs.
- If the business has accounting profit below implicit costs then the business tends to earn a negative economic profit. If the business earns negative economic profits, it should generally divest itself.
- Hence, the equilibrium is for the economic profit if the business’s implicit costs are equivalent to the explicit costs wherein both debtholders and equity holders earn their necessary rate of return.
Accounting Profit vs Economic Profit Comparison Table
Let us look at the comparison table of Accounting Profit vs Economic Profit.
|
Accounting Profit |
Economic Profit |
| The accounting profit is a metric that is of importance to the accountant. | Economic profit is a metric that is of importance to the economist. |
| The accounting profit is defined in terms of net income that the business generates or earns during the accounting or financial year. | The economic profit is the surplus that remains with the business after total opportunity costs are deducted from the revenues earned. |
| The accounting profit is regarded as relevant regarding accounts and financial perspective. | The economic profits are from certain assumptions and estimations and generally cannot be relevant as the metric is just a precision. |
| The accounting profits reflect the true profitability of the business in accounting terms. | Economic profit indicates the efficiency level of the business in terms of how they utilize its resources to drive maximum value generation. |
| The accounting profit is the difference in total sales or revenues generated by the business with the explicit costs. | Economic profit is the difference between the total revenue or sales by the business and the sum of explicit and implicit costs. |
It is important that the opportunity costs can never be negative as a general principle of economics. Hence, the economic profit has to exceed the accounting profit so that the opportunity costs tend to be positive. The reason why opportunity costs cannot be negative is that the business may not choose to act on the opportunities that they have on hand, making them either avoid an opportunity to earn as well as to bear expenses.
Conclusion
A business would tend to exist only when the business is to generate economic profit that is more than accounting profit. It indicates the profit earnings capability of the business even in the near future as well as how they have performed in the past. For the shareholders, the accounting profit is of the utmost importance as it presents a true picture of financial performance. Generally, investors are not that learned to compute economic profits by themselves. Economists and internal stakeholders generally determine the economic profit and perform internal analysis by assuming assumptions and taking all opportunity costs into account as they are pursuing or choosing to pursue certain activities. Economic profit can deliver an approximation as to which desired direction the business has headed to.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Accounting Profit vs Economic Profit. Here we also discuss the Accounting Profit vs Economic Profit key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –