Updated November 9, 2023
What is Accounts Receivable?
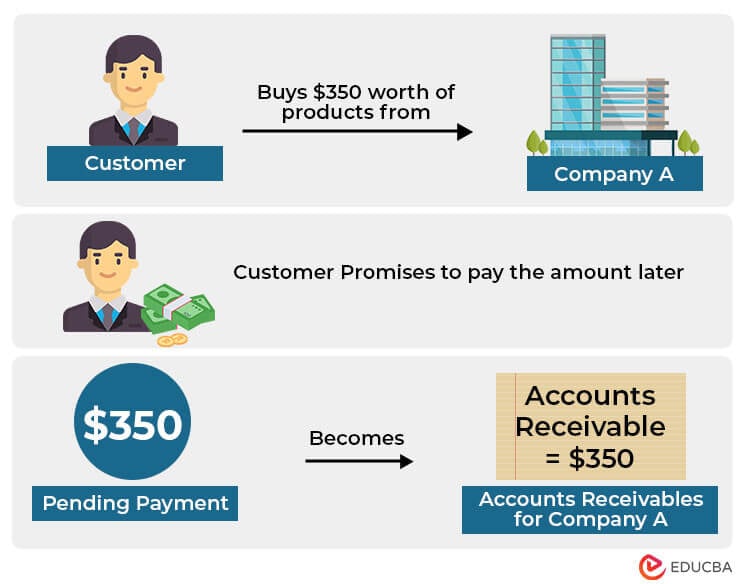
When a business sells on credit to customers, it records the pending payments as accounts receivable, also known as AR.
Suppose a customer buys $350 worth of products from a company and promises to pay in the future instead of immediately. So, this amount becomes accounts receivable until the customer pays $350.
Where to Find it in Financial Statements?
You can find accounts receivable on a company’s balance sheet under Current Assets, as it is the most liquid asset after the cash. It is considered a short-term asset as the credit period generally ranges from 15 days to 2-3 months.
Example:
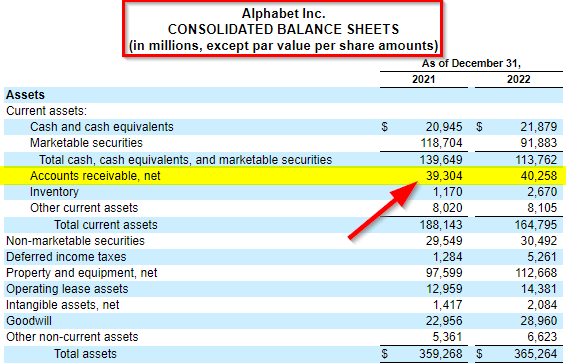
Let us see the balance sheet from Alphabet’s annual report for 2022.
(Image Source: Alphabet Annual Report 2022)
We can see that, under current assets, the company had AR of $39,304 million and $40,258 million in the years 2021 and 2022, respectively. There is a clear $954 million (2.42%) increase in the receivables.
The increase can mean the company has increased the amount of goods sold on credit. It sometimes may also mean that the company had lesser revenue in cash. However, if that is not the case, as we can see for Alphabet, then an increase in AR is considered a good thing.
How To Calculate Accounts Receivable? – Excel Examples
Example:
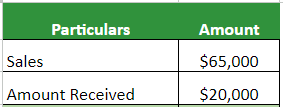
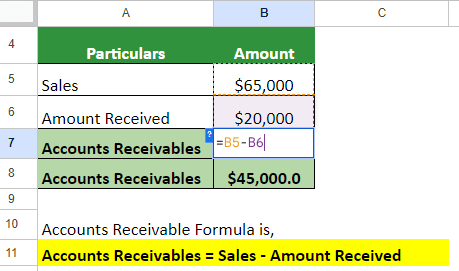
Adam purchases goods from Company A, majorly on credit. The most recent sales are $65,000. Adam pays $20,000 right away, keeping the rest on credit. As the company follows a 90-day credit cycle, it will convert the sales to cash. Calculate its AR.
Given:
Solution:
=$65,000 – $20,000 = $45,000
Accounts receivable are $45,000. The amount is reduced from the accounts if paid within 90 days; otherwise, it’ll count as bad debt.
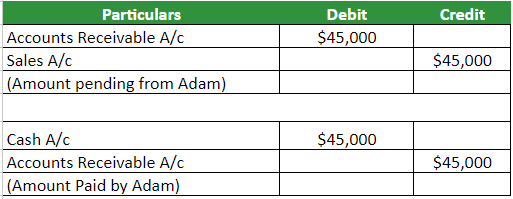
Journal Entry:
The accounts receivables journal entry for the above example will look as follows. Here, we credit the pending $45,000 from sales and debit it to accounts receivable. Next, when Adam pays the $45,000, we will credit it to cash, debiting it from accounts receivable.
Process
The accounts receivable process manages the operating activities of the organizations efficiently and effectively. Here are four essential steps in managing AR:
#1: Creating Proper Policies for Selling on Credit
- First, set a proper approach and guidelines for credit sales.
- Not every customer is creditworthy, so use the right filter to select trustworthy customers.
- Lay down necessary credit policies like the credit limit, payment time, interest rates, etc.
#2: Sending Invoice to the Customer
- Use an accurate billing process and issue invoices promptly after providing goods or services.
- Include all necessary details like a clear description of products or services, payment terms, due dates, and contact information.
- Clarity and accuracy in invoices help prevent disputes and encourage timely payment.
#3: Tracking Payments from Customers
- Establish a systematic approach to collections and send reminders to customers as payment due dates approach.
- When you receive the payments, create the necessary records like journal entries, reconciling the ledger, etc.
- Monitor overdue payments and develop a strategy for dealing with delinquent accounts. It may involve phone calls, collection letters, or engaging a collections agency if necessary.
#4: Accounting for Outstanding Receivables
- If a customer cannot pay the receivable, you must account for the respective amount as unpaid or bad debt.
- You will have to create the necessary accounting documents for accurate financial reporting.
Importance
Following are the reasons why AR is important.
- Controlled Cash Flow Management: A reliable AR plan helps you manage your money better. You know when the money should be coming in, making planning for your expenses easier. It means you don’t have to constantly bug your customers for payments, saving you time and stress.
- Informative for Investors: Shareholders and investors use your AR performance to judge how well you collect money. It tells them if your business is running efficiently and making a profit.
- Increased Revenue: It is a crucial strategy for any business to survive in the long run as it helps companies boost revenue by providing sales on credit.
Accounts Receivable Vs. Accounts Payable
The following table lists the major differences between accounts payable and receivable.
| Basis | Accounts Receivable | Accounts Payable |
| Definition | It is the money the customer owes to the business. | It is the money the business owes to its stakeholders, creditors, suppliers, etc. |
| On Balance Sheet | Recorded as Current Asset | Recorded as Current Liability |
| Impact on Cash Flow | Results in cash inflow | Results in cash outflow |
| Types | It can either be trade or non-trade receivables. | There are several APs like sales tax, interest, trade, etc. |
| Formula | AR = Total Sales – Amount Received – Allowances – Discounts | AP = Cost of Purchase |
| Example | If a customer buys an item for $10 on credit from you, your AR will be $10. | If you buy raw materials for $400 on credit from a supplier, your AP will be $400. |
Final Thoughts
It is an essential current asset that helps strengthen working capital requirements. With the right accounting tools and management, sales can increase. However, a company should be able to draw a line between too-high and too-low receivable values.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What does AR aging mean?
Answer: Companies record receivables in AR aging reports according to how long a payment has been unpaid. They display receivables that are due now and those that are already late. It helps evaluate a firm’s clientele’s stability and financial standing.
Q2. What happens when clients do not pay the credit they owe?
Answer: Businesses write off accounts receivable as a bad debt or one-time cost when it becomes evident that a client won’t pay the credits.
Q3. How is AR connected to a company’s working capital?
Answer: Essentially, accounts receivable provide insight into the company’s credit terms with its customers. It plays a vital role in the working capital cycle of the organization. High working capital indicates that the company sells too much of its product on credit. However, if it is too low, it depicts the company dealing primarily in cash, which can be difficult for sales. Therefore, the faster the collection against the receivables, the more the working capital flow will be to the organization, which increases the company’s liquidity position.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide to Accounts Receivable was helpful. Visit the following articles to learn more: