What is the Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio?
Accounts receivable turnover ratio (ART) is a formula that calculates how often a business collects its accounts receivables in a particular period (usually 1 year). For instance, if a company’s ART ratio is 6, it means it collects its receivables six times a year (within every 60 days).
Thus, this ratio helps us check how effectively businesses are able to collect their credit sales payments.
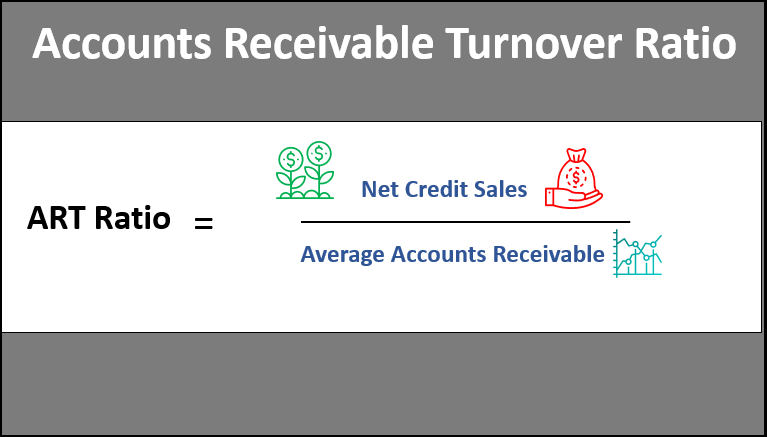
Accounts Receivable Turnover Formula
Here is how to calculate accounts receivables turnover:
Where,
- Net Credit Sales: Total revenue earned by selling products/services on credit.
Formula: Net Credit Sales= Gross Credit Sales – Sales Returns - Average Accounts Receivable: The average amount yet to be received from customers.
Formula: Average Accounts Receivables= (Opening Balance + Closing Balance)/2
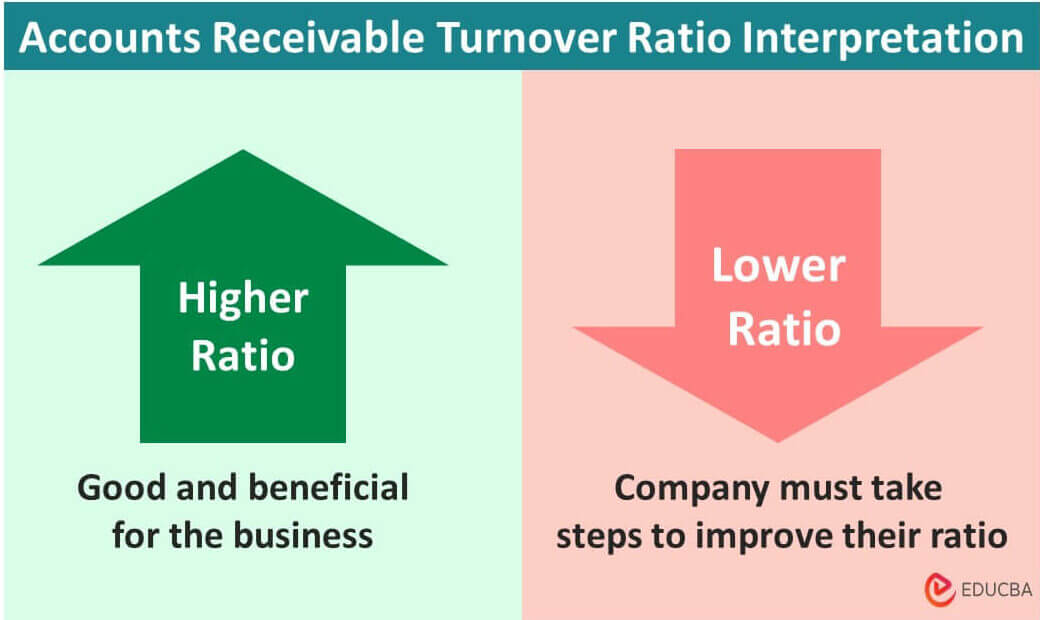
Interpretation – What is a Good Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio?
Here is a basic interpretation of the accounts receivables turnover formula:
- Higher Accounts Receivables Turnover (ART): This indicates that the company is able to swiftly collect outstanding payments. For instance, a ratio of 4 means the company collects its receivables four times a year (with a 90-day cycle).
- Lower Accounts Receivables Turnover (ART): This means that the company delays in collecting accounts receivables, which may lead to liquidity issues. For instance, a ratio of 1 means the firm collects its outstanding credit payments only once a year.
The ideal ratio can differ based on a company’s working capital requirements. Usually, businesses that have higher working capital needs try to maintain higher turnover ratios.
Let us look at a few real company examples.
Example #1: Walmart Inc.
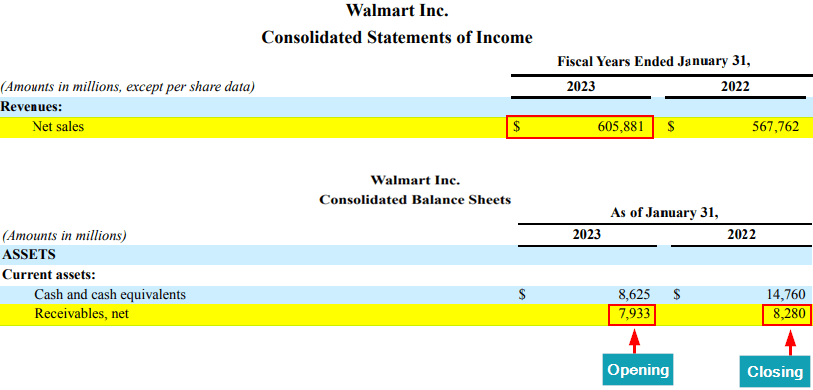
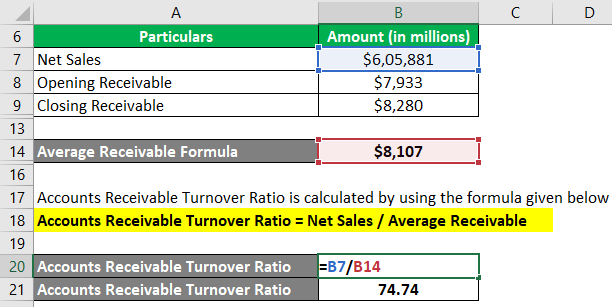
Given image is from Walmart’s latest annual report (2023):
As we can see from the above image, Walmart had the following financials in 2023:
- Net sales of $605,881 million
- Opening accounts receivable of $7,933 million
- Closing accounts receivable of $8,280 million.
Let us calculate the ART ratio of Walmart Inc. for the year 2023.
Solution:
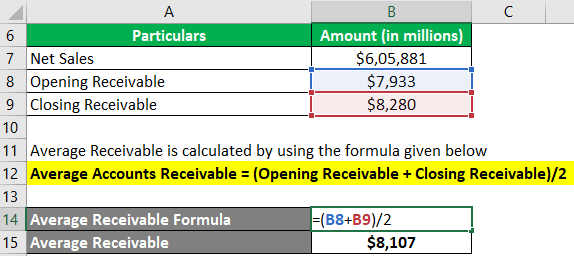
Step #1: Let us first determine the average accounts receivable for Walmart.
Average Accounts Receivable = (Opening Receivable + Closing Receivable)/2
= ($7,933 million + $8,280 million) / 2
= $8,107 million
Step #2: Now, let’s calculate the accounts receivable turnover ratio for Walmart.
Accounts Receivable Turnover Formula = Net Sales / Average Receivable
= $6,05,881 million / $8,107 million
= 74.74
Therefore, Walmart Inc. collected its receivables 74.74 times during 2023. A higher turnover ratio is generally a positive sign. It indicates the company has more cash available for working capital needs, like paying bills and short-term liabilities.
Example #2: Apple Inc.
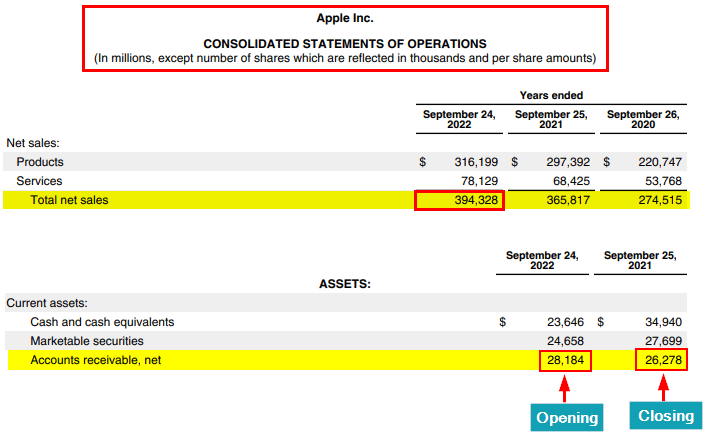
Given is the income statement of Apple for 2022 from its annual report.
As we see, Apple has the following financial data in 2022:
- Net sales of $3,94,328 million
- Opening accounts receivable of $28,184 million
- Closing accounts receivable of $26,278 million
Let us calculate Apple’s accounts receivable turnover ratio.
Solution:
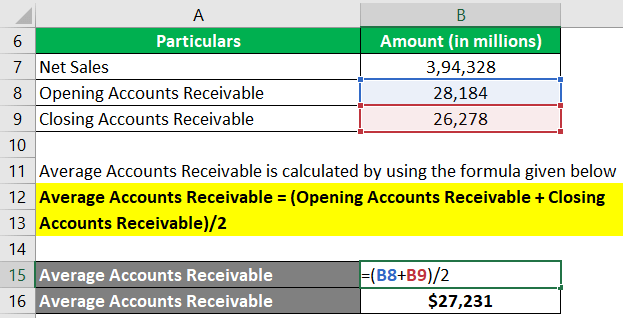
Step #1: First, we will calculate the average accounts receivables for Apple.
Average Accounts Receivable = (Opening Accounts Receivable + Closing Accounts Receivable)/2
= ($28,184 million + $26,278 million)/2
= $27,231 million
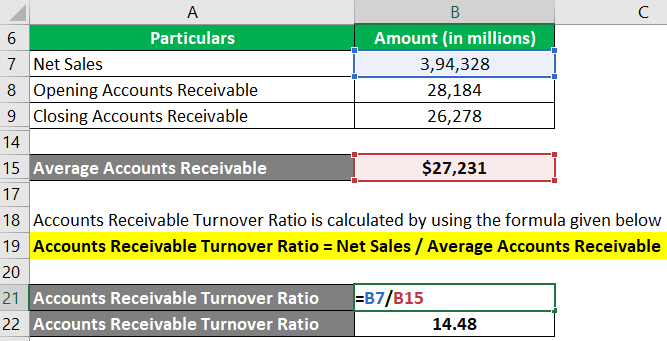
Step #2: Finally, let us find the ART ratio for Apple for 2022.
Accounts Receivables Turnover Formula = Net Sales / Average Accounts Receivable
= $3,94,328 million/$27,231 million
= 14.48
Therefore, Apple Inc. managed to collect its receivables 14.48 times during 2022. We can see that it is a high ratio. A higher ratio implies timely collection of credit sales, which is beneficial.
Excel Examples
Let us see a few simple hypothetical examples to understand how to find the account receivables turnover ratio.
Example #1
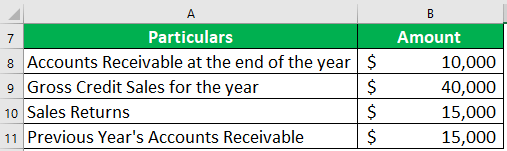
Harvey Foods is a grocery retail store that provides credit options to its customers. Calculate Harvey Foods’ account receivables turnover ratio using the following financials:
Solution:
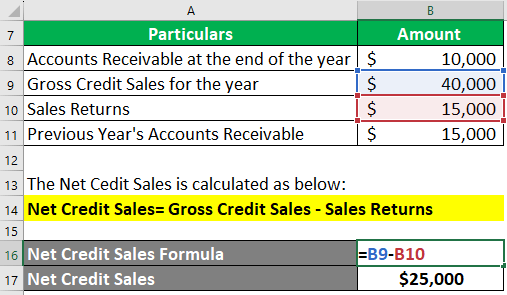
Step #1: First, let us calculate net credit sales and average accounts receivable.
- Net Credit Sales = Gross Credit Sales – Sales Returns
= $40,000 – $15000
= $25,000
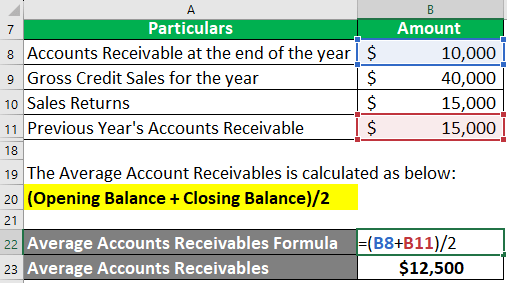
- Average Accounts Receivables = (Opening Balance + Closing Balance)/2
= ($10,000 + $15000)/2
= $12,500
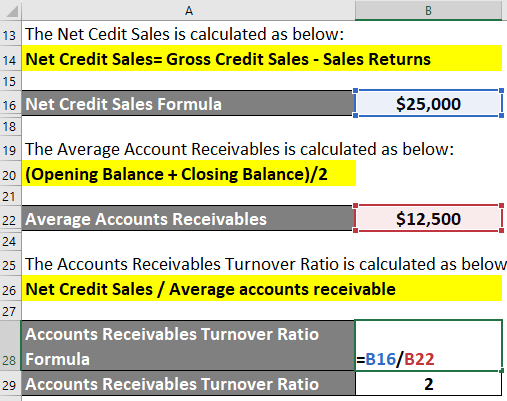
Step #2: Now, calculate Harvey Foods’ accounts receivable turnover using the formula:
Accounts Receivables Turnover Formula = Net Credit Sales / Average accounts receivable
= $25,000/$12,500
= 2
This shows Harvey Foods’ turnover is 2, meaning the store collects its receivables twice a year (once every 180 days). We can say that the ratio is not very high. Thus, if Harvey Foods, being a retail store, has a higher working capital requirement, it must improve its ART ratio.
Example #2
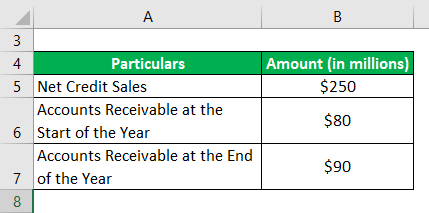
Suppose a wholesale Californian company that sells groceries has the following data in its latest annual report:
Let us compute the ART ratio for the company.
Solution:
Step #1: Let us find the average account receivable using the given formula:
Average Accounts Receivable = (Opening Accounts Receivable + Closing Accounts Receivable)/2
= ($80 million + $90 million)/2
= $85 million
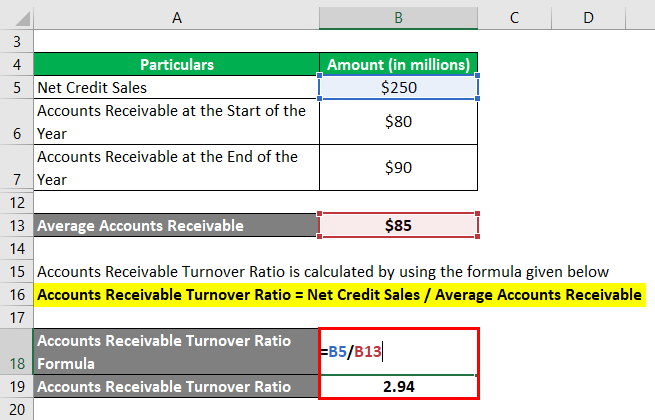
Step #2: Use the below formula to calculate the ratio.
Accounts Receivables Turnover Formula = Net Credit Sales / Average Accounts Receivable
= $250 million/$85 million
= 2.94
Therefore, the company collected its receivables 2.94 times during the year. Assuming that it is a wholesale store, the company’s working capital requirements are low. In this case, the ratio of 2.94 is not bad.
Uses of Accounts Receivables Turnover Formula
The importance of the accounts receivables turnover formula is as follows:
- It provides insight into a company’s effectiveness in collecting receivables.
- Businesses often use accounts receivable as collateral. Thus, the turnover ratio can help check the quality of receivables to ensure companies can use them as collateral.
- It helps management in making informed decisions regarding credit policies and collections.
- It provides a basis for benchmarking a company’s performance against its past performance or industry standards.
- Companies can use it to assess their liquidity position and ability to meet short-term obligations.
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio Calculator
You can use the following accounts receivables turnover formula calculator.
| First Value | |
| Second Value | |
| Formula = | |
| Formula = | = |
|
|
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How to improve accounts receivable turnover?
Answer: To improve the ratio, a company can do the following:
- Create robust credit policies, like setting a limit on the maximum credit amount, providing a deadline for the payment, etc.
- Offer discounts on early payments.
- Review and simplify the invoicing process.
- Actively contact customers with overdue accounts for collection.
Q2. Differentiate between accounts receivables turnover formula and days sales outstanding (DSO)?
Answer: The accounts receivable turnover ratio is related to DSO. While the ratio measures how many times receivables are collected in a year, DSO calculates the average number of days it takes to collect outstanding payments. You can convert one into the other using the following formula:
Q3. What are the limitations of the accounts receivables turnover formula?
Answer: The following are the limitations of using the accounts receivable turnover formula:
- Requires accurate and consistent data, which can be challenging to maintain in some business structures.
- A high turnover ratio may mean that the company prioritizes speed over credit quality, potentially leading to bad debt.
- Comparing the ratios between different industries may not be meaningful due to differences in business models.
- It may not capture the full picture and can be misleading if not considered with other financial metrics.
Q4. What is the accounts receivables turnover industry average?
The common industry average accounts receivable turnover ratio is 7.8. Most businesses consider a ratio of 7.8 to be a good indication. It means the company is able to collect its receivables more often and efficiently.
Recommended Articles
We are hoping this detailed article on the accounts receivable turnover ratio formula was beneficial to you. For more such articles, refer to the following recommendations.