Updated November 23, 2023
Difference Between Accrual vs Provision
The accrual basis of expense accounting means reporting that expense and the related liability in the given period in which accrual expense occurs. For example, if the company schedules an employee expense in November, it will pay in December. The provision means keeping safety money aside against any probable future losses or payments the firm might need. It is uncertain and cannot be calculated exactly in advance. Still, the firm must make provisions for future losses in advance to cover these losses.
Accrual
Accrual basis of accounting of sales to the reporting of that receipt and the related receivable in the given period in which accrual of sales is earned and that period is later or before the cash receipt of that revenue. For example, interest income on the investment of bonds in November, but the cash will not come until January of next year.
Examples of Accruals include
- Interest Income and interest expenses
- when a company delivers a good or service before taking cash
- when a company records a salary expense before paying the employee with cash
- Employee Bonus
- Interest on Loans and advances
- Insurance Premium
- Interest Payable
Provisions
Provisions for account receivables that the firm makes generally in advance made on future receivables that some of the receivables will turn bad and might not be recovered. A certain regulatory guideline needs to be met, and the firm should be able to justify the provisions for the given period.
Types of Provisions
An organization may have different provisions, such as a non-performing assets provision, a standard provision on assets, a provision for depreciation, probable future losses on the sale of the fixed asset, and a provision for the debtor that might not recover. IFRS refers to a provision as a reserve; generally, provisions and reserves are not the same concepts. An organization earns profit through reserves while it prepares for future liabilities by setting aside funds as provisions to support its financial position during expansion or growth.
Few other examples of provision
- Provision for Depreciation
- Provision for non-performing assets
- Standard provision for advances
- Pension provision
- Guarantees
- Provision for bad debts
Head To Head Comparison Between Accrual vs Provision (Infographics)
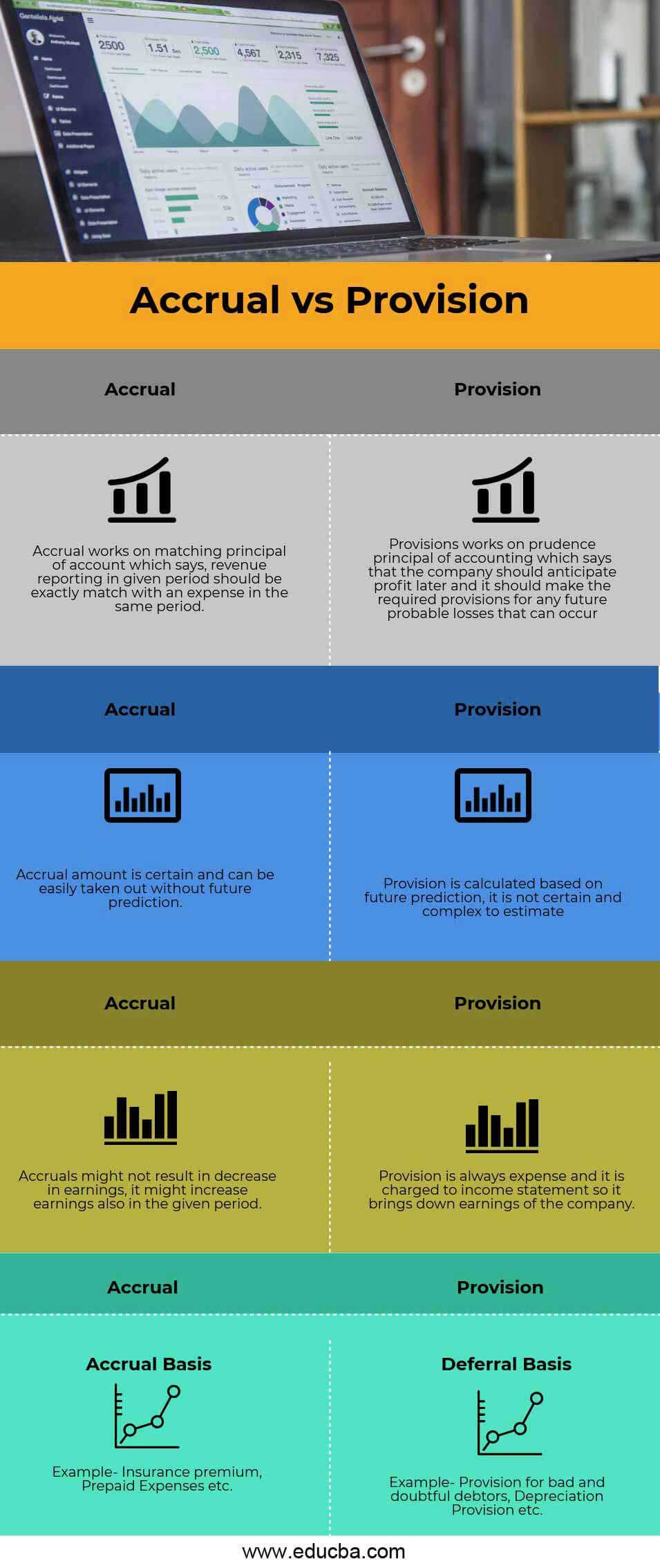
Below is the top 4 difference between Accrual vs Provision
Key Differences Between Accrual vs Provision
Accrual vs Provision are popular choices in the market; let us discuss some significant differences between Accrual vs Provision.
The accrual basis of expense accounting means reporting that expense and the related liability in the period in which the accrual expense occurs. The provision means keeping safety money aside against any probable future losses or payments the firm might need. It is uncertain and cannot be calculated exactly in advance.
The accrual amount is certain, and we can quickly deduct it without future predictions. Provision is calculated based on future prediction; it is not certain and complex to estimate
Accruals might not result in a decrease in earnings; they might increase earnings in the given period. The provision always incurs expenses and reduces the company’s earnings when charged to the income statement.
Accrual vs Provision Comparison Table
Below are the four topmost comparisons between Accrual vs Provision
|
Accrual Basis |
Deferral Basis |
| Accrual works on the matching principle of an account, which says revenue reporting in a given period should be exactly matched with an expense in the same period. | Provisions work on the prudence principle of accounting, which says the company should anticipate profit later and make the required provisions for probable future losses. |
| The Accrual amount is certain and can be easily removed without future prediction. | Provision is calculated based on future prediction; it is not certain and complex to estimate |
| Accruals might not result in a decrease in earnings; they might increase earnings in the given period. | Provision is always expensive and is charged to the income statement, bringing down the company’s earnings. |
| For example, Insurance premiums, prepaid expenses, etc. | Examples- Provision for bad and doubtful debtors, Depreciation Provision, etc. |
Conclusion
Thus, Accrual vs provision is an essential method for financial accounting and reporting. The basic is to check the firm from making any cash inflows and outflows, and it is always good to recognize expenses whenever they occur. It is always good to make provisions whenever management feels a certain amount can go bad in the future because management runs the show, and they know about their clientele more than any other third-party member. Accrual accounting is an industry-standard. New concepts like Accrual vs Provision are gaining traction to make accounting more ground connected to reality and meaningful to all the readers of financial statements.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the top difference between Accrual vs Provision. We also discuss the Accrual vs Provision key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more.