Updated November 27, 2023

Acid-Test Ratio Formula (Table of Contents)
- Acid-Test Ratio Formula
- Acid-Test Ratio Formula Calculator
- Acid-Test Ratio Formula in Excel (with Excel Template)
Acid-Test Ratio Formula
Acid-Test ratio is also known as the quick ratio. The acid-test ratio evaluates an enterprise’s short-term solvency or liquidity position.
In simple language, it measures the capability of the company to pay its debt with its current assets. Current assets are assets that can be converted to cash within 90 days. It is often desirable to know a firm’s more immediate position or instant debt-paying ability than that indicated by the current ratio for this acid-test ratio. It relates the most liquid assets to current liabilities. Acid-test ratio formula is the sum of cash, short-term investment, and current receivables minus inventory minus prepayment divided by current liabilities. It can be written as
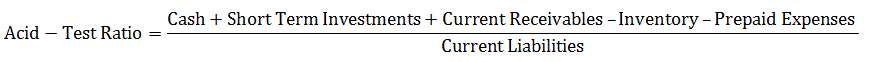
In short, a test can be written as –
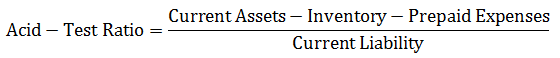
Examples of Acid-Test Ratio Formula
Let’s see an example to understand it better.
Acid-Test Ratio Formula – Example #1
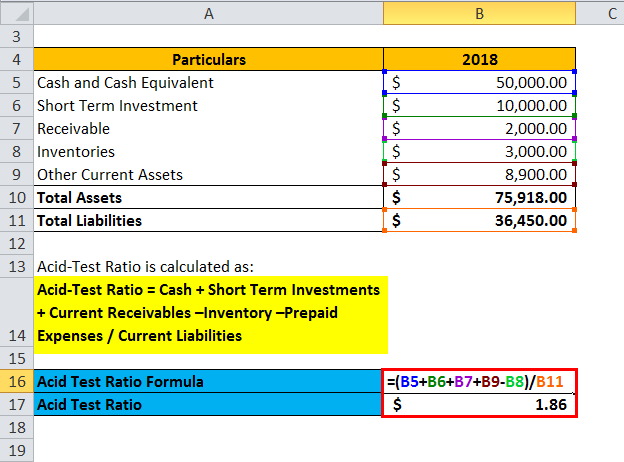
A financial analyst wants to study the liquidity position of HML Pvt. Ltd below its balance sheet for 2018 for analysis.
| Particulars | 2018 |
| Cash and Cash Equivalent | $50,000.00 |
| Short Term Investment | $10,000.00 |
| Receivable | $2,000.00 |
| Inventories | $3,000.00 |
| Other Current Assets | $8,900.00 |
| Total Assets | $75,918.00 |
| Total Liabilities | $36,450.00 |
The formula for the test is –
Acid-Test Ratio = Cash + Short-Term Investments + Current Receivables –Inventory –Prepaid Expenses / Current Liabilities
Put the value from the balance sheet in the above formula.
- Acid-Test Ratio = 50 000 + 10,000 + 2,000 + 8,900 – 3,000 / 36,450
- Acid-Test Ratio = 1.86
So, the acid-test ratio of HML Pvt. Ltd is 1.86, which means it has a lot of liquid assets and high liquidity.
Acid-Test Ratio Formula – Example #2
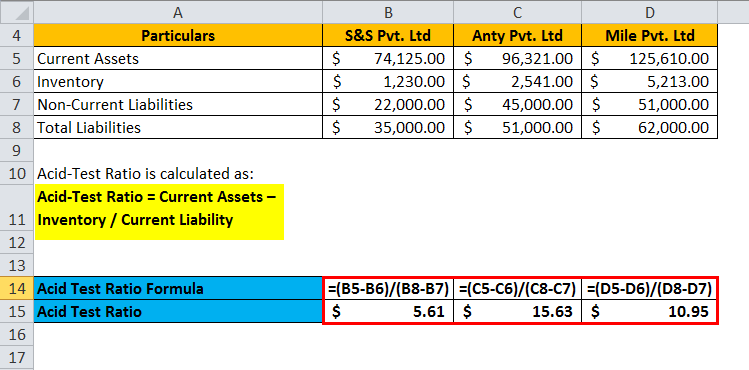
Three companies have the following current assets and current liabilities, through which we will calculate the acid-test ratio.
| Particulars | S&S Pvt. Ltd | Anty Pvt. Ltd | Mile Pvt. Ltd |
| Current Assets | $74,125.00 | $96,321.00 | $125,610.00 |
| Inventory | $1,230.00 | $2,541.00 | $5,213.00 |
| Non-Current Liabilities | $22,000.00 | $45,000.00 | $51,000.00 |
| Total Liabilities | $35,000.00 | $51,000.00 | $62,000.00 |
| Acid-test Ratio | 5.60 | 15.63 | 10.94 |
Where,
Acid-Test Ratio = Current Assets – Inventory / Current Liability
Put value for three companies in the above formula.
S&S Pvt. Ltd:
- Acid-Test Ratio of S&S Pvt. Ltd = (74,125 – 1,230) / (35,000 – 22,000)
- Acid-Test Ratio of S&S Pvt. Ltd = 72,895 / 13000
- Acid-Test Ratio of S&S Pvt. Ltd = 5.60
Anty Pvt. Ltd:
- Acid-Test Ratio of Anty Pvt. Ltd =(96,321 – 2,541) / (51,000 – 45,000)
- Acid-Test Ratio of Anty Pvt. Ltd =93,780 / 6,000
- Acid-Test Ratio of Anty Pvt. Ltd =15.63
Mile Pvt. Ltd:
- Acid-Test Ratio of Mile Pvt. Ltd =(125,610 – 5,213) / (62,000 – 51,000)
- Acid-Test Ratio of Mile Pvt. Ltd =120,397/11,000
- Acid-Test Ratio of Mile Pvt. Ltd =10.94
This is how the company’s acid-test ratio is calculated, and investors do an analysis to invest in the right company.
Let us see one more example to understand the Acid-test ratio formula.
Acid-Test Ratio Formula – Example #3
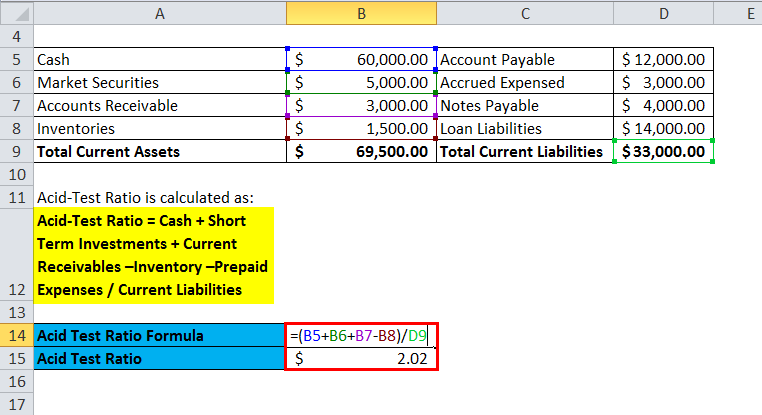
Below is the balance sheet of Ultra Pvt. Ltd for the year 2018, we have to calculate the Acid-test ratio for the same.
| Cash | $60,000.00 | Account Payable | $12,000.00 |
| Market Securities | $5,000.00 | Accrued Expensed | $3,000.00 |
| Accounts Receivable | $3,000.00 | Notes Payable | $4,000.00 |
| Inventories | $1,500.00 | Loan Liabilities | $14,000.00 |
| Total Current Assets | $69,500.00 | Total Current Liabilities | $33,000.00 |
The formula for the test is-
Acid-Test Ratio = Cash + Short Term Investments + Current Receivables –Inventory –Prepaid Expenses / Current Liabilities
Put the value in the above formula.
- Acid-Test Ratio = 60,000 + 5,000 + 3,000 –1,500 / 33,000
- Acid-Test Ratio = 2.01
So, the acid-test ratio for Ultra Pvt. Ltd is 2.01, which means it has a lot of liquid assets and high liquidity.
Explanation
The acid-test ratio is the sum of the current assets to current liabilities. A current asset is the sum of a company’s assets, which can be converted into cash within 90 days. Current assets are cash, short-term investments, and cash equivalent cash, receivable minus inventories minus prepaid expenses divided by current liabilities. Inventories are not considered in the current asset as they cannot be converted into cash, and prepaid expenses are subtracted as they cannot be reversed back to cash easily. And the current liabilities are debts that the company has to repay.
If a company has a higher ratio, the better the company liquidity will be, which results in better overall financial health. But if the ratio is very high, it is also unfavorable as the company may have excess cash, but it is not using it beneficially. It is also possible that the company’s receivables are too high and cannot collect the same, which implies a collection problem.
The acid-test ratio depends on the type of industry, its market, the kind of business, and the nature and financial stability of the company.
Acid-test ratio formula can be written as –
Acid-Test Ratio = Quick Assets / Current Liabilities
Where a quick asset is a current asset.
Significance and Uses of Acid-test Ratio Formula
There are many advantages and uses of the Acid-test ratio formula, and they are as follows-
- The acid-test formula provides an appropriate picture of the company’s liquidity.
- It is most useful when the proportion of current illiquid assets to total current assets is high.
- It helps to find the financial condition of the company.
- This formula helps the investor choose the right company for investment depending on the value acid-test ratio.
- It also helps one to monitor the company’s collection system.
Disadvantages of Acid-Test Ratio Formula
There are some issues with the acid-test ratio. They are as follows-
- The acid-test ratio alone is not sufficient to find the company’s liquidity.
- The acid-test ratio does not include inventory, so it will not provide a clear picture as the company may have high inventories.
- In this formula, cash receivable is considered a current asset, but the company may not be able to collect the funds against it.
The acid-test ratio formula is valuable for assessing a company’s liquidity and ability to repay its debts. The ratio indicates whether a company can meet its financial obligations by comparing its quick assets to its current liabilities. A ratio of 1 signifies that the quick assets are equal to the current assets, indicating that the company can fulfill its debt obligations. On the other hand, a ratio of 2 suggests that the company has twice as many quick assets as current liabilities, which is a positive sign. However, an excessively high ratio, such as 10, is not considered favorable.
Acid-Test Ratio Calculator
You can use the following Acid-Test Ratio Calculator
| Cash | |
| Short Term Investments | |
| Current Receivables | |
| Inventory | |
| Prepaid Expenses | |
| Current Liabilities | |
| Acid Test Ratio = | |
| Acid Test Ratio = |
|
|
Acid-Test Ratio Formula in Excel (With Excel Template)
Here, we will do the same example of the Acid-Test Ratio formula in Excel. It is very easy and simple. You need to provide the three inputs i.e, Current Assets, Inventory, and Current Liability
You can easily calculate the Acid-Test Ratio using Formula in the template provided.
Acid-test for HML Pvt. Ltd is calculated as:
The test for all three Companies is calculated as:
Acid-test for Ultra Pvt. Ltd is calculated as:
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to an Acid-Test Ratio formula. Here, we discuss its uses along with practical examples. We also provide you with an Acid-Test Ratio Calculator with a downloadable Excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –

