Updated July 11, 2023
Definition of Ad Valorem Tax
The term “ad valorem tax” (adT) refers to the tax that is determined on the basis of the assessed value of the asset or transaction. Regarding real or personal property, (adT) imposes annually. On the other hand, it imposes during the transaction in transactional cases, such as value-added tax (VAT) or sales tax.
Explanation
In Latin, the term “ad valorem” means “according to value”, which implies these types of taxes are variable and are purely dependent on the assessed value of the assets or transactions. Municipal and state government authorities typically charge (adT). The most commonly used ad valorem tax for assets is the property tax, while VAT and sales tax are common examples of (adT) on transactions.
How Does Ad Valorem Tax Work?
Ad valorem taxis are charged on the basis of the assessed value of the item to be taxed. In municipal property tax, a public tax appraiser periodically determines the valuation of the owner’s real or personal property using the concept of adT. The tax authority uses the asset’s assessed value to compute the tax charged to the property’s owner. On the other hand, for transactional taxes, such as VAT and sales tax, ad valorem taxis are levied at the time of a transaction on the basis of the transaction size. The formula calculates the ad valorem tax by multiplying the ad valorem tax rate with the assessed value of the asset or transaction.
Examples
Following are the examples given below:
Example #1
Let us take a simple example of a real estate property to illustrate the concept of (adT). The property tax the government authorities charge in the area is 8% annually. Determine the property tax to be paid for during a year if the property’s assessed value is $500,000.
- Given the Assessed value of property = $500,000
- Property tax rate = 8%
Solution:
Property Tax calculates as,
Property Tax = Property Tax Rate * Assessed Value of Property
- Property Tax = 8% * $500,000
- Property Tax = $40,000
Therefore, the annual property tax to be paid is $40,000.
Example #2
Let us take another example to illustrate the concept of (adT) in the case of transactional tax. Suppose the applicable sales tax charged in a particular country is 20% of the transaction. Determine the sales tax that has to be paid in the given country for a sales transaction of $10,000.
- Given the Assessed value of the transaction = $10,000
- Sales tax rate = 20%
Solution:
Sales Tax calculates as,
Sales Tax = Sales Tax Rate * Assessed Value of Transaction
- Sales Tax = 20% * $10,000
- Sales Tax = $2,000
Therefore, the sales tax that has to be paid at the time of the transaction is $2,000.
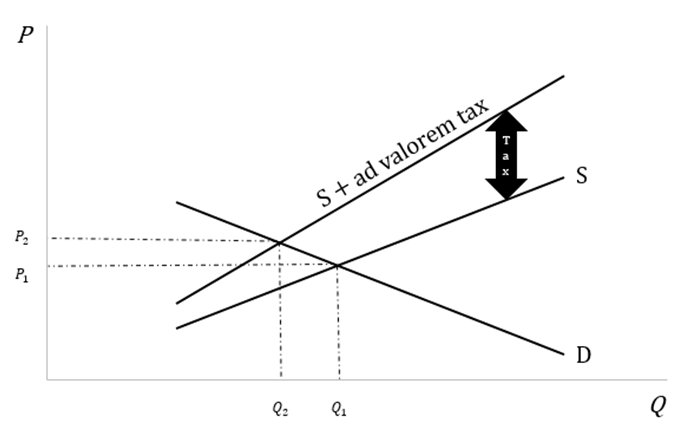
Ad Valorem Tax Diagram
In the below diagram, line S represents the pre-tax supply curve, line (S + ad valorem tax) represents the after-tax supply curve, and line D represents the demand curve. P1 and Q1 represent the equilibrium price and quantity for the pre-tax supply and demand scenario. In contrast, P2 and Q2 represent the equilibrium price and quantity for the after-tax supply and demand scenario. The growing gap between the pre-tax supply curve and the after-tax supply curve represents the impact of (adT), which grows with increased quantity. Effectively, the pre-tax supply curve shifts toward the left and outwards owing to the incidence of ad valorem tax that results in the price increase, which can be seen in the diagram below.
Impact of Ad Valorem Tax
The (adT) is calculated as a percentage of the assessed value, which means the tax value is directly proportional to the assessed value, i.e., at a lower price, the tax will also be relatively less. In comparison, the levied tax will be higher at a higher price. Nevertheless, in the short and long run, different economic parameters behave differently due to the imposition of (adT).
The short-run impacts of the imposition of (adT) are – price increases, firms’ output decreases, and firms incur higher losses. On the other hand, in the long run, the impacts of the ad valorem tax are price increases, firms’ output remaining unchanged, and firms booking normal profit.
Advantages
Some of the major advantages of (adT) are as follows:
- Given that it is proportional to the assessed value, it helps overcome the shortcomings of a specific tax regime.
- It also helps avoid discrimination against low-priced items by using the escalated value.
Conclusion
So, it can be seen that (adT) uses the assessed value of an asset or a transaction for tax calculation, which is a better and more progressive approach than the specific tax rule. It is important to note that it is one of the major sources of income for any county, state, municipal authorities, etc.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Ad Valorem Tax. Here we discuss the introduction and How does Ad Valorem Tax Works? Along with examples and advantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –