Updated May 10, 2023
Advanced Filter in Excel
Advanced Filter in Excel is the next level filter option available in the Data menu tab under Sort & Filter section, which filters the selected data per the criteria we set for this. For this, first, we need to scrub the data by removing the blank cell and keeping the header in all the columns. To advance filter, we need to define the criteria by which we need to filter the data, and the criteria should be placed in separate cells from the table. Once we select the Advanced Filter Option, select the complete range we want to filter, then select the cell where we defined the criteria.
What is the difference between regular and advanced filter?
- You can use the advanced filter for more complex criteria filtering. (I will explain in detail with an example.)
- A regular filter will filter data on the existing dataset, while with the latter, you can extract data to some other location keeping the original data intact.
- The advanced filter can use to extract unique entries in our dataset.
- A regular Filter is a sequential filter. You can only use one criteria simultaneously to extract records from one dataset; you have to extract data satisfying each criterion, ultimately leading to duplicity.
E.g., Suppose you want to extract records where Reporting Manager is “Aakash Harit” or the Employee name is “Vishal Kumar”. In that case, you have to extract data 2 times using a regular filter, the first data having Aakash Harit is RM, and the second, when Emp name is Vishal, while using an advanced filter, you can extract all unique records in one go.
How to Use Advanced Filter in Excel?
This Advanced Filter is very simple easy to use. Let us now see how to use the Advanced Filter in Excel with the help of some examples.
Advanced Filter in Excel Example #1
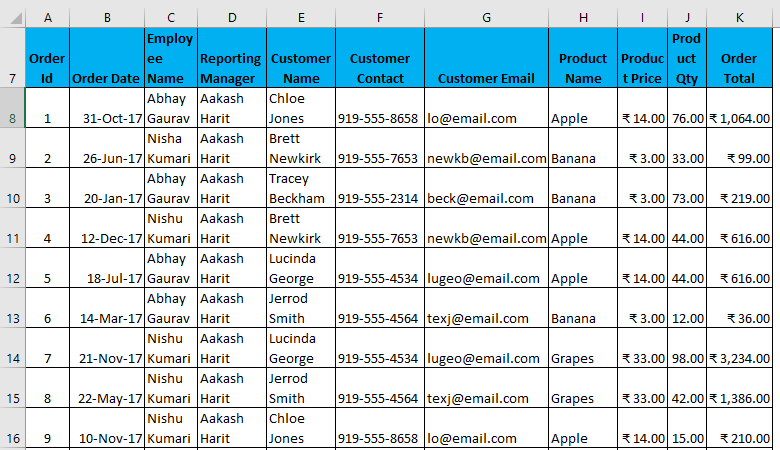
- Suppose you have the following dataset and have to get all the records where the order total is greater than 900, and the employee name is “Nishu Kumari”.
- To use an advanced filter with some criteria, first, you must copy all the headers & paste them somewhere else in the worksheet. (In my case, I will use blank rows to make it easier to understand.
- Now, specify the conditions under these headers according to your requirement, which will act as an input in a filter.
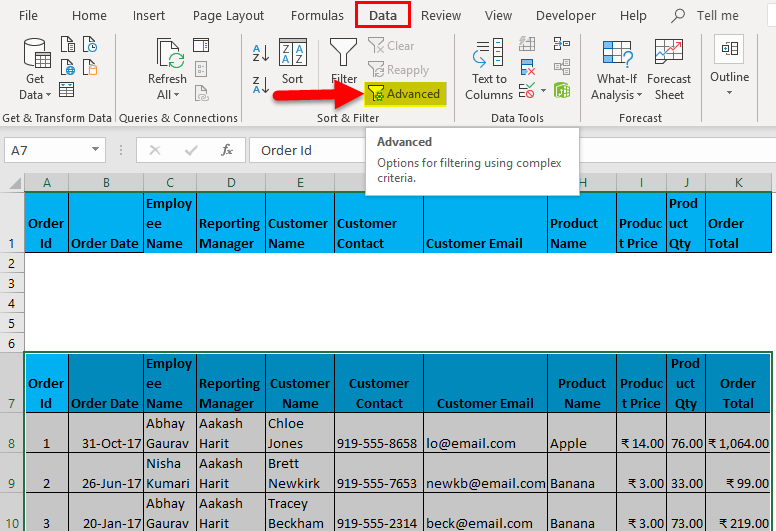
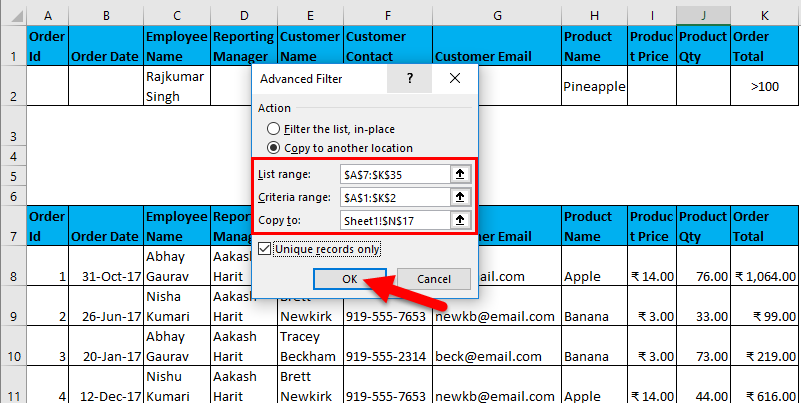
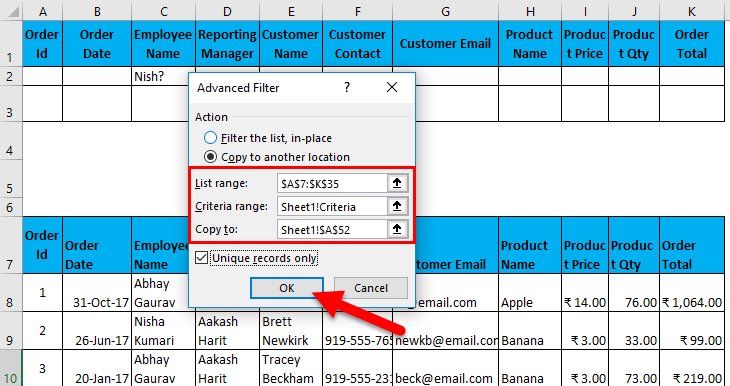
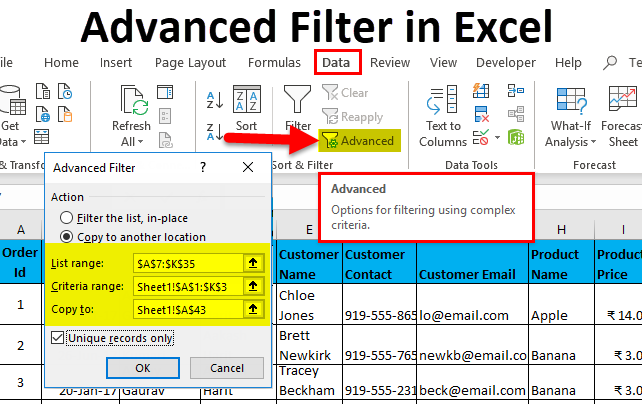
- Now, select the entire data set, headers, and Go-To Data tab – Sort & Filter. This will open the Advanced Filter dialog box.
- Hotkey to applying the advanced filter after selecting the dataset is (Alt key+ A+ Q).
-
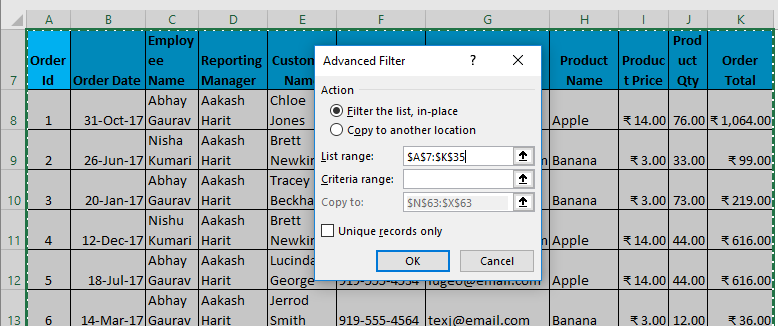
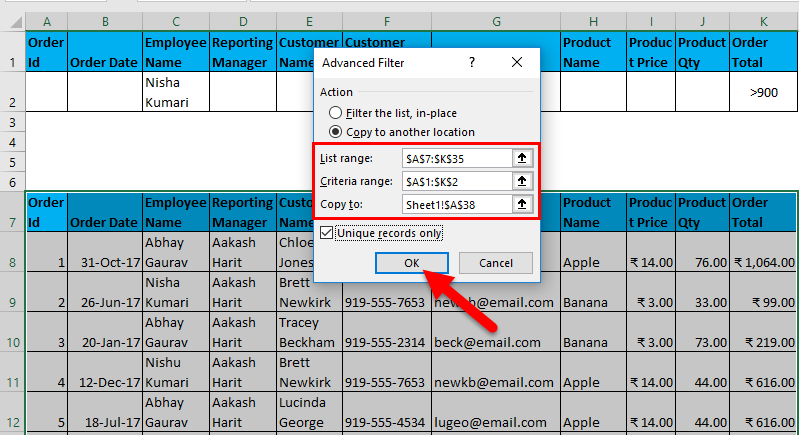
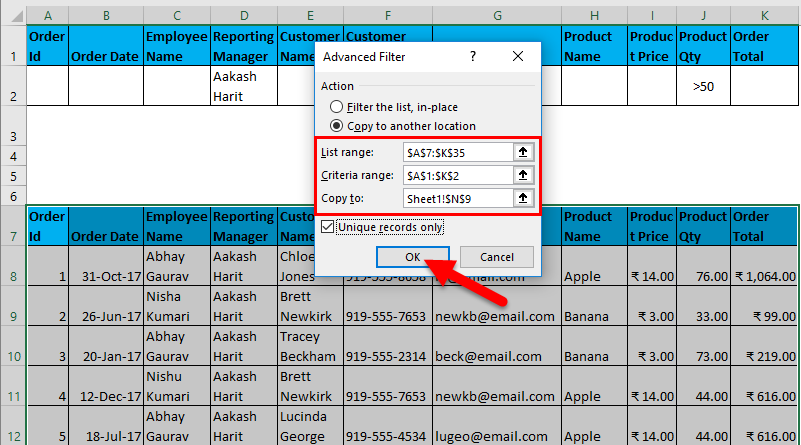
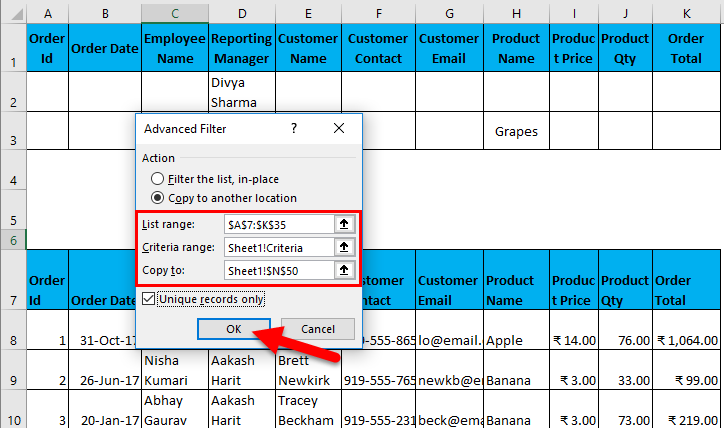
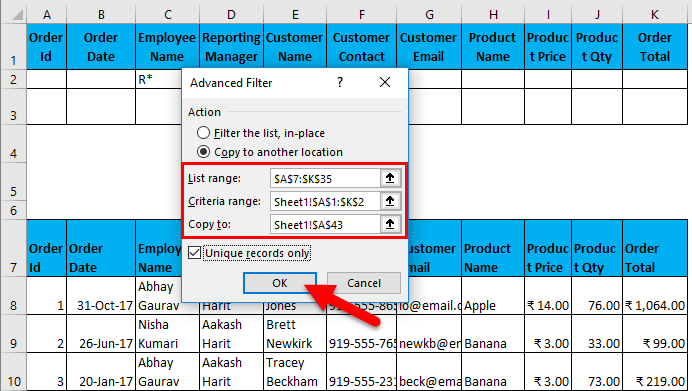
- Now, as shown above, you have to enter the following details:
- Action: It has 2 options. First, filter the list in place (this will remove the original data, and the result of this filter will place in the same location), and Second, copy another location. (this will allow you to save filtered data on location)
- List Range refers to the dataset from where you want to find data. (Here it’s A7: K35)
- Criteria Range: In this, Criteria are mentioned (A1: K2)
- Copy To: This cell will be activated using the second option in the Action criteria.
- Copy Unique Records Only: Check this only if you require unique records.
- I have entered all the details in this dialogue box and chose to copy them to another location(A38) with unique records.
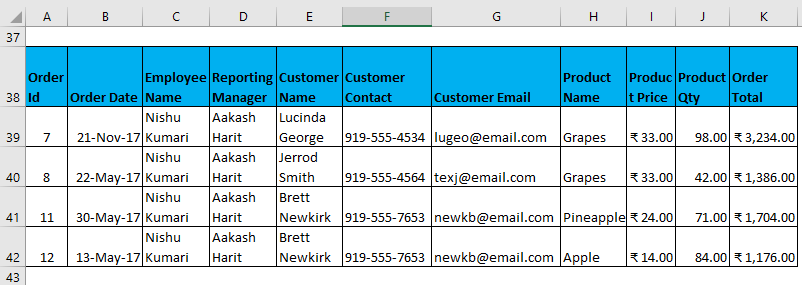
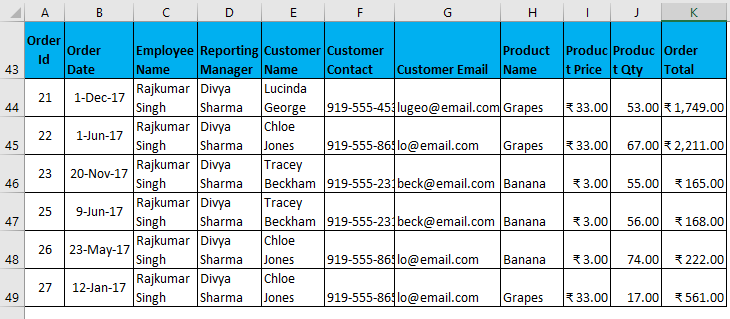
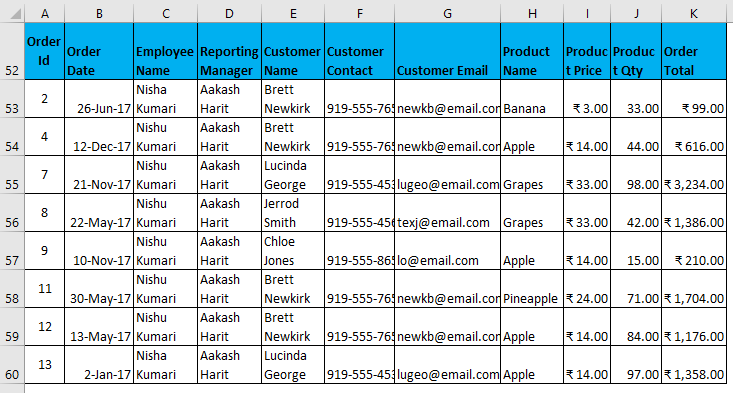
- It will look as in the Screenshot on the next page. Now click ok, and it will give all unique records.
The output is given below, showing only those data containing the Employee name Nishu Kumari.
Filtered data with complex criteria as constructed above.
Advanced Filter in Excel Example #2
Now, many combinations of criteria can use in Advanced Filter. (Using AND and OR Criteria) Some examples are:
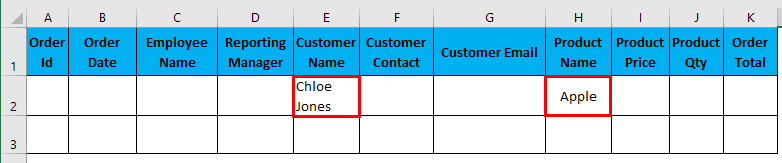
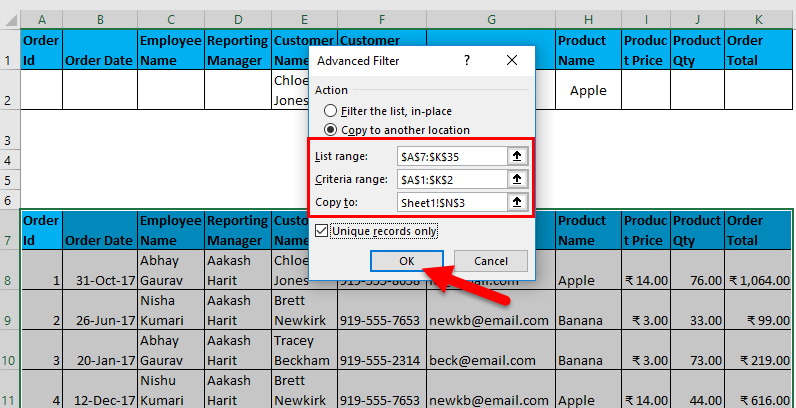
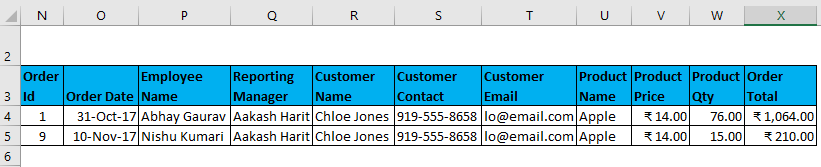
- Filter data where Customer Name is “Chloe Jones” AND Product name is “Apple”.
I have entered all the details in this dialogue box and choose to copy them to another location(N3) with unique records.
The output is given below:
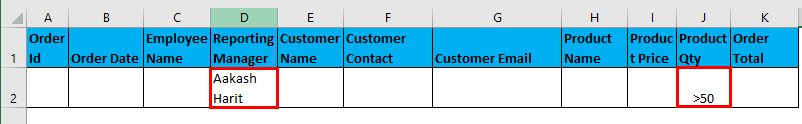
- Filter data where the Reporting Manager is “Aakash Harit” AND Product Qty is greater than 50.
I have entered all the details in this dialogue box and choose to copy them to another location(N9) with unique records.
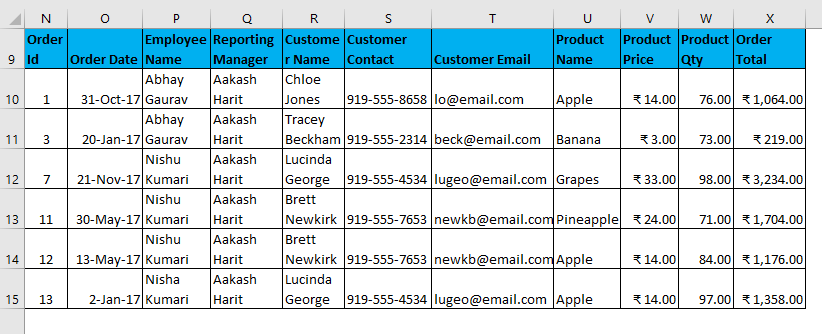
The output is given below:
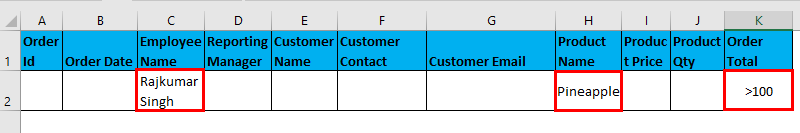
- Filter data where Employee name is “Rajkumar Singh” AND Product Name is “Pineapple”, AND order total is greater than 100.
I have entered all the details in this dialogue box and choose to copy them to another location(N17) with unique records.
The output is given below:
The above table shows empty data because it does not matches the given condition.
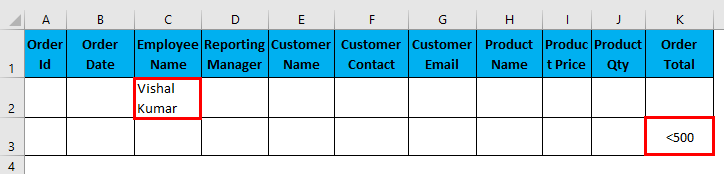
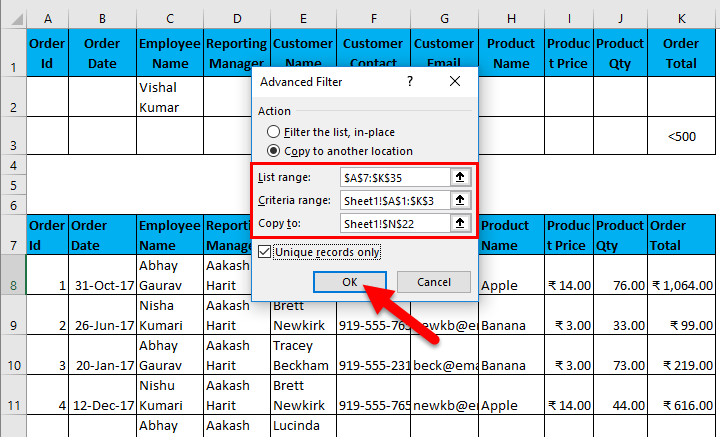
- Filter data where Employee Name is “Vishal Kumar” OR Order Total is less than 500.
I have entered all the details in this dialogue box and choose to copy them to another location(N22) with unique records.
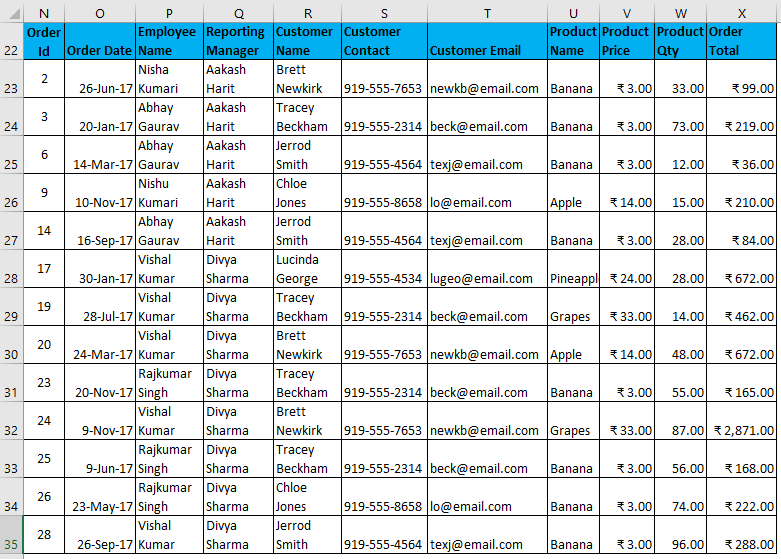
The output is given below:
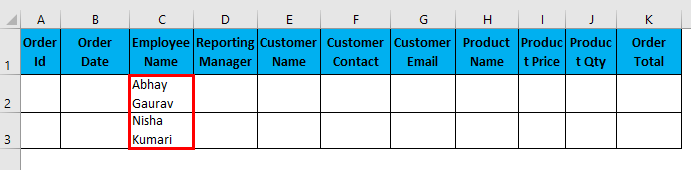
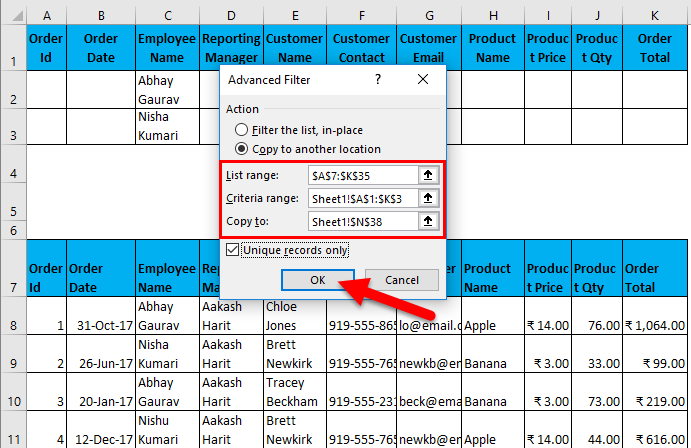
- Filter data where Employee Name is “Abhay Gaurav” OR “ Nishu Kumari”.
I have entered all the details in this dialogue box and choose to copy them to another location(N38) with unique records.
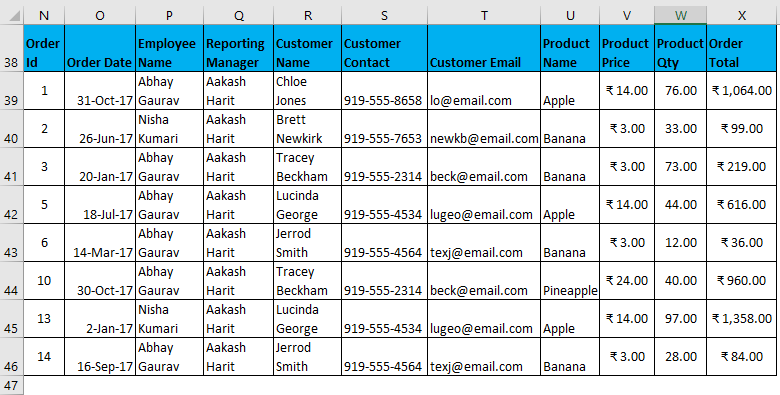
The output is given below:
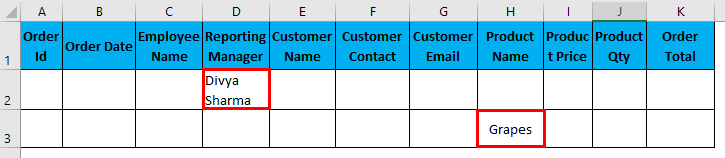
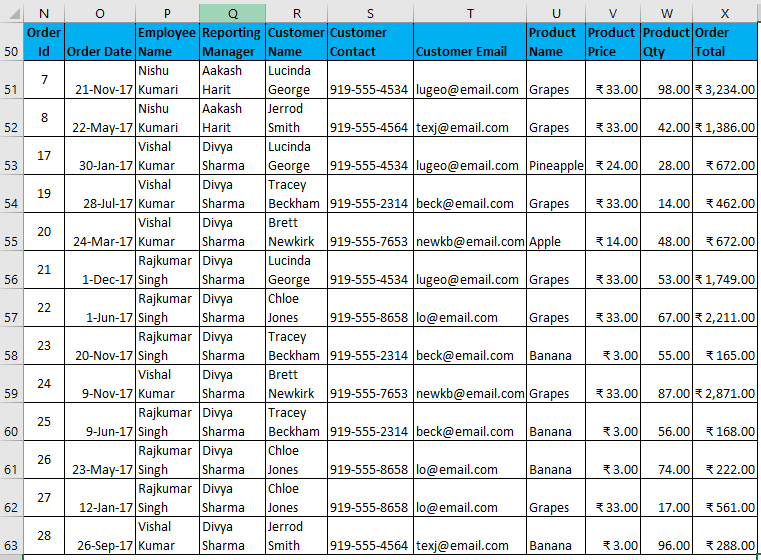
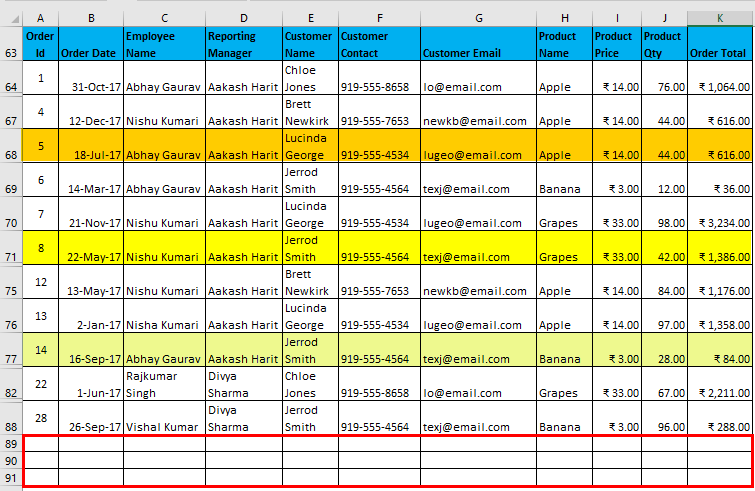
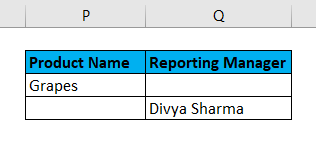
- Filter data where the Reporting Manager is “Divya Sharma” OR Product Name is “Grapes”.
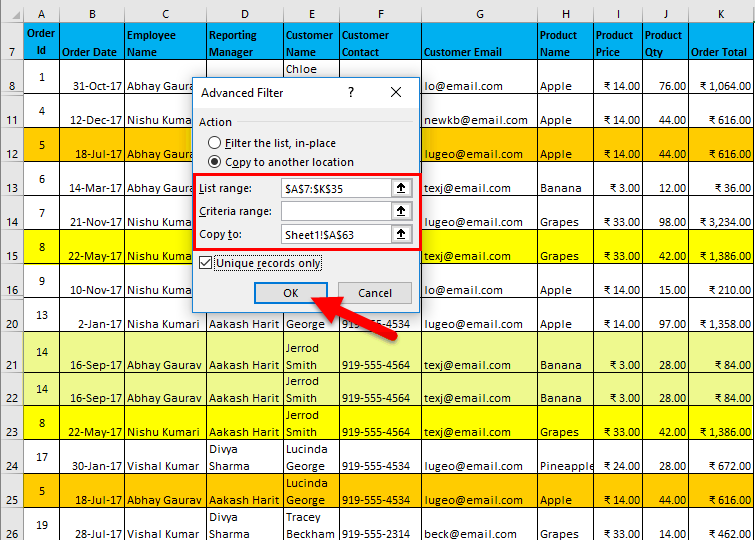
I have entered all the details in this dialogue box and choose to copy them to another location(N50) with unique records.
The output is given below:
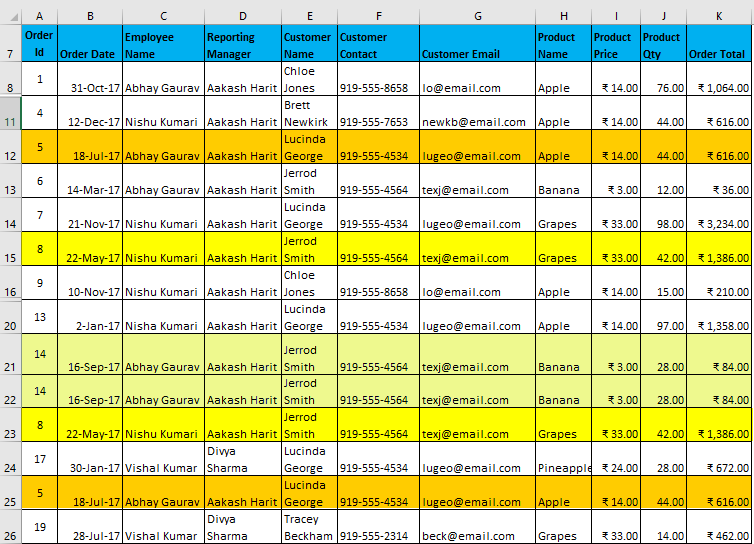
You may have observed that the dataset extracts unique entries when one mentions all values in the same row while using AND criteria, and when all values are in different rows while using OR criteria.
Advanced Filter in Excel Example #3
Another important feature in Advanced Filtering is filtering data using Wild Card Characters. There are wildcard characters:
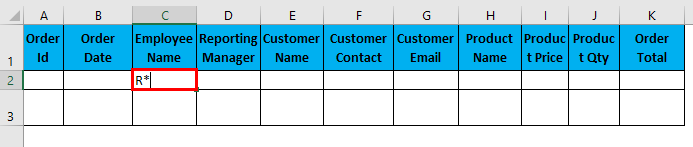
- An asterisk (*): It represents any number of characters. E.g. To filter data with Employee name starting from “R”,. You will write “R*”, So any employee name starting with initials R will be filtered out.
I have entered all the details in this dialogue box and choose to copy them to another location(N9) with unique records.
The output is given below:
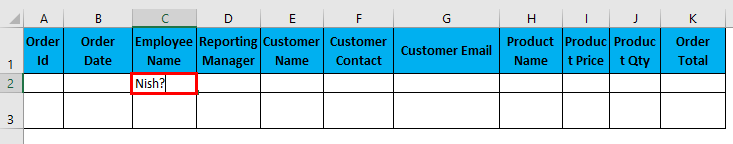
- Question Mark (?): It represents one single character. E.g. filter data with where employee name initials are “Nish”. Filter criteria will be like, “Nish?” and it can mean Nishu or Nisha.
I have entered all the details in this dialogue box and choose to copy them to another location(N9) with unique records.
The output is given below:
- Tide (~): It is use to find any wildcard character within a text.
Advanced Filter in Excel Example #4
You can also remove duplicates or quickly extract the unique records from the data set.
- Now suppose you have the following data set, which has some duplicate entries(highlighted), and you want to extract unique records from a dataset; you can use the advanced filter option to do it, keep in mind that there is no need to mention any values in criteria option and simply check unique records option. This will give you records with unique values.
- After applying the filter, it will give a result, as shown below:
- You can notice in the below image; all duplicates are removed. The last 3 rows are empty
- However, latest versions of Excel (mainly after Excel 2007), we have an option to remove duplicates from a dataset (Go to Data Tab.Remove Duplicates or use hotkey Alt Key+ A+ M), but it will alter the original dataset. But if you want to keep original data intact, you can use an advanced filter to get a dataset with unique entries at some other location.
Key Notes:
- While applying an advanced filter, always take care that headers in the criteria should be exactly the same as in the data set. Viz. there should be no spelling errors, space errors or even case errors, although alignment can be mixed. E.g. in the above, you can mention criteria like Product name first and employee name second. But headers should be exactly the same, as shown below.
- You can’t UNDO advanced filtering when copied to some other location.
- If you are using an advanced filter to extract unique entries, make sure to select headers also, the otherwise first entry will be taken as headers in it.
Things to Remember
- Advanced Filter is an advanced version of a regular filter used to filter data with complex criteria and multiple conditions.
- The dataset extracts unique entries through its use.
- You must include headers while selecting the data set, and the headers in the criteria must be exactly in the same order as in the dataset.
- You can’t undo it if filtered data is copied to another location.
- The shortcut to apply an advanced filter after selecting the dataset is (Alt key+ A+ Q).
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide on Advanced Filter in Excel. Here we discuss how to Advanced Filter in Excel along with excel examples and downloadable excel templates. You may also look at these useful functions in excel –