Updated May 13, 2024
Genetic Engineering Technology
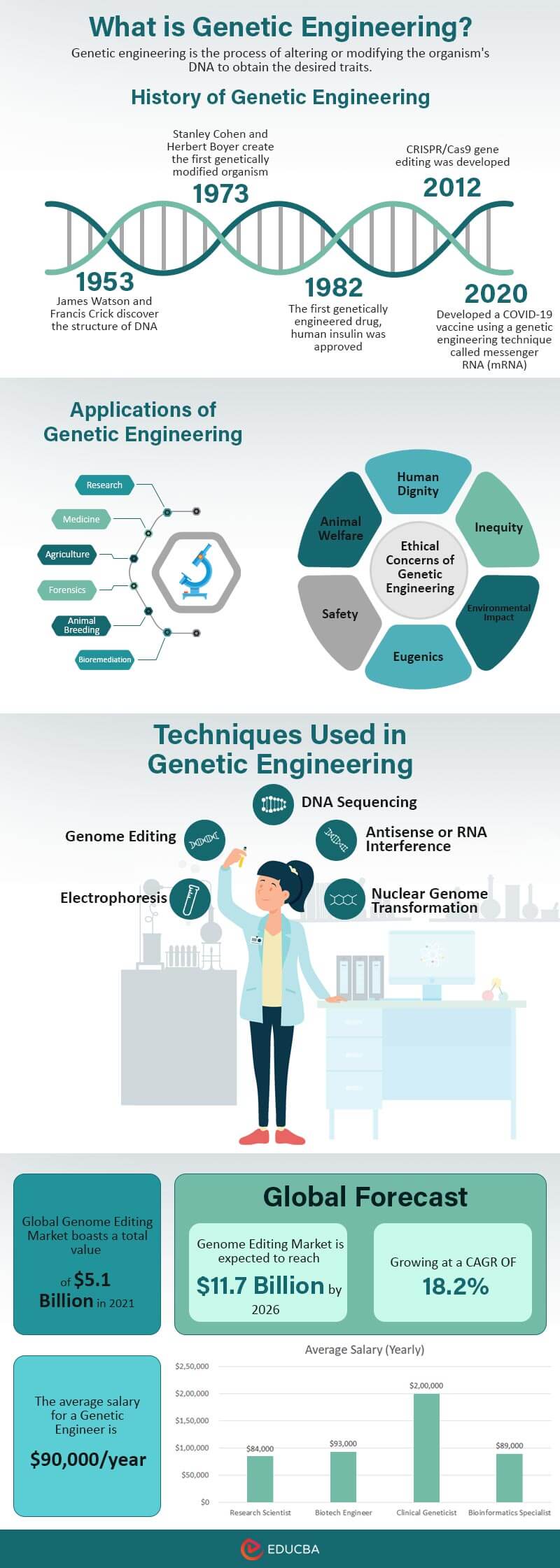
Genetic engineering is a process by which an organism’s genetic material is altered or modified, usually by introducing foreign DNA. It helps to create desired traits or a new organism with certain qualities. Genetic engineering helps produce crops resistant to pests, develop new medicines, and modify organisms to make valuable substances like insulin.
Genetic engineering is a controversial topic, with many people raising ethical concerns about the use of this technology. In this article on the advantages and disadvantages of Genetic Engineering, we understand the process of genetic engineering, examples of genetically modified foods, and the public perception of the technology.
Advantages of Genetic Engineering
1. Increased Crop Production
Genetic engineering helps in increasing crop production by making plants more resistant to pests, diseases, and harsh environmental conditions. This results in higher yields and longer shelf-life for crops.
2. Improved Quality of Food
Genetic engineering helps in producing crops with improved nutritional value, such as higher levels of vitamins, minerals, texture, taste, and enhanced flavor. For example, golden rice is genetically modified to combat vitamin A deficiency.
3. Improved Animal Health
Genetic engineering aims to develop animals with improved disease resistance and overall health. For example, animals can undergo genetic modification to produce different coats and body muscle tissue.
4. Reduced Use of Pesticides
Genetic engineering can help in reducing the use of chemical pesticides by introducing pest-resistant, fungal-resistant, and virus-resistant crop varieties. As a result, it leads to less release of toxins in the environment and maintains soil health.
5. Reduced Cost of Food Production
Genetic engineering can help reduce production costs by introducing plants and animals with improved disease resistance and higher yields. For example, cows and buffalo can undergo genetic modification to produce more milk.
6. Improved Medical Treatments
Genetic engineering helps develop better and more effective medical treatments like gene therapy to cure diseases or ailments. For instance, it has helped in producing important medicines, vaccines, and other drugs, such as human insulin.
7. Increased Environmental Sustainability
Genetic engineering can help reduce the negative environmental impacts of food production by making crops more resistant to pests and diseases. As a result, this reduces the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
Disadvantages of Genetic Engineering
1. Unpredictable Results
One of the primary disadvantages of genetic engineering is that it involves manipulating an organism’s genes, which can produce unpredicted results. For example, genetically modified organisms (GMOs) may produce toxins and allergens or have random environmental impacts.
2. Health Risks
Another disadvantage of genetic engineering is its potential to cause negative health consequences. For example, some researchers have suggested that genetically modified foods may have a link to allergies, cancer, and other problems.
3. Impact on Biodiversity
Genetic engineering can harm and limit biodiversity. Introducing genetically modified organisms into the environment can disrupt the ecosystem by harming other species, including endangered species.
4. Unethical Practices
Genetic engineering raises many ethical concerns, such as creating genetically modified crops for human consumption. Furthermore, researchers alter the gene to develop “perfect or designer babies” with specific desired traits. This is unethical tampering with the human gene.
Examples
Genetic engineering has yielded both favorable and unfavorable results. Here are some examples to illustrate the positive and negative impact of genetic engineering.
Positive Examples
1. Plastic Degrading Microorganisms
In 2023, scientists created genetically engineered marine microorganisms capable of breaking down polyethylene terephthalate (PET). This plastic is commonly found in water bottles and other plastic materials. This significant breakthrough can potentially revolutionize how we handle plastic waste.
2. Golden Rice
Golden Rice is a genetically modified plant developed in the 1990s to combat vitamin A deficiency in developing countries. It produces beta-carotene, a precursor of Vitamin A; the human body converts beta-carotene into Vitamin A.
In 2021, Golden Rice was approved in the Philippines for commercial propagation, and it is under regulatory review in Bangladesh. Despite significant controversies and debates surrounding it, Golden Rice could provide a long-term solution to deficiencies in vitamin A and improve health outcomes for millions of people in developing countries.
3. Insulin
Diabetes mellitus (Type 1 and Type 2) is a metabolic disease that impacts how the body utilizes blood sugar (glucose). In the early 1990s, the only treatment for Type 1 diabetes was stringent carbohydrate-restricted diets.
Scientists first made insulin from animals like cows and pigs to maintain patients’ health. The discovery of recombinant DNA technology helped scientists in producing human insulin in bacterial cells. This insulin was further purified for medicinal use. Furthermore, the WHO has listed insulin as an essential medicine for human disease treatment. Innovative techniques like nanotechnology, stem cells, and other recent advancements are more effective in producing insulin due to the increased number of diabetes patients worldwide.
Negative Examples
1. Flavr Savr Tomato
The first genetically engineered tomato is the Flavr Savr tomato, approved for human consumption by the FDA in 1994. Calgene developed Flavr Savr by using antisense RNA technology. However, it failed due to high production and distribution costs, the company’s inability to handle financial troubles, and negligence in its decision-making and production processes. Later, Monsanto bought Calgene in 1997, and Flavr Savr disappeared from the market.
Recently, scientists at the School of Biological Sciences at the University of Hong Kong (HKU) have collaborated with other institutes to develop a method for boosting tomatoes’ vitamin and antioxidant content. Further, the researchers increased concentrations by six times of lycopene, vitamin E, provitamin A, and other nutrients with health benefits.
2. Bt Cotton in India
Bt cotton is a genetically modified cotton developed by Monsanto to resist pests. It was introduced in India in 2002 and has increased yields by 24–27% while decreasing the use of pesticides by 40%.
However, it negatively impacts soil fertility and biodiversity, developing pink and American bollworms. Farmers in India face many problems, such as costly seeds, new varieties of worms, and increasing indebtedness. Moreover, scientists can produce new types of Bt cotton with advanced technology for a sustainable environment.
Genetic Engineering: Infographic
Process of Genetic Engineering
1. Isolation of the gene of interest
The first step in genetic engineering is identifying and isolating the desired gene of interest. It involves various techniques, such as restriction digestion, PCR, etc.
2. Insertion of the gene into a vector
The desired gene is inserted into a vector, usually a plasmid, which can self-replicate and express in a host cell.
3. Transformation of the vector into a host cell
The above recombinant plasmid containing the gene of interest is inserted into a host cell, such as a bacterial cell.
4. Expression of the gene
The bacterial cell multiplies and produces the desired protein.
5. Selection and screening
The bacterial cells successfully expressing the gene are selected and screened for the desired protein.
6. Purification and characterization of the protein
The desired protein is collected, purified, and characterized by various techniques.
Public Perception of Genetic Engineering Foods
Genetic engineering is a rapidly growing technology, but the implications of using genetically-engineered crops are often controversial and debatable. There are many advantages and disadvantages of genetically modified organisms. Many surveys revealed that public perception toward GMOs is negative, believing that genetically modified products might negatively affect offspring, future generations, society, and the environment. People fear that it might negatively impact human health by causing organ damage, cancer, toxicity, change in the nutritional composition, and other undesirable side effects. Moreover, public opinion about the safety of GM foods is closely related to their perceptions of scientific knowledge and technological trust.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, genetic engineering can have positive impacts; however, weighing all of these benefits against the potential risks is crucial. The above article provides all the necessary information about the Advantages and Disadvantages of Genetic Engineering. Adopting the right approach can maximize the benefits and minimize potential harm. Hence, careful consideration and regulation are essential to ensure the ethical and responsible usage of genetic engineering.
Recommended Articles
We hope this EDUCBA information on “Advantages and Disadvantages of Genetic Engineering” benefited you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.