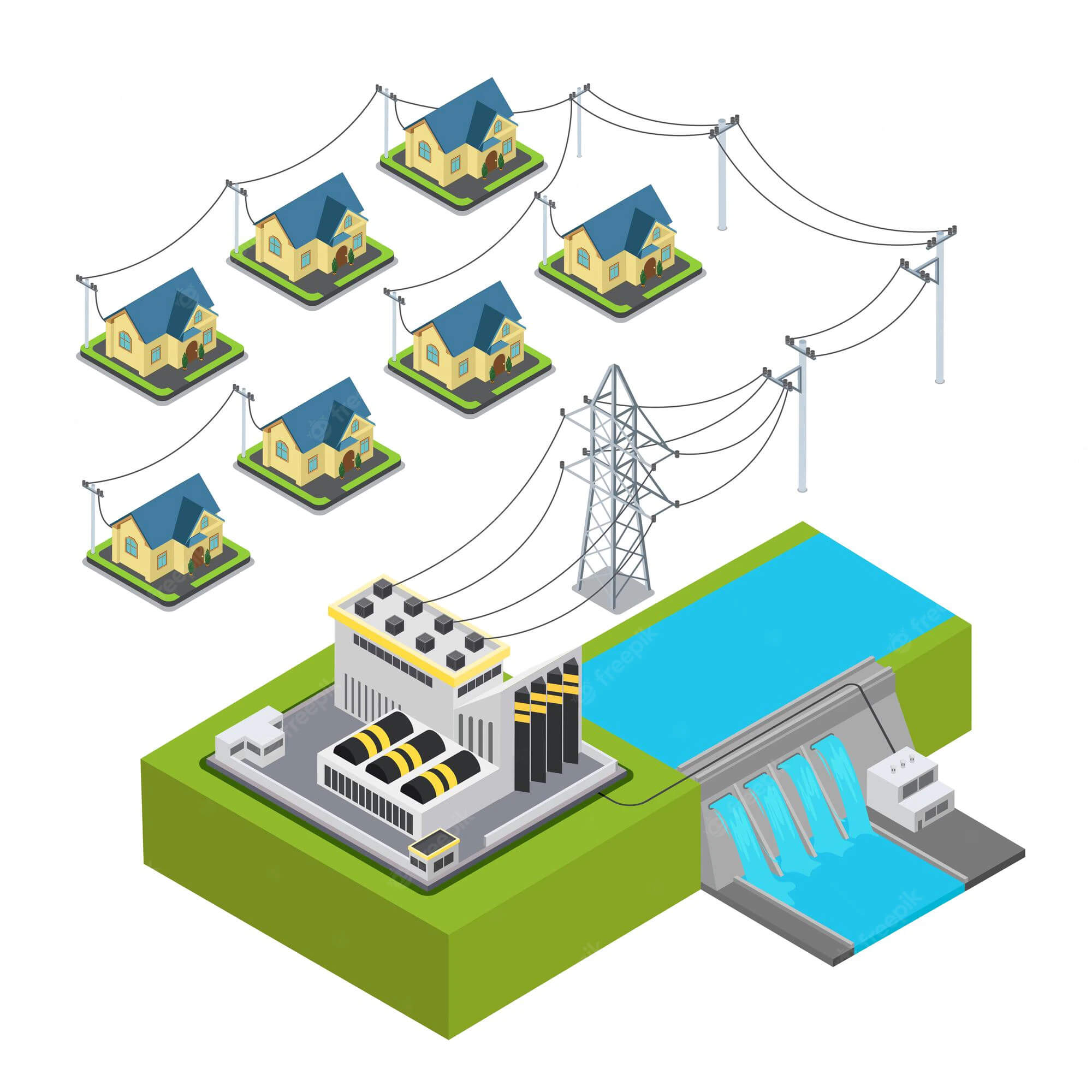
Hydroelectric Power Plant
Nowadays, we are using a variety of energy supplies in our everyday lives, with electricity being one of the most significant. We couldn’t fathom our lives without it. Electricity generation is possible via various power facilities such as thermal, nuclear, hydropower, solar, geothermal, and many other power plants. Hydropower plants are the most practical and conveniently accessible electricity plants that produce the least pollution. Because hydro denotes water, energy is generated in hydropower facilities by the flow of rushing water. Let’s dive further into facts about Hydroelectric Power Plant.
What is a Hydroelectric Power Plant?
Hydropower plants generate energy by using impounded water from streams that have dams built on them. The dam constructions are such that beneath the falling water lies a turbine. The turbine rotates because of the water, and the turbine’s stored energy turns into mechanical energy. It happens because of the kinetic energy of the rapidly flowing water.
Hydropower facilities, also referred to as hydropower-generating plants, are often built in areas with abundant hydropower-generating plants and areas with abundant water. Following energy generation, these power plants deliver power to several local regions, enterprises, marketplaces, etc.
Advantages of Hydropower Plants
- Water is a renewable resource that is accessible year-round: Its quality and amount may decrease owing to seasonal changes or other artificial factors, but it is renewable over time. Anyone constructing hydropower facilities will ensure that water is freely available in the plant’s locations.
- The operating and maintenance costs are lower than those of other power plants: Building hydropower facilities require massive infrastructure to construct dams. Thus, money or finance is necessary for the early phases, but less than in other plants.
- Fuel is not required: Hydropower plants do not require fuel because the flow of water powers everything. Plants do not use water to create energy in the same way that other plants do.
- Working personnel needed are less: The number of people required to monitor the plant’s operation is low. It reduces the operating costs of hydropower facilities, making them more cost-effective for a country.
Disadvantages of Hydropower Plants
- The expense of building a dam is substantial: The initial cost of infrastructure building, such as the dam, is significant. Hydropower demands a large initial investment in money, but other electricity-producing facilities require less cash to build plants and set up machinery.
- The amount of land required for setup is substantial: Because an elevation or dam is on the river, the land needed for the massive infrastructure is vast.
- Harmful for aquatic life: Embankment lowers the ability of fish to access their spawning grounds, which impacts other creatures that rely on fish for sustenance. The neighboring habitat of rivers is limited when the passage of water decreases, and they cannot reach the water.
- The floodplains necessitate the evacuation of the embankment area: A hydroelectric plant built anywhere significantly impacts the surrounding community and area because residents must relocate to meet the demands of the plants. The dam, despite its strength, would occasionally damage many people nearby because of excessive rains or tropical storms.
In the End
There is no perfect power source. However, hydropower may provide a nice mix of renewable energy that delivers steady electricity while having little environmental influence. Hydropower will become an essential component of the global energy mix to tackle climate change. It is because it produces no greenhouse gases and is a reasonably easy and dependable method of producing clean energy.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Advantages and Disadvantages of Hydroelectric Power Plant” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information,