Introduction to Advantages of DBMS
Before understanding DBMS’s advantages, let us briefly look at Data. Any information that comes out is tagged with the name “Data.” What I am typing right now has already become the data for me, and once it is published on the World Wide Web (WWW), it will also become data for everyone else. Now, these data play a key role in making the most out of our available systems, Software, Companies, Enterprises, Governments, Hospitals, Research Centers, Astronomy Organizations, NGOs, and much more spread across our planet. A brief look at today’s IT Operations:
But how would data probably benefit today’s Enterprises? The developer builds an application or Software, but Software needs Data to perform day-to-day operations, and analytics over processed data is driving businesses nowadays to excel in their respective areas of operations.
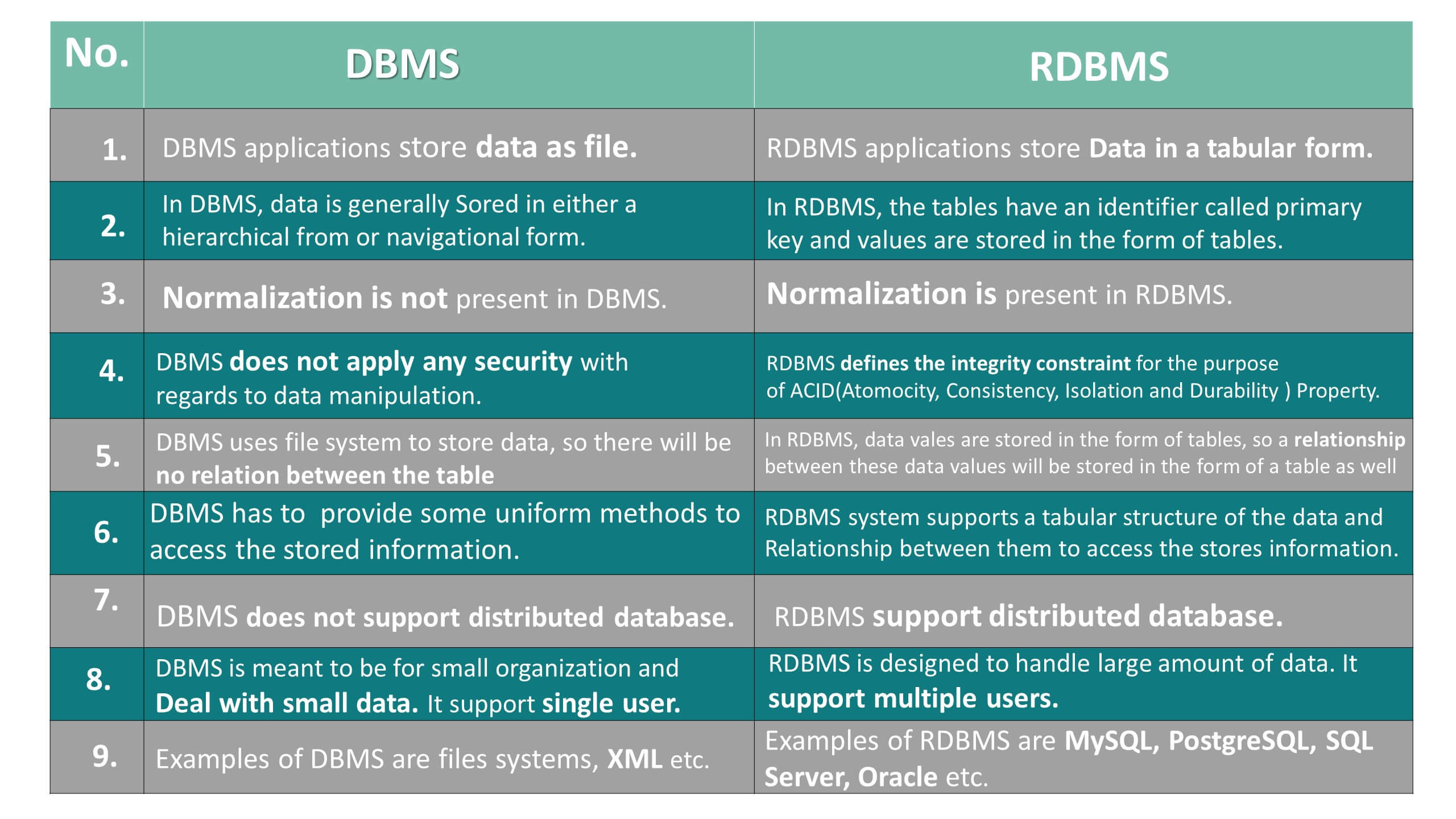
So as a developer, we need a Data Base Management System to create, update, delete, administer, and analyze the data. We have two most popular ways of storing and managing Data Base.
These are DBMS and RDBMS:
- DBMS(Database Management System) – Stores Data as files
- RDBMS(Relational Database Management System) – Stores Data in a tabular format.
Advantages of DBMS
Following are the top 15 advantages are as follows:
1. Data Redundancy
Unlike traditional file-system storage, Data Redundancy in DBMS is nonexistent. Data redundancy happens when the same data is stored unnecessarily in multiple locations. DBMS reduces or eliminates data redundancy by centralizing all data storage, preventing individual user and application duplication.
For e.g: Application A and Application B have the same user MARVEL, and we need to store personal information about the user, such as Name, age, address, Date of Birth, etc. This user also has access to different applications, so in a traditional file-based system, there is a need to maintain a separate file system for each application to store the user’s information. At the same time, in the DBMS approach, there could be just one centralized location where information can be down streamed to the different applications as and when needed.
2. Data Inconsistency
In traditional file system storage, the changes made by one user in one application don’t update the changes in another, given both have the same set of details. While this is not the case with DBMS systems, as there is a single repository of data that is defined once and is accessed by many users, and data are consistent.
3. Data Sharing
Data Sharing is the primary advantage of Database management systems. DBMS system allows users and applications to share Data with multiple applications and users. One or more servers in the network store the data, and a software locking mechanism prevents simultaneous changes to the same set of data by two people. While the file system doesn’t have this capability.
4. Data Searching
Searching and retrieving data is very easy in DBMS systems. In the case of a traditional file-based approach, the need to write separate programs for each search is eliminated. In DBMS, we can write small queries to search for multiple pieces of information at a time from the data from DB servers.
5. Data Security
DBMS systems provide a strong framework to protect data privacy and security. DBMS ensures that only authorized users have access to data, and there is a mechanism to define access privileges.
6. Data Concurrency
One or more servers in the network store data in a DBMS, and a software locking mechanism prevents simultaneous changes to the same data set by two people.
7. Data Integration
Data integration combines the data residing at different locations and presents the user with a unified view of data. DBMS systems allow Data Integration with much feasibility.
8. Data Access
While in the traditional file-based approach, it might take hours to look for precise information needed in some business emergency, DBMS reduces this time to a few seconds. This is a great advantage of DBMS because we can write small queries which will search the Database for you, and it will retrieve the information the fastest way possible due to its inbuilt searching operations.
9. Decision Making
Improved Data Sharing and better-managed data allow businesses to make quality business decisions to promote the organization’s growth.
10. Data Backup and Recovery
This is another advantage of DBMS as it provides a strong framework for Data backup; users are not required to back up their data periodically and manually; DBMS automatically takes care of it. Moreover, in a server crash, DBMS restores the Database to its previous condition.
11. Data Migration
Users frequently access some data, while they access other data less frequently. So, DBMS provides the capability to access the frequently accessed data as quickly as possible.
12. Low Maintenance Cost
Though DBMS systems might be costly at purchase, their maintenance involves minimal cost.
14. Data Loss is almost Eliminated
With DBMS, one can keep information for thousands of years, provided we don’t see doomsday. Data security and very low storage cost (compared to our previous generations) in the current century cut any possibility of Data Loss.
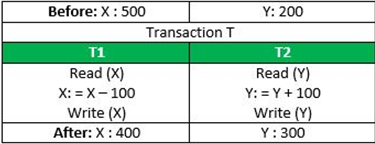
15. Data Atomicity
An atomic transaction is one in which all database actions occur, or none do. DBMS must store a complete transaction in the database. If any transaction is partially completed, then it rolls back them.
For e.g: If we make an online purchase, money is deducted from our account, while if the purchase is somehow failed, no money is deducted, or if it gets deducted, it gets returned within a few days.
Source Link: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/acid-properties-in-dbms/
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the Advantages of DBMS. Here we have discussed the introduction and advantages of DBMS in the real world. You can also look at the following article to learn more –