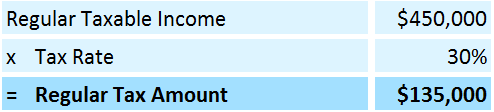What is Alternative Minimum Tax?
Suppose company A generates a lot of money in income but uses deductions and exceptions to reduce their tax liability. This way, they end up paying way less than they should. This harms the government funds and is also unfair to other taxpayers. That is why the US Congress introduced a new tax system, AMT, which works alongside the regular income tax system. It ensures that wealthy individuals and firms at least pay a minimum amount of tax.
The Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) is a special tax system for high-income individuals and businesses that use tax deductions, credits, or exemptions to pay lower taxes on their higher income.
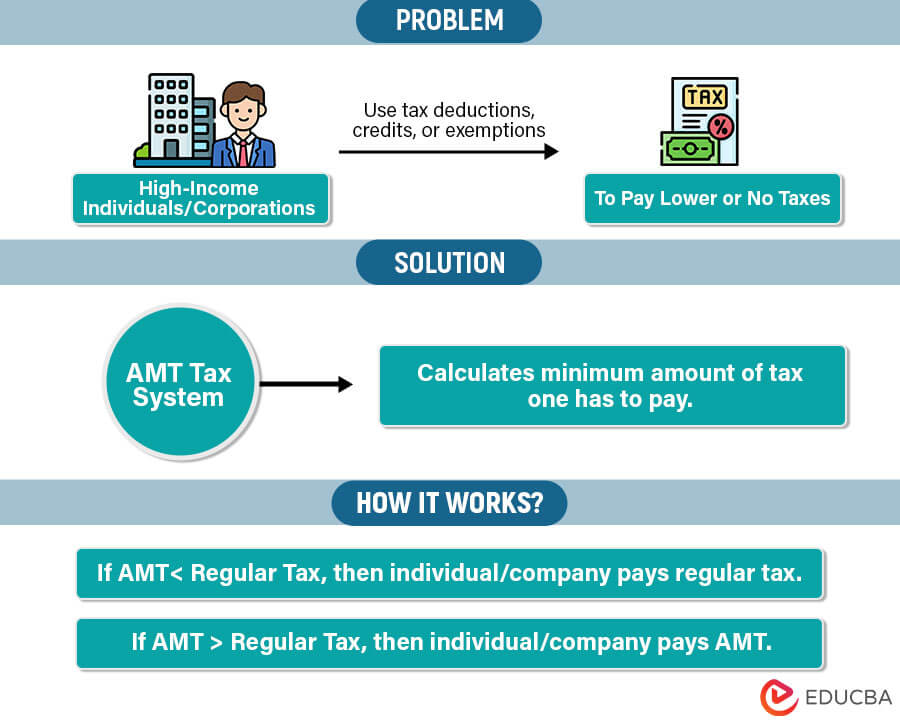
Table of Contents
- What is Alternative Minimum Tax?
- What Triggers It?
- How to Calculate?
- Example
- Who Pays It?
- Credit
- How to Report It?
Alternative Minimum Tax Explained – What Triggers It?
Firstly, taxpayers calculate their regular taxable income by considering deductions and exemptions. Then, based on this income, they find the taxes they have to pay. Once they know their regular taxes, they calculate the alternative minimum tax. For AMT, they add back some deductions and exemptions like itemized deductions and special stock options to the regular taxable income. This way, they find the alternative minimum taxable income. Then, they calculate the tax payable on this new income. After calculating both the regular and the AMT taxes, they must compare them.
If the AMT tax is higher than the regular tax, the taxpayer must pay the higher AMT amount. However, if the regular tax is higher than the AMT tax, the taxpayer pays the regular tax.
How to Calculate Alternative Minimum Tax?
Follow these steps to calculate alternative minimum tax:
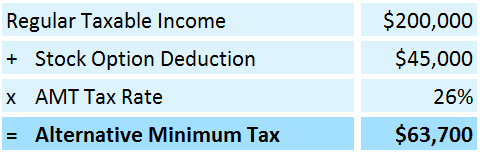
Step 1: Calculate the regular taxable income. For example, suppose your taxable income after deduction is $200,000.
Step 2: List all deductions that are not allowed under AMT. For instance, let’s say you deducted $45,000 under incentive stock options.
Step 3: Find the AMT amount by adding the regular taxable income & deductions and exemptions. As per the example, your AMT amount will be $245,000 ($200,000 + $45,000).
Step 4: Find the applicable AMT tax rate. For instance, the tax rate for your income range is 26%.
Step 5: Calculate the alternative minimum tax. For example, your AMT, as per this example, would be $63,700.
AMT Example
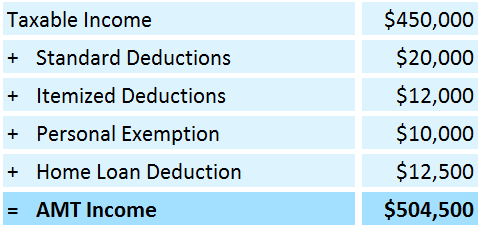
Company ABC wants to determine whether it will be subject to regular taxes or alternative minimum tax (AMT). Its financial details are as follows:
- Taxable Income = $450,000
- Regular Tax Rate = 30%
- Deductions:
- Standard Deductions = $20,000
- Itemized Deductions = $12,000
- Personal Exemption = $10,000
- Home Loan Deduction = $12,500
Solution:
#1: The company’s regular tax amount will be:
#2: Then, let us calculate AMT taxable amount as follows:
#3: As per the AMT income, let us take the AMT tax rate as 28% so that the alternative minimum tax would be:
#4: When we compare both regular tax ($135,000) and AMT tax ($141,260), we can see that AMT taxes are higher. It means that Company ABC will have to pay the alternative minimum taxes of $141,260.
Who Pays Alternative Minimum Tax?
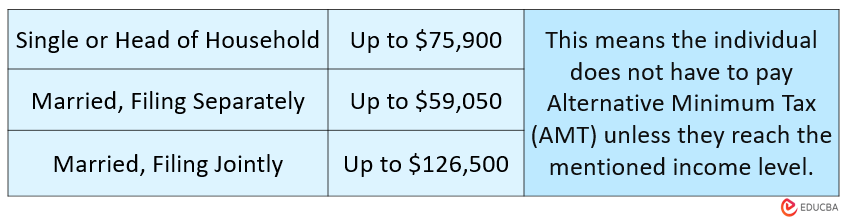
Here is the applicability of AMT for India and the US.
USA
The AMT exemptions are as follows:
Applicability:
The AMT tax system applies to all higher-income individuals, corporations, etc. However, for the exemptions mentioned above, the individual must use the AMT system only if their income exceeds the exemption amount.
Tax Rates: 26% for income up to $175,000 and 28% for income more than $175,000.
India
The AMT exemptions are as follows:
1. These individuals do not have to pay Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) unless their alternative taxable income is more than Rs.20,00,000.
- Individual taxpayers
- Hindu Undivided Family (HUF)
- Association Of Persons (AOP)
- Body Of Individuals (BOI)
- Artificial juridical person
2. Any individual or business that follows the following tax regimes does not need to pay AMT.
- Section 11BAD
- Section 115BAE
- Section 115BAC
3. If the person calculates their taxable income using section 115BAC(1A), they don’t have to pay AMT.
Applicability:
For anyone who does not fall under the exemptions as mentioned earlier, they should pay AMT only if they have claimed deductions under the following tax laws:
- Section 80H to 80RRB (except 80P)
- Section 35AD
- Section 10AA
Tax Rates: 18.5% on adjusted total income, i.e., AMT taxable income.
AMT Credit
Imagine, in 2022, you paid taxes under the AMT system because it was higher than the regular taxes. Now, to prevent taxpayers like you from paying extra taxes in the future after paying AMT, there is another concept known as AMT credit.
AMT credit is a deduction you can claim on your regular taxes for up to the next 15 years from the year you paid AMT (E.g., 2037). It applies to all non-corporate taxpayers.
Calculating AMT Credit
To calculate the AMT credit, we simply subtract the regular tax amount from the AMT taxes you paid in 2022. For instance, if your AMT was $200,000 and regular taxes were $150,000, then your AMT credit would be $50,000 ($200,000 – $150,000).
How and When Can You Claim AMT Credit?
As per the law, if your regular tax is higher than the AMT in any year, you can claim AMT credit that year. You can calculate the amount you can claim by subtracting that year’s AMT from that year’s regular tax.
For example, let’s say your regular tax and AMT in 2023 are $120,000 and $100,000, respectively. So you can claim $20,000 ($120,000 – $100,000) in AMT credit. It means you will only have to pay $100,000 in taxes that year.
Moreover, your new credit amount would be $30,000 ($50,000 – $20,000) due to your claiming the credit. You can claim this value in the upcoming years.
How to Claim AMT Credit?
You can claim the AMT credit by filing IRS Form 8801.
Please note that this is a simplified explanation, and you should consult with a tax professional to determine if you are eligible for the AMT credit and how to claim it.
How to Report AMT?
Reporting Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) involves several steps to ensure accurate calculation and compliance:
Begin by completing your standard tax return as you would under regular circumstances. Then, use Form 6251, provided by the IRS, to calculate your alternative minimum tax (AMT). This form is specifically designed to capture the adjustments necessary for AMT calculations.
Compare the calculated taxes once you complete both your regular tax return and Form 6251. Then, pay the higher of the two calculated taxes.
Recommended Articles
We hope this article on alternative minimum tax (AMT) was informative and helpful. For more similar concepts, visit the following recommendations.