Updated July 21, 2023
What is Amalgamation?
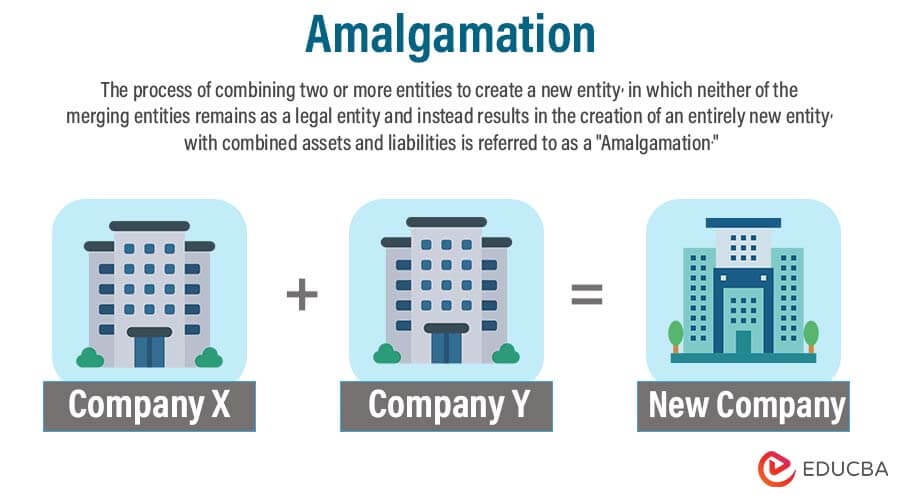
The term “amalgamation” refers to the process of combining two or more entities to form a new entity, in which neither of the two merging entities survives as a legal entity and instead ends up creating an entirely new entity that houses the combined assets and liabilities of all the combining entities.
However, it is to be noted that the amalgamation and merger of the terms are used interchangeably in certain counties. For instance, countries like the United States popularly use mergers or consolidation instead of amalgamation, while in India, amalgamation is still in vogue.
Explanation
Typically, amalgamation occurs when two or more companies are engaged in the same line of business decisions to combine their business existence. Most entities decide to amalgamate to expand their range of services or to diversify their activities. This happens between a stronger transferee company and a weaker transferor company, in which the more worthless company is absorbed, the more substantial company resulting in the formation of an entirely different entity. As it involves the merger of two or more, it results in the formation of a new entity that is larger with a much more robust and more significant customer base.
Objectives of Amalgamation
Some of the main objectives are mentioned below:
- Companies sometimes amalgamate to avail of various benefits under the corporate tax regime.
- This also brings in the advantages of significant economies of scale.
- There are instances where companies enter into amalgamation with close competitors to eliminate competition in the market. However, in some cases, it creates a monopoly in the market, which is not a desirable outcome.
- It offers opportunities for future growth and development – both financial and capital.
- Inherently, it provides synergy benefits, meaning that the companies enjoy benefits from combining operations.
Amalgamation Process
The process can be broken into the following five steps:
- The board of directors of the combining entities finalizes the detailed terms and conditions of the amalgamation agreement.
- Preparation of the scheme of amalgamation, which is then submitted to the respective High Court for approval.
- Obtain the consent of the shareholders of the combining companies, which is submitted to SEBI for approval.
- Form a new company and issue its shares to the shareholders of the transferor company.
- Liquidate the weaker transferor company and transfer all the assets and liabilities to the stronger transferee company.
Examples of Amalgamation
Some of the significant examples have been discussed below:
- Arcelor S.A.: In 2002, French steel maker Usinor, Spanish steel maker Aceralia, and Arbed of Luxembourg amalgamated to form the new company named Arcelor.
- Maruti Suzuki India Limited: In 2002, India’s Maruti Udyog Limited amalgamated with Suzuki Motor Corporation based in Japan to form the new entity – Maruti Suzuki.
- Tata AIG General Insurance Company Limited: In 2001, Tata Group and the American International Group, Inc. (AIG) amalgamated to form the new Tata AIG General entity.
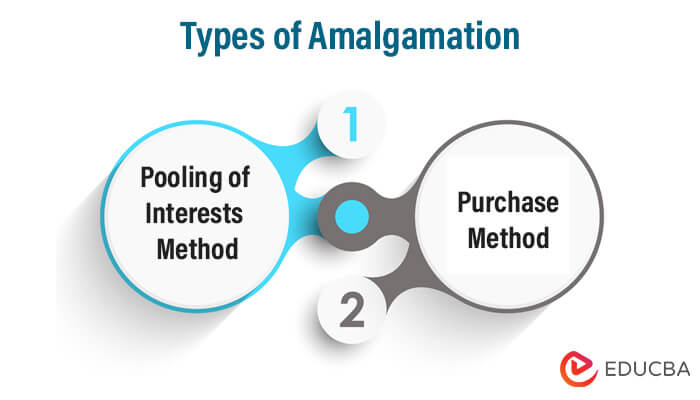
Types of Amalgamation
There are two major types, and they are as follows:
- Pooling of Interests Method: In this accounting method, the transferor entity’s assets and liabilities are transferred to the books of the transferee entity at their current carrying value.
- Purchase Method: In this amalgamation method, the transferee entity records the assets and liabilities of the transferor entity either at their current carrying value or based on their fair value on the date of amalgamation.
Who is Involved in Amalgamation?
The process of amalgamation typically involves the following:
- Investment bankers build various financial models to evaluate and determine the value of the potential transaction.
- Lawyers work with bankers and their corporate clients to select the best legal structure for the transaction.
- Accountants to support the bankers in the evaluation of the transaction value.
Amalgamation vs Merger
Some of the significant differences between amalgamation and merger are as follows:
- In amalgamation, companies combine to form an entirely new entity. In contrast, in a merger, companies combine, either in the formation of a new company or the existence of one of the combined companies is retained.
- The process in most cases consists of three companies, while a merger in most cases involves only two companies.
- Companies of comparable sizes usually get involved in an amalgamation process. In contrast, the size of companies involved in mergers varies significantly as an entity acts as the absorbing company that absorbs the relatively more minor company.
- The asset and liabilities of the combining companies are transferred to the newly formed entity. In contrast, in the case of a merger, the assets and liabilities of the relatively minor entity are consolidated into the absorbing entity.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Below are the advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages
Some of the significant advantages of amalgamation are as follows:
- It helps eliminate competition between companies operating in the same industry.
- Transfer of technical know-how among companies enhances R&D capabilities.
- The companies result in a reduction in operating costs.
- Lower competition results in the stability of prices of goods.
Disadvantages
Some of the significant disadvantages of amalgamation are as follows:
- Amalgamation among substantial players in the industry might result in a monopoly market, which eliminates healthy competition.
- It might result in the reduction of employees.
- Deterioration of capital structure due to the additional debt of one of the entities.
- Loss of goodwill and identity of the existing companies.
Conclusion
So, it can be seen that amalgamation is considered one of the tools companies use to either manipulate market competition or expand their market offerings. It is a mutual advantage shared between the acquired companies and the acquirer.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to amalgamation. Here we discuss what amalgamation is, with explanations, examples, processes, types, advantages, and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –