Updated November 2, 2023

Annual Turnover Meaning
The total money a business earns in a specific year by selling its products or services is known as its annual turnover.
It is a crucial financial metric that helps businesses in financial planning, budgeting, and resource allocation. Companies usually calculate it at the end of either the fiscal or calendar year and disclose it in its financial statements (as regulated by US GAAP and IFRS). However, it only determines the total revenue the firm generated from sales, not the net profit.
Moreover, it does not only refer to a business’s sales but also measures an individual’s or business’s annual trading activity when it comes to investments. For instance, it shows how often a company buys or sells mutual funds or exchange-traded funds within a year. A high annual turnover ratio for investments indicates that the company uses an active investment strategy, while a lower ratio reflects a passive investment approach.
Table of Contents
Key Highlights
- Annual turnover refers to the total revenue a business generates annually by selling goods and services.
- To calculate it, multiply the total units sold by their respective prices.
- It provides insight into a business’s overall financial performance, helping companies to plan their operations, budget, and investments accordingly.
- It is not the same as profit. A business can have high turnover but low profits if its costs and expenses are too high.
Formula
1. For Sales Revenue:
2. For Mutual funds or ETFs:
3. For Service Businesses:
How to Calculate Annual Turnover?
Here are the steps to calculate it for any business:
- Determine the selling cost of the product, e.g., $15 per unit.
- Calculate the total number of units sold annually, e.g., 1000 units.
- Find the result by multiplying product cost and total units sold, e.g., $15,000 ($15×1000).
Excel Examples
The following are some examples of how to calculate annual turnover.
Example #1
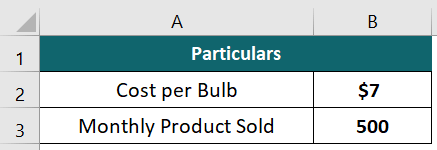
Suppose a retailer sells 500 bulbs monthly at $7 each. Let us calculate the yearly turnover.
Given:
Solution:
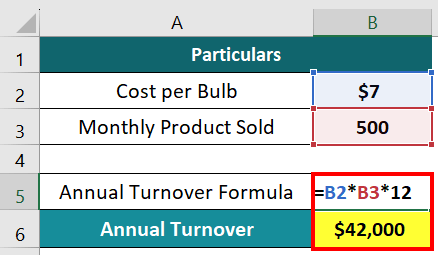
To calculate the desired value for the retailer, we will use the turnover formula and then multiply the result by 12 (for 12 months in a year).
Annual Turnover = Cost per bulb x Monthly product Sold x 12
= $7 x 500 x 12 = $42,000
Thus, the yearly turnover from the bulb’s sales is $42,000.
Example #2
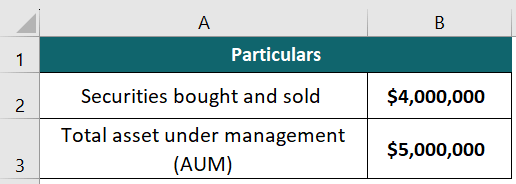
Smart-Funds is a mutual fund that manages assets worth $5,000,000 annually. Suppose in the same year, the firm actively buys and sells stocks and bonds with a total value of $4,000,000. Let us find the turnover value for the firm.
Given:
Solution:
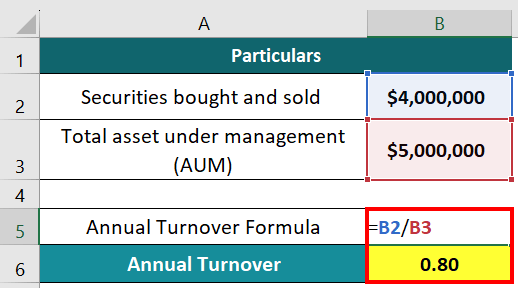
Annual Turnover = Total Securities Bought & Sold / Total Assets Under Management (AUM)
= $4,000,000/$5,000,000 = 0.8 or 80%
Thus, the turnover of Smart-Funds is 80%. This indicates a high level of trading activity, meaning the firm bought and sold securities equivalent to 80% of the total assets it manages.
Example #3
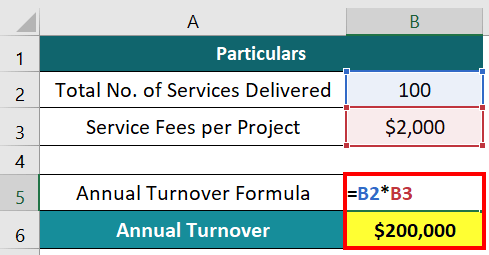
Consider PLK Solutions, a consultancy firm that offers advisory services to other businesses. The firm completed 100 projects for various clients within a year and charged $2,000 for each project. Let us calculate its annual turnover.
Given:
Solution:
Annual Turnover = Total Number of Services Delivered x Service Fees
=100 x $2000 = $200,000
The yearly turnover for PLK Solutions is $200,000.
Importance & Limitations
Following are the various reasons annual turnover is important, as well as a few of its limitations.
Importance
- It indicates a company’s ability to generate profit from sales, reflecting its market value and customer satisfaction.
- Companies can compare their turnover year to year to assess growth or decline in sales revenue.
- It determines whether the company is meeting its target sales goals.
- Investors can use it to determine if their invested funds are managed actively or passively.
Limitations
- As it calculates revenue from sales and not profit, companies with higher turnover can still have low profitability.
- If a company misreports its financial data, the turnover will be incorrect and may not reflect the true performance.
- It doesn’t consider external factors or market conditions that can influence a company’s performance.
- It provides no information on the quality of a company’s assets, which can be crucial for financial health.
Annual Turnover Vs. Profit
Here are the key differences between annual turnover and profit.
| Particulars | Annual Turnover | Profit |
| Definition | Total amount a business earns in a year from its sales. | Amount a company generates after deducting its expenses from its revenue. |
| Calculation | Add the total sales revenue of each month in a year. | Subtract total expenses from total revenue. |
| Example | A clothing store generates an annual turnover of $500,000. | The same clothing store reports a net profit of $50,000 after deducting expenses of $450,000. |
| Significance | It measures the company’s sales and revenue-generating abilities. | It measures the financial performance and viability of a business. |
| Limitations | It does not consider the expenses involved in generating the sales revenue. | It does not consider the sources of revenue. |
Final Thoughts
Annual turnover is a valuable financial metric for evaluating a company’s revenue generation. However, to gain a better understanding of a company’s financial health, it’s necessary to consider other metrics, such as profit, expenses, and asset quality. Investors and stakeholders can make informed financial investment decisions by analyzing the company’s turnover value.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. How can companies increase annual turnover?
Answer: The following are the measures a company can use to increase its annual turnover.
- Introduce new products or services to attract new customers and meet market needs.
- Invest in more resources to increase the product quantity, which in turn will increase sales and boost the turnover.
- Invest in marketing, e-commerce platforms, and digital advertising campaigns to expand online sales.
- Consider competitive pricing and offer discounts to attract a wide range of customers.
- Maintain proper inventory levels to reduce production costs without compromising quality.
Q2. Which ratio is good in terms of the annual turnover ratio?
Answer: A higher turnover ratio is good as it indicates the company is selling its inventory properly, leading to reduced costs and high cash flow. On the other hand, a low ratio suggests improper inventory management. However, the ideal turnover ratio can vary by industry and company size, and the right ratio is a balance between efficient inventory management and profitability.
Recommended Articles
We hope this article on annual turnover is helpful for you. For further guidance on business-related topics, we recommend the following articles: