Updated November 30, 2023
Anti-Dumping Duty Meaning
An anti-dumping duty is an extra tax the importing country imposes on imported goods. The exporting country has to pay the taxes only if they sell their products at a lower price than the price at which the importing country sells similar products.
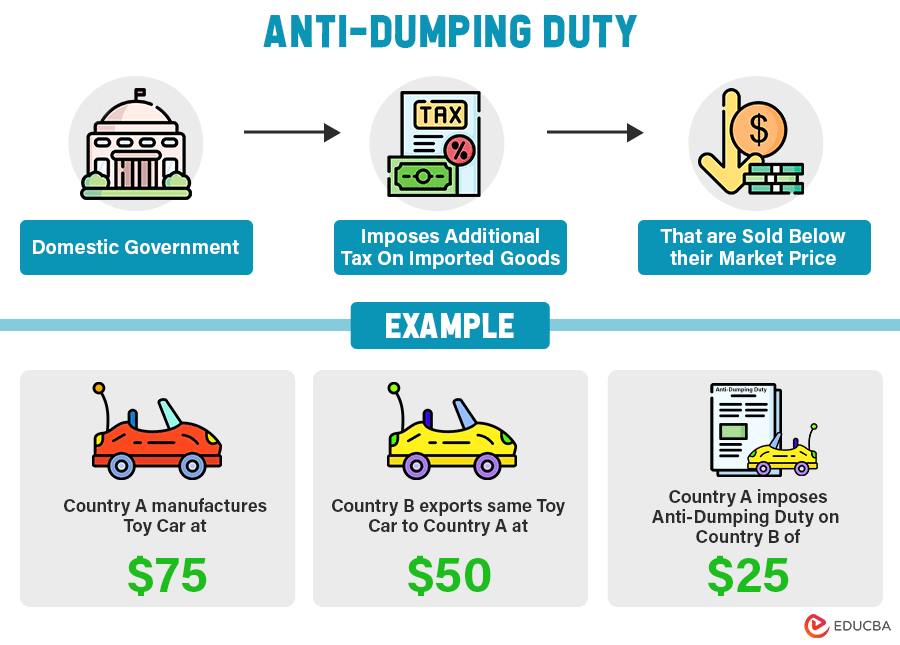
When a company sells products to another country at a lower price than their market price or normal value, it’s called dumping. If the importing country recognizes this as unfair, they can impose “anti-dumping” fees on those imported goods. This measure aims to protect local industries from unfair competition and save jobs. It supports local businesses by making the imported goods prices similar to local products. According to Article VI of the GATT, countries can take anti-dumping measures only when dumping harms the domestic industries of importing countries.
Table of Contents
- Meaning
- Formula
- Examples
- Anti-Dumping Vs. Countervailing Duty
- How to Avoid It?
- Advantages & Disadvantages
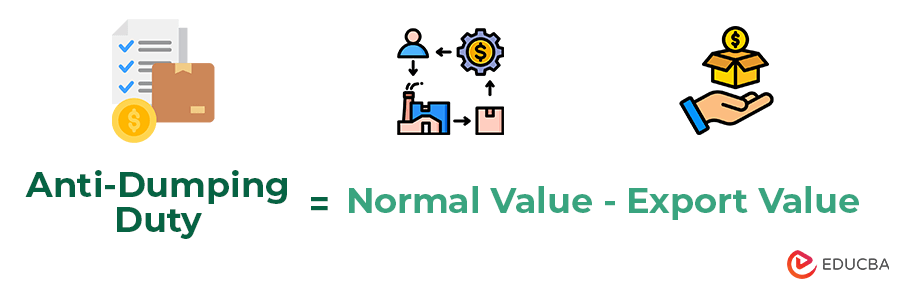
Formula
The calculation of anti-dumping duties is a complex process. It considers the impact on the domestic industry, the fees necessary to rectify the injury caused by dumping, export price, and the normal value.
However, the basic formula to calculate anti-dumping fees is as follows.
Where,
- Normal Value: It is the market price of a product in the exporting country. If the product is unavailable in the domestic market, the Government can use the price of similar products. However, they can also consider the cost of production, including profit margin, to calculate normal value, which represents the product selling price under normal circumstances.
- Export Value: It is the price at which the product is sold in the importing country.
Examples
Let’s understand how to calculate anti-dumping fees with the help of the following examples.
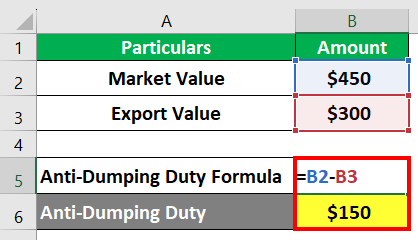
Example #1
Let’s say company A in Europe produces leather shoes. The normal value for a pair of shoes in Europe, including production costs and profit, is $450. However, company B from Germany is exporting and selling similar shoes to company A for $300, which is lower than the normal value. Let’s calculate the anti-dumping price.
Solution:
The formula to calculate anti-dumping duty will be as follows,
Anti-Dumping Duty = Normal Value – Export Value
= $450 – $300= $150
Here, the difference between the normal and export values is $150, so Company A might impose an anti-dumping fee of $150 per shoe to level with its local shoe price.
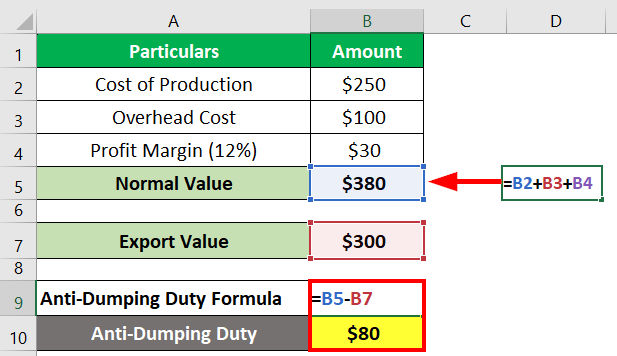
Example #2
Let’s assume that Company B exports or sells shoes to many countries, and Company A is one of them. However, there are no similar products in Company A’s country to compare the shoes’ value. Because Company B exports similar products to other countries, we have the following information about the costs incurred in producing those shoes. Here, we have to calculate the normal value and the anti-dumping fees.
Given:
Cost of Production = $250
Overhead cost =$100
Profit Margin = 12% = $30 (12% x $250)
Solution:
The formula to calculate the normal value of the shoe is as follows.
Normal Value = Cost of Production + Overhead Costs + Profit Margin
= $250 + $100 + $30 = $380
Now,
Anti-Dumping Duty = Normal Value – Export Value
= $380 – $300= $80
Thus, the anti-dumping fee will now be $80.
Difference Between Anti-Dumping Duty Vs. Countervailing Duty
| Particulars | Anti-Dumping Duty | Countervailing |
| Definition | Imposed when prices of imported goods are below their market or normal value. | Imposed when another country’s government provides advantages, like tax subsidies, to the importing country’s manufacturers, so that the exporting country can sell their products at a lower price than local industries. |
| Objective | To neutralize unfair pricing of imported goods below their market value. | To neutralize foreign subsidies on exported goods harming domestic industries. |
| Imposition Process | Imposed by the importing country after investigation and evidence of dumping. | Imposed by the importing country after investigating foreign subsidies. |
| Calculation Based on | The difference between the export price and the fair market value in the importing country. | The amount of subsidy provided to the exported goods. |
How to Avoid it?
The following are some strategies to avoid anti-dumping fees or duties.
- Knowing Products: If you are importing a product from a foreign country, you must verify whether that product falls within the scope of an anti-dumping or countervailing duty order. Ensure that you do not include goods subject to ADD/CVD shipments.
- Fair Pricing: You can ensure that the prices of imported goods align with or are higher than the market value of their country.
- Documentation: Maintain transparent documentation, including the pricing process, production costs, pricing strategies, and import compliance manual covering anti-dumping duties measures.
- Choose a Customs Clearance Broker: You can hire a licensed customs clearance broker to deal with anti-dumping and avoid unexpected legal issues. A licensed broker is well aware of the recent laws and can advise you on forms like “Importer Security Filing” and more.
Advantages & Disadvantages
The following are the advantages and disadvantages of anti-dumping fees or duty.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Protects domestic industries from unfair competition caused by imported goods sold at low prices. | Increased prices of imported goods might lead to higher costs for end consumers. |
| It promotes fair pricing and equal opportunity for local producers. | It can cause a trade war or risk tensions and conflicts in international trade relations. |
Final Thoughts
Many governments worldwide have used anti-dumping duties to safeguard their domestic industries. The United States is among these nations that utilize this measure to protect its steel, paper, and other manufacturing sectors. However, using this measure has been a topic of debate as it can increase consumer prices and adversely affect the international trade economy.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are the types of dumping?
Answer: The types of dumping are as follows:
- Predatory dumping: It involves permanently selling foreign goods at a price lower than the market value. It’s intended to establish a monopoly and eliminate competition in the markets.
- Persistent dumping: It occurs when a country sells its products at a lower price in the foreign country than the local prices for a prolonged period. It happens when there is a constant demand for that product in the foreign market.
- Sporadic dumping: It occurs when goods are occasionally sold at a price below their normal value to remove excess inventory stocks.
- Reverse dumping: It occurs when a company sells products at a higher price in a foreign country and a lower price in their home or local market.
Q2. Why is anti-dumping duty important?
Answer: Anti-dumping duty measures encourage fair pricing practices, meaning selling foreign and domestic goods at the same price in the market. It ensures market stability, prevents disturbance caused by low pricing, and maintains healthy trade relationships between nations.
Q3. Who levies anti-dumping duty in India?
Answer: In India, the “Designated Authority” under the Directorate General of Anti-dumping and Allied Duties (DGAD) of the Ministry of Commerce handles anti-dumping duties, anti subsidies & countervailing measures to ensure fair trade.
Recommended Articles
We hope this article on “Anti-Dumping Duty” was informative and useful to you. We suggest the following articles for additional information.