Updated July 4, 2023
GIS Meaning
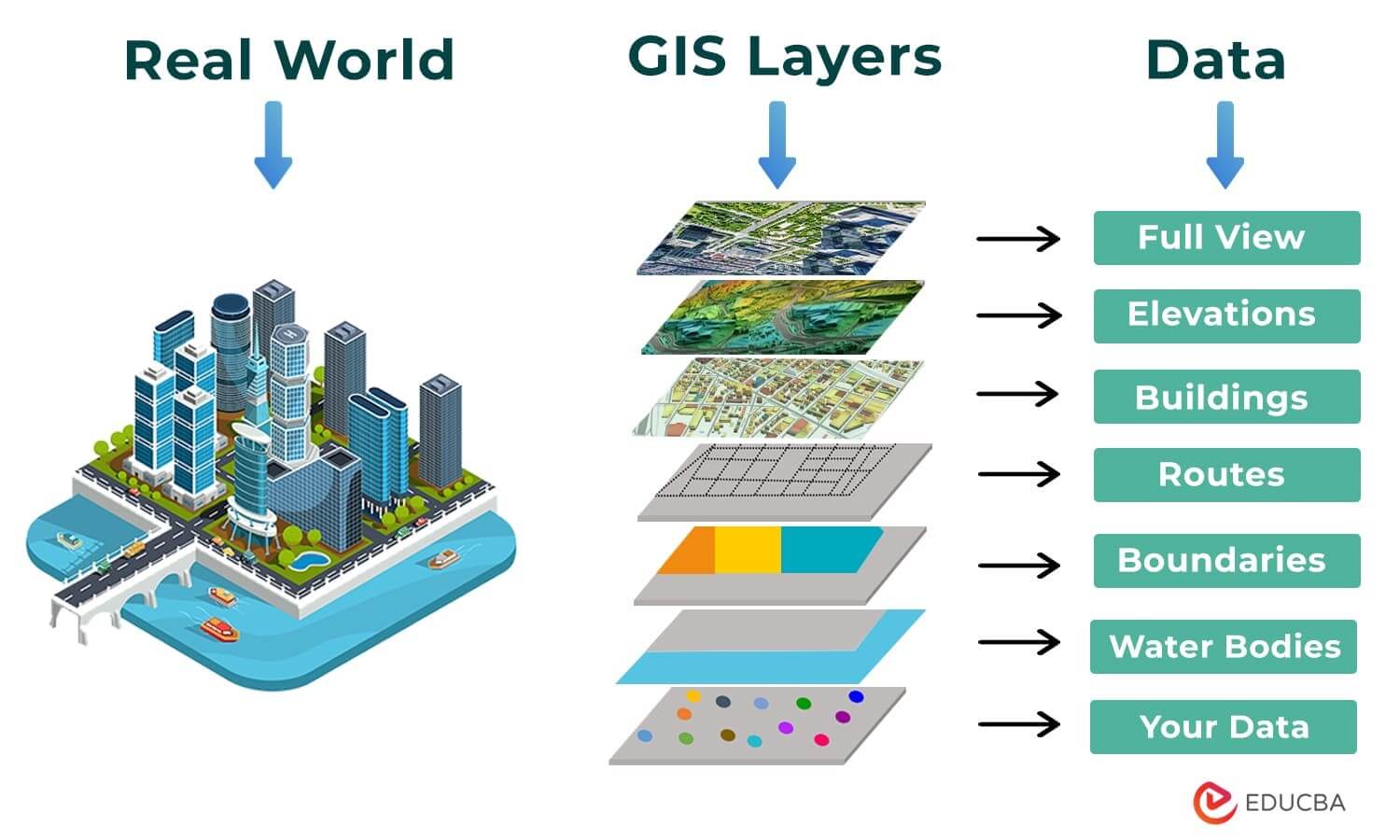
GIS (Geographic Information System) is a technology that collects data to create a special digital map. This map has different layers that show where all living things (humans, water sources, trees) and non-living things (buildings, roads, vehicles) are situated.
GIS technology emerged in the 1960s due to the growing need for managing and analyzing geographic information. It can display data like population density, land use, transportation networks, etc., and shows us how each of these things relates to each other. For example, it can help us find an ideal location to construct an airport, nuclear plant, or army base. Authority bodies can use it to observe their surroundings, analyze how different layers of data interact, and then understand things like city expansion plans or emergency plans.
Table of Contents
What are the Applications of GIS?
Geographic Information Systems can be helpful in various domains. Some of the most common among them are:
1. Agriculture
GIS is a useful tool in agriculture. It uses data about farms, weather, and water resources to help determine the best agricultural practices. Researchers can assist farmers in finding suitable weather conditions for specific crops and locating nearby water sources for irrigation. Governments can utilize GIS to create resource management policies and identify appropriate agricultural lands.
Applications of GIS in Agriculture:
- Drought management: GIS helps manage droughts by identifying areas or lands that are experiencing a lack of water. It helps prevent damage to plant seeds, human efforts, and expensive fertilizers.
- Pest control: It is also used for pest control by predicting attacks from pests like locusts and rodents by analyzing spatial data of specific agricultural lands. It allows the government and farmers to plan how to deal with these pests.
- Land and soil analysis: By studying previous data sets, satellite images, or even analyzing the field directly, field workers can gather information about the land and soil conditions.
- Planning of future food demand: By considering the population’s needs, the government and farmers can plan and produce enough crops to meet the demand.
Useful Tools: ArcGIS and QGIS.
Real Example: Rice Crop Plantation
A software named “Image Processing and Analysis Software (ENVI) program” is a useful tool that helps with the plantation of rice crops worldwide. It uses GIS to create layers of agricultural land and allows farmers to decide what parts are best for rice production.
2. Environment
GIS can monitor how clean the air is in a specific area. It uses data from satellites that monitor air quality to create maps that show places with high pollution. Government can use this map to create policies to improve the air quality in those places.
Applications of GIS in Environment:
- Quality of Life: It helps monitor the air and water quality to analyze real-life habitat conditions.
- Planning: It simplifies the process of selecting the proper location for new infrastructure plans by checking the project’s impact on the environment.
- Resource management: Governments can locate areas with natural resources like water bodies, forests, and agricultural lands.
- Climate change: They can analyze climate data to assess the risks associated with climate change.
Useful Tools: ENVI and GRASS GIS
Real Example: Construction Project Approval
Parivesh is an online system in India where people can submit construction proposals for approval. Using GIS, the software checks if the project can harm the environment, which lets the government decide whether to accept or reject these proposals. Government officials claim that it can reduce the time it takes to approve proposals by 30%.
3. Urban Planning and Transportation
GIS helps city planners and transportation experts combine different types of information like maps, satellite pictures, population statistics, and infrastructure data. It helps them make better decisions when designing cities and transportation systems that are sustainable and good for the environment.
Applications of GIS in Urban Planning and Transportation:
- Growth Forecast: It’s useful in developing models to predict and plan for the future expansion of cities.
- Planning Land Usage: It lets infrastructure experts analyze and allocate land for various purposes like residential, commercial, and industrial use in urban areas.
- Transportation network: Countries can improve transportation systems, including roads, public transit, and pedestrian infrastructure, to ensure smooth movement within cities.
- Infrastructure management: Cities can efficiently manage urban infrastructure, such as bridges and public facilities, to support sustainable development.
Useful Tools: GRASS GIS and Whitebox GAT.
Real Example: Dubai Integrated Rail Master Plan
Dubai’s Roads and Transport Authority (RTA) wanted to make sure that people could travel freely while the country’s population was growing. So they developed the Dubai Integrated Rail Master Plan. This plan uses GIS to manage its transportation system by improving the use of traffic signals as well as checking the flow of traffic. GIS helps RTA collect data like land space, population, traffic zones, etc., to create suitable transport networks.
4. Disaster Management
GIS can keep an eye on places that have a higher chance of natural disasters. So, it can alert the environment-related authorities in case of emergencies, and they can act accordingly. It can help them reach the affected areas in time, respond to victims, develop recovery plans, and take measures to prevent future disasters.
Applications of GIS in Disaster Management:
- Risk-Prone Locations: It helps in identifying risk-prone locations such as hospitals.
- Isolation Centers: It assists in establishing isolation centers near high-risk zones.
- Calamity Records: Government officials can use them to maintain records of past calamities in an area.
- Previous Impact: GIS helps analyze the impact of previous disasters to plan for future contingencies.
Useful Tools: QGIS and Google Maps.
Real Example: HAZUS (Hazards US)
FEMA is a US agency that helps the US government prepare for natural disasters, mainly earthquakes. They have a GIS system called HAZUS that predicts how disasters will affect specific areas. This information helps FEMA create safety plans, such as strengthening buildings and establishing emergency recovery programs in high-risk locations.
5. Business and Marketing
Businesses and companies can use GIS tools to evaluate their competitors as well as analyze the markets. This way, they can create impactful marketing strategies to maintain a strong position in the market. They can also improve production processes to make operations more efficient and effective.
Applications of GIS in Business Management:
- Target Markets: It lets businesses understand customer demographics and behavior patterns to find target locations for new business ventures.
- Choosing Advertising Sites: It can help companies find suitable places for billboards or other advertising mediums.
- Managing Product Distribution: Businesses can select the best transport routes to save money and make their distribution process more efficient.
Useful Tools: CARTO and MapInfo Pro
Real Example: Starbucks
Starbucks uses GIS to find ideal locations for new stores. They use the system to check the income level of people living in high-population areas. They also check if there are any competitors in the area and if opening a store in the area will be profitable or not.
6. Health and Human Services
The government can use GIS to find areas where the population may suffer from specific health conditions. It can help health professionals take the necessary actions in time. GIS can also help coordinate with emergency services during disease outbreaks.
Applications of GIS in Health and Human Services:
- Identifying High-Risk Zones: By mapping the distribution of diseases in a specific location, authorities can find areas at high health risk.
- Educating about Health: GIS can assist the government in raising awareness about health-related issues, promoting healthy behaviors, and achieving other objectives.
- Emergency Response: GIS helps coordinate emergency responses by mapping healthcare facilities, emergency services, evacuation routes, and more.
Useful Tools: MapInfo and Google Earth.
Real Example: Sightsavers
The Sightsavers team in Kenya helps people by treating diseases that can cause blindness. They use GIS to find such houses amidst hundreds of houses. GIS uses data about the town’s population to identify homes in urgent need of care. It also keeps track of previously visited houses, saving time by avoiding revisits to the same families.
7. Tourism
GIS helps the tourism industry find popular tourist spots and use the knowledge for effective marketing. It also promotes sustainable tourism practices to enhance visitor experiences.
Applications of GIS in Tourism:
- Navigation: GIS can create maps with routes, landmarks, and more to make navigation easier.
- Destination Marketing: Tourism authorities can promote tourist destinations by highlighting attractions, accommodations, restaurants, and other points of interest.
- Preserving Cultural Heritage: GIS helps protect important historical landmarks, archaeological sites, and significant places for nations.
Useful Tools: ArcGIS and Google Maps API
Real Example: Connecting with hidden tourist spots
The Bulawayo City Council (BCC) is a local governing body responsible for managing and administrating the city of Bulawayo in Zimbabwe. BCC have started using the GIS system to connect with hidden gems like local hotels and heritage sites to promote tourism, increasing their global earnings. They use GIS maps to find places that are unsanitary and improve them for better visitor experiences.
8. Oil and Gas
GIS uses spatial data to explore the world and find areas with oil and gas resources. It also helps test the benefits of a new project and check if these projects affect the environment in any way.
Applications of GIS in Oil and Gas:
- Finding locations: Organizations can find the best places to drill for oil and gas by looking at the Earth’s features.
- Pipeline Management: GIS is important for planning pipeline routes and ensuring they are leak-free and secure.
- Regulatory Compliance: GIS assists companies in meeting regulations by utilizing data on who owns the land, lease agreements, environmental rules, and zoning restrictions.
Useful Tools: Petrel and GeoGraphix
Real Example: Niti Aayog and ISRO
Niti Aayog and ISRO collaborated to create a system that uses GIS to find all the places in India that have energy (oil and gas) reserves. This system creates a simple map with all the routes for safe and cost-effective transportation of these resources.
9. Astronomy
GIS technology helps astronomers visualize and understand information about space, allowing them to explore the universe. This way, they can discover new things and also learn about its evolution. They can also use it to study the different parts of space and various celestial phenomena.
Applications of GIS in Astronomy:
- Track Celestial Objects: It helps astronomers accurately track and locate celestial objects using celestial coordinate systems.
- Space Mapping: GIS helps create 3D maps and models of celestial bodies in our solar system, allowing us to visualize astronomical data.
- Observation Sites: It makes it easier to select optimal sites for observatories, considering factors like light pollution and atmospheric conditions.
Useful Tools: Starlink and Stellarium
Real Example: Confirming the presence of water on Mars
According to a study by Gaetano Di Achille and Brian Hynek from the University of Colorado at Boulder, Mars had a large ocean covering around one-third of its surface approximately 3.5 billion years ago. They used the GIS mapping system to analyze data from NASA and the European Space Agency. The researchers created a model resembling the surface of Mars and examined features such as deltas, valley networks, and topography.
10. Banking
Banks can use GIS to make better decisions in various areas of their operations. They can study factors like population density, income levels, and existing branches to find the best location for their new branches. They can analyze all this data to customize their products and services to meet the specific needs of their customers. It helps them enhance their customer service.
Applications of GIS in Banking:
- Risk evaluation: Banks can assess risk indicators like property values, environmental risks, etc., to create appropriate lending strategies.
- Fraud detection: They can use GIS to find any unusual patterns in financial transactions that may indicate fraudulent activity.
- Asset Management: GIS helps banks study real estate assets like offices and properties to make informed decisions about acquiring or leasing properties.
Useful Tools: PostGIS and GeoDjango
Real Example: Providing banking services to underbanked areas
United Bank of Africa (UBA) uses GIS to study maps and data of regions with limited access to banking services. By doing so, they understand the challenges people in these areas face regarding financial services. This understanding enables them to provide customized services to areas with poor or no banking services.
11. Crime & Defence
Defense authorities can use GIS to create maps of borders and critical areas. These maps can help in the development of effective security policies and plans. Moreover, by uploading important spatial data into GIS, they can monitor resource allocation for better crime prevention.
Applications of GIS in Crime and Defence:
- Enforcing Policy: It allows law enforcement to examine criminal incidents, understands criminal activity patterns, and find areas where incidents happen frequently.
- Crime Scene Mapping: Officials can use GIS to create maps of crime scenes, helping them investigate cases, gather evidence, track suspects, and reconstruct crime scenes.
- Facility Management: Defense agencies can use GIS to find suitable locations for facilities like military bases, training grounds, and equipment storage.
Useful Tools: IBM i2 and ERDAS.
Real Example: Preventing illegal activities near defense zones
The Centre of Excellence on Satellite & Unmanned Remote Vehicle Initiative (CoE-SURVEI) in India uses GIS-based software. This software uses satellite images to find any suspicious activities in the country’s defense lands. It can also find authorized or unauthorized constructions, helping to prevent illegal activities.
12. Education
GIS technology is useful in education for making subjects like geography and environmental studies easier to understand. It can also help decide where to build schools to provide education to students who don’t have many opportunities. Additionally, GIS helps improve the student experience by making sure resources are allocated properly through careful planning.
Applications of GIS in Education:
- Geographical data: It enhances geography education by enabling students to delve into geographical data, create maps, and comprehend spatial relationships
- Studying the Ecosystem: It aids in the study of ecosystems, tracking habitat changes, and assessing the impact of human activities on the environment.
- Historical mapping: It lets students explore historical maps, analyze social patterns, and gain insights into the evolution of cities and civilizations over time.
- Hazards: It assists students in simulating potential risks and creating effective evacuation plans.
Useful Tools: ArcGIS StoryMaps and OpenStreetMap.
Real Example: Teaching using GIS
Esri UK, an England-Based software company, created a program called “Teach with GIS” to help teachers in their classrooms. This program offers different resources such as lesson plans, videos, interactive maps, and dashboards. These resources can help teachers effectively educate students aged 7 to 18.
Challenges and Limitations of GIS
There are various challenges and limitations of GIS, such as:
- Costs: It can be difficult for some organizations to buy and use, as GIS technology can be very costly.
- Huge Data: GIS deals with a large amount of data, which can take a lot of time and require powerful hardware and efficient software.
- Technical Expertise: Using the GIS system effectively requires specific knowledge and technological expertise.
- Integration Problem: Combining data from many sources can be challenging and time-consuming.
- Privacy and Security: A major concern is keeping private and confidential data safe from unauthorized access.
Final Thoughts
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is a useful technology that helps us analyze and understand information easily. In the future, it can change how we visualize data by creating 3D maps using virtual reality. It also has the potential to change how we use technology to solve real-world problems, as we may be able to combine it with AI, machine learning, and other high-level technologies.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is GIS full form?
Answer: GIS stands for Geographic Information System, meaning it is a system that gathers and uses information connected to geography, space, or specific locations.
Q2. What are the components of GIS?
Answer: There are three key components of the Geographic Information System:
- Hardware: It consists of physical devices like servers, GPS devices, scanners, etc., for converting physical maps or documents into digital files.
- Software: These are specific computer programs to manage data, analyze patterns, and visualize spatial maps.
- Data: It is real-world information, including maps, satellite images, elevation models, data about populations or roads, etc.
Q3. Name the types of spatial data in GIS.
Answer: The primary types of data in geographic information systems are:
- Vector data: Vector data includes points, lines, and polygons. Points indicate specific map locations, lines represent features like roads or rivers, and polygons define areas like districts or borders.
- Raster data: Raster data consists of grids or boxes that create visual images of geographical elements like elevations or aerial views.
- Tabular data: Tabular data is organized in columns and rows, providing relevant information associated with different locations on the map.
Q4. Can GIS be integrated with other softwares?
Answer: Yes, it is possible to integrate GIS with other software systems. We can link it with databases, spreadsheets, and other programs in order to exchange data and carry out spatial analysis within those systems.
Q5. How does GIS benefit decision-making?
Answer: GIS provides spatial analysis to assist in decision-making. It helps users analyze data, identify patterns, and understand relationships in a geographical context. The spatial perspective supports informed decision-making and the evaluation of alternative options.
Recommended Articles
This article lists all the main applications of GIS. It covers the usage of GIS in different fields and the tools available, including real-world examples for each application. If you’re interested in delving deeper, here are a few more articles you can read to expand your knowledge: