Updated July 14, 2023

Definition of Asset-Based Lending
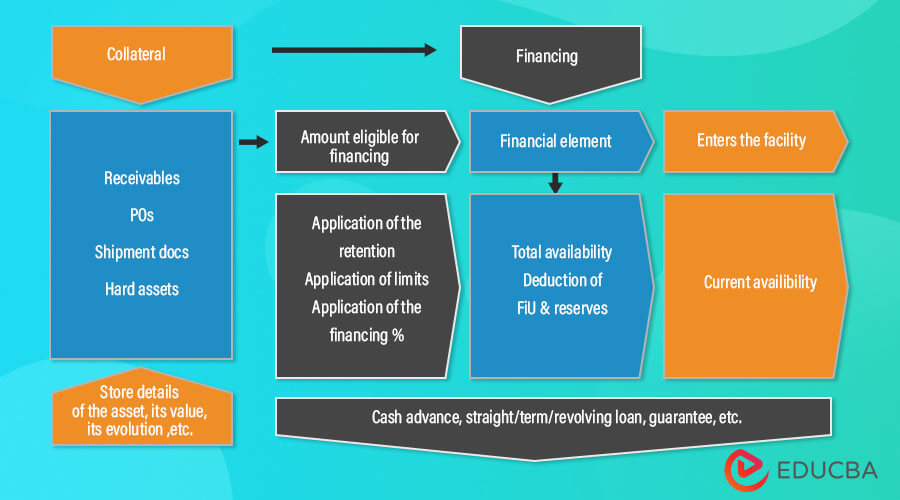
Asset-based lending, or asset-based financing, is a form of business lending where the loan agreement is backed by collateral. This collateral can include equipment, inventory, accounts receivable, or properties owned by the borrower.
Features of Asset-Based Lending
- Lending occurs by using the borrower’s assets, referred to as collateral, as security.
- Liquid collaterals are preferable to illiquid assets, such as equipment.
- It usually attracts lower interest rates, as in the event of a default, the lender can recover the outstanding amount by liquidating the borrower’s assets.
- While large enterprises use it for financing strategic projects, small to medium business owners use it to cover short-term cash flow demands.
How Does Asset-Based Lending Work?
Asset-based lending, due to its reliance on collateral provided by the borrower, is generally regarded as a less risky form of lending in comparison to unsecured lending. Consequently, it tends to attract a reduced interest rate. Further, the liquidity of the collateral also influences the interest rate – the higher the liquidity of the asset, the lower the interest rate charged.
There is a term called loan-to-value ratio or LTV ratio. The LTV ratio states how much loan the borrower can avail against the asset offered as collateral. The lenders are usually willing to offer a higher LTV ratio for more liquid assets. Mathematically, the LTV ratio is represented as:
Example
Let us assume that XYZ Inc. has applied for an asset-based loan worth $50,000 to cover short-term business requirements. The lender has offered to provide the loan as per the following LTV ratios:
- Machinery & equipment: 40%
- Inventory: 60%
- Marketable securities: 80%
The borrower has the option to offer any one of the following as the collateral for the loan:
- Machinery & equipment valued at $100,000
- Inventory valued at $90,000
- Marketable securities valued at $60,000
Determine which asset the borrower should offer to secure the loan.
The maximum loan amount that each asset can secure can be calculated based on the LTV ratio and asset value as,
Machinery & Equipment is calculated as
Machinery & Equipment = 40% * $100,000 = $40,000
- Inventory = 60% * $90,000 = $54,000
- Marketable securities = 80% * $60,000 = $48,000
Therefore, XYZ Inc. should use inventory to secure the asset-based loan of $50,000.
Usage of Asset-Based Lending
Companies use it for various purposes. Some of the major usages are as follows:
- It is usually used by companies only after they have exhausted all other options for raising capital for project financing, such as mergers & acquisitions, debt purchasing, etc.
- Various lenders use asset-based lending for curating structured and leveraged financial services.
- Many lenders also offer short-term loans against luxury assets, which may include luxury watches, vintage cars, wine collections, etc.
Difference Between Factoring and Asset Based Lending
Factoring of account receivables and asset-based lending is often confused with being similar. But some factors differentiate factoring from asset-based lending:
- In factoring, the company sells its receivables at a discount. On the other hand, in asset-based lending, the company borrows money against its receivables as collateral.
- Factoring is a frequently utilized financing option for small or start-up companies that do not meet the criteria for traditional bank loans. In contrast, larger and more established companies primarily employ asset-based lending.
- There are no monthly payments in factoring, and factoring of invoices takes place with each sales transaction. On the other hand, asset-based lending involves scheduled loan payments.
- The factoring fee is expressed as a percentage of the invoice value. On the other hand, asset-based lending is priced as an annual percentage rate charged on the loan amount.
- The approval process for factoring is faster as it only involves reviewing the credit ratings of the borrower and its debtors, which only takes a few days. On the other hand, asset-based lending requires the valuation of the collaterals, which takes several days or even weeks.
Advantages
- A business can utilize available assets to access additional business funding.
- Offered at a lower interest rate than an unsecured loan.
- It requires very little documentation as the asset value of the collateral remains the main criterion.
- It provides a cushion during times of financial stress when no other fundraising options are available.
Disadvantages
- All assets don’t qualify for collateral. Lenders usually prefer assets with low depreciation and high liquidity.
- There is a risk of losing valuable assets as the lender has the right to confiscate the asset pledged as collateral and sell it to recover the loan amount if the borrower defaults.
Key Takeaways
- Asset-based lending offers mutual benefits to both borrowers and lenders. By leveraging their assets as collateral, borrowers can secure loans at more favorable interest rates. Simultaneously, lenders have the added assurance of having collateral that can be liquidated in the event of borrower default. This arrangement creates a mutually advantageous situation for both parties involved.
- A borrower resorts to it only when other routes have been exhausted. The lender of an asset-based loan is only in the asset value of the collateral and is less concerned with the borrower’s cash flow in the past, profitability, etc.
- People usually confuse factoring as both use receivables as collateral. However, a borrower sells its receivables at a discount in the case of factoring, whereas a borrower borrows money against its receivables as collateral in the case of asset-based lending.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Asset Based Lending. Here we discuss the introduction and how asset-based lending works. Along with advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –