Updated July 4, 2023
Definition of Asset Retirement Obligation
Asset Retirement Obligation is a legal and accounting requirement in which a company must make provisions for the retirement of a tangible long-lived asset to bring the asset back to its original condition after the business uses the asset.
Companies in several industries have to get an asset back to its original state after the asset is taken out of service. This may involve industries like oil drilling, power plants, mining, and many others industries. It also applies to the properties taken on lease, where the properties must be returned to their original shape. After the use, the asset may have to detoxicate like in nuclear plants, or machinery must be removed like in oil drills. The expected expenses to be incurred on such restoration are taken care of by Asset Retirement Obligations.
How does Asset Retirement Obligation Work?
The restoration expenses are incurred at the end of the useful life of the asset, but a discounted liability is created on the balance sheet along with a corresponding asset right after the construction or initiation of the project or when the fair value of the restoration can be determined. This liability is then gradually increased at a fixed rate to match the expected obligation at the end of the asset’s life.
The recognition and accounting of asset retirement obligations are published by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) in the United States and by the International Financial Reporting Standards in the rest of the world. These institutions provide detailed guidelines on the treatment of Asset Retirement Obligations.
For the right liability measurement, the company must determine the liability’s fair value when it incurs it. If the fair value of the liability cannot be determined, the liability should be recognized at a later date when the fair value becomes available. Prompt recognition of the liability can benefit stakeholders as they are high-value liabilities, and their recognition shows a better picture of the liabilities.
Accounting for Asset Retirement Obligation
Accounting for Asset Retirement obligation requires recognizing the present value of the expected retirement expenses to be recognized as a liability and fixed asset. The interest rate used for discounting is the risk-free rate adjusted for the effect of the entity’s credit standing. The liability is then increased yearly at the risk-free rate and measured at subsequent periods for the change in expected cost. The increase in liability is recognized as an accretion expense on the income statement and is calculated by multiplying the liability amount by the risk-free rate. Any change in the expected expense is adjusted to the liability balance after every revision. The asset recognized on the balance sheet is depreciated, and the expense is recorded on the income statement.
Differences between Us GAAP and IFRS
|
Basis of Comparison |
US GAAP |
IFRS |
| Initial Measurement of Asset Retirement Obligation (ARO) Liability | The fair value is recognized as a liability as and when it becomes available. The discount rate used is the risk-free rate | The liability is measured as the best estimate of the expenditure to settle the obligation discounted at the pre-tax rate |
| Asset Recognition from ARO | ARO amount is added to fixed assets at the time of the estimate | Generally included in property plant and equipment. Recognized in inventory if incurred during a period when the property was used to produce an inventory |
| Subsequent Measurements | Revision is done from time to time to either the amount or timing of cash flows. Upward and downward revisions are discounted using current and original risk-free rates. | Checked for change on every balance sheet date. Both the expected cash flow and the discount rate can be changed, and adjusted liability can be shown based on new assumptions. |
Example of Asset Retirement Obligation (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example better to understand the Calculation of Asset Retirement Obligation calculation.
Example #1
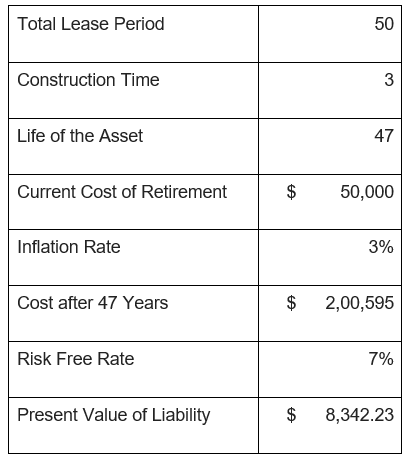
Assume a power company builds a power plant at a site with a 50-year lease. The asset takes three years to be built and has to be necessarily retired at the end of 47 years after it was built. The cost of dismantling the equipment, detoxification of the site, and cleaning the site is $50,000 in today’s dollars. Because retirement has to be done after 47 years, so this cost will definitely be higher then. Consider that the retirement cost will increase at the rate of inflation. Assuming an inflation rate of 3%, the cost of retirement at the end of 47 years will be $200,595. Assuming a risk-free rate of 7%, this obligation’s present value is $8.342. See the illustration below for details.
Cost After 47 years is calculated as
- = $50,000 * (1 + 3% ) 47
- = $200595
For Detail, the Calculation refers to the above template.
Advantages and Disadvantages
The advantages and Disadvantages of Asset Retirement Obligation are:
Advantages
- As asset retirement obligation will be a real and big expense, it makes sense to provide for it as soon as the liability’s fair value can be determined.
- Asset retirement obligations help pre-plan the restoration of the property to its original state.
- Asset retirement obligations show the fairness and accuracy of the financial statements.
Disadvantages
- Asset retirement obligations are based on estimates and are prone to judgment errors.
- The liability changes frequently.
- The rates used while recognizing the liability may change going forward and may change the liability.
- Asset retirement obligations do not cover work done after other events that affect the assets like natural calamities (earthquakes, floods, etc.)
Conclusion
Asset Retirement Obligations are essential from an accounting point of view. Had it not been for the regulatory requirement, businesses would have used their discretion in disclosing these costs, which could have hurt the stakeholders badly. These costs could cause a severe drain on the company’s cash balances and may adversely impact the business. Accounting for the obligation well in advance gives the business the time to plan and set aside resources for the event.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Asset Retirement Obligation. Here we discuss the Example and How does Asset Retirement Obligation Work? along with Advantages and Disadvantages. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –