Table of Contents
Meaning of Assets
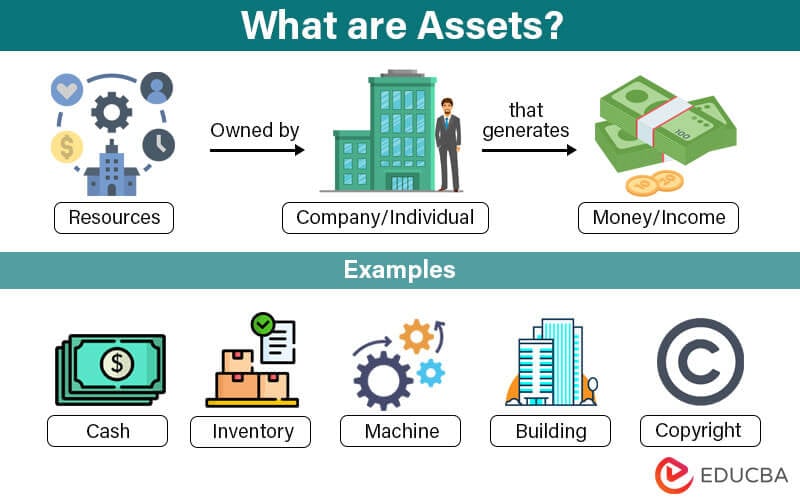
Assets are resources like inventory, property, stocks, etc., that a company/individual owns, which help them make money by either using or selling the item.
For example, a small retail business has resources like inventory and a store. The inventory is items the company sells to make money, while the store is where the company sells the items. It makes both these assets a medium to earn money for the business.
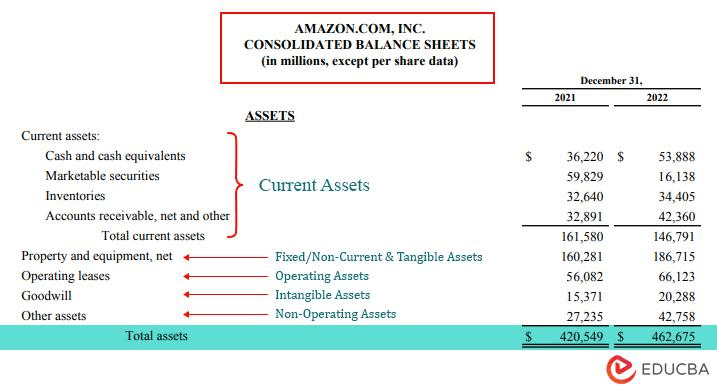
Assets are important for a company as they show how much the business is worth. Companies present the value of these resources on their balance sheet. For example, as we can see below, Amazon’s assets for the year 2022 were $462,675 million.
(Source: Amazon Annual Report 2022)
Types of Assets
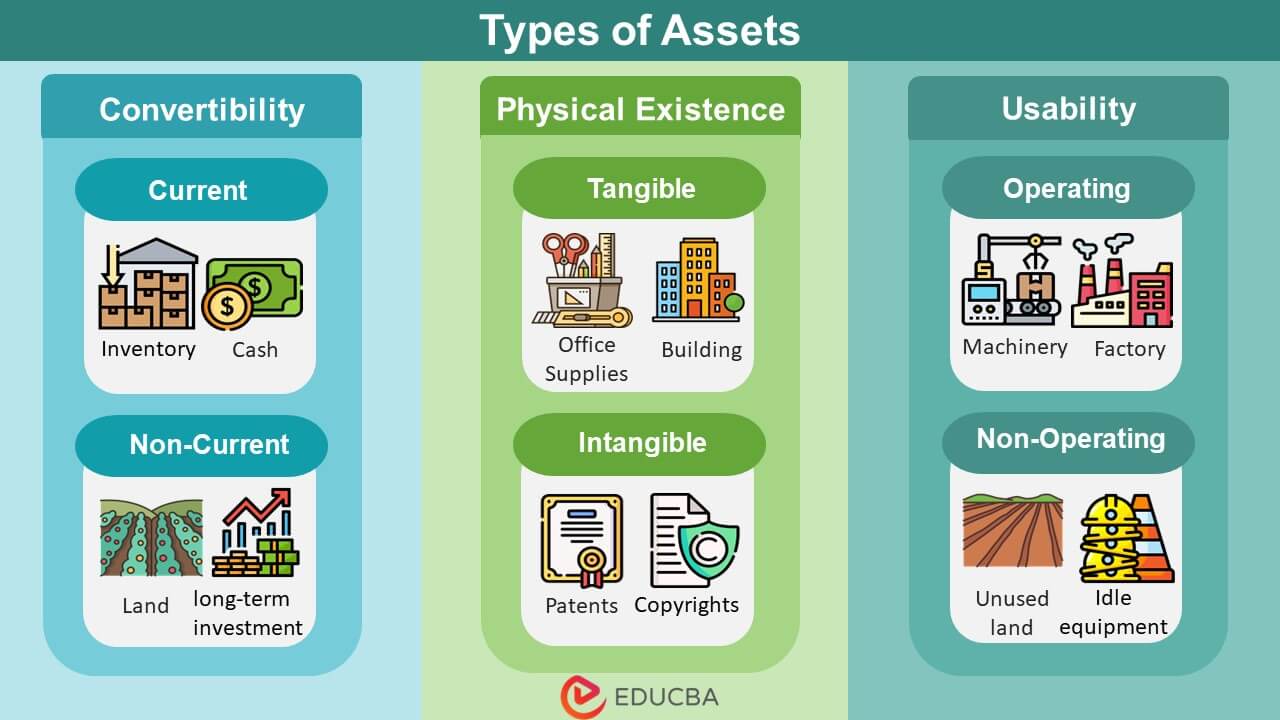
Asset classification is usually based on convertibility, physical existence, and usability.
1. Convertibility
a) Current
These assets have high liquidity, which means we can easily convert them into cash, mostly within 12 months or less.
Examples: Cash in hand, cash at the bank, treasury bills, inventory, and accounts receivables.
b) Fixed or Non-Current
These are assets that companies own for a long time, which are difficult to convert into cash quickly.
Examples: Land, Machinery, Factories, etc.
2. Physical Existence
a) Tangible
It is an asset a person can see or touch. The value of these is usually the same as its historical cost, i.e., the item’s purchase price.
Examples: Office supplies, tools, land, building, etc.
b) Intangible
It is an asset you can’t see or touch, which gets its value from the privileges it gives (licenses), its intellectual value (copyright), etc.
Examples: Patents, royalties, goodwill, trademarks, or copyrights.
3. Usage
a) Operating
A business’s operating assets are resources to carry out its main operations and generate revenue. They are directly involved in the company’s day-to-day functioning and contribute to its primary business activities.
Examples: Machinery, factory building, copyrights, etc.
b) Non-operating
Businesses own non-operating assets that are not directly related to their main business operations. Instead, they are usually held for investment purposes or as a secondary function.
Examples: Unallocated cash, unused land & buildings, Idle equipment, etc.
How to Calculate Assets? (Formula, Examples, and Template)
In this section, we will discuss two different formulas to calculate assets. We have included the Excel template with all the calculations and formulas for easy understanding.
Formula #1
Here,
- Current Assets are cash, inventory, accounts receivable, etc., which you can use within a year.
- Non-Current Assets are non-convertible, like property, plant, equipment, long-term investments, etc., which last more than a year.
Formula #2
Here,
- Liabilities are a company’s total debts and obligations to external parties.
- Stockholders equity represents the total shares owned by the shareholders in the company.
Example #1
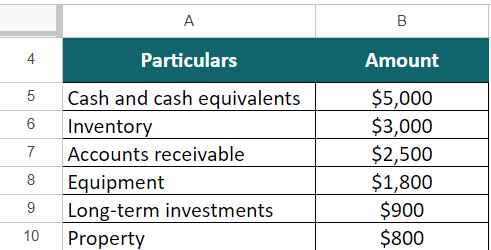
Marcus owns a retail business in the USA and wants to calculate its assets worth. Below are the details Marcus provided.
Given,
Solution:
We first need to find both current and non-current assets.
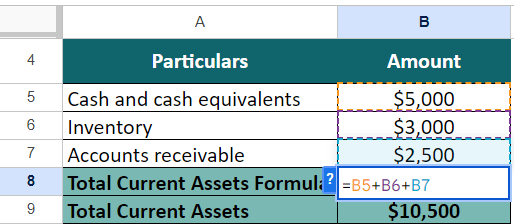
Step 1: Find Current Assets
Current assets = Cash and cash equivalents + Inventory + Accounts receivable
= $5,000 + $3,000 + $2,500
= $10,500
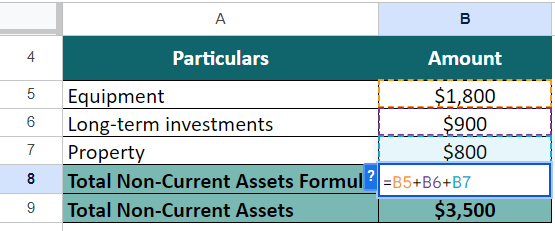
Step 2: Find Non-Current Assets
Non-current assets = Equipment + Long-term investments + Property
= + $1,800 + $900 + $800
= $3,500
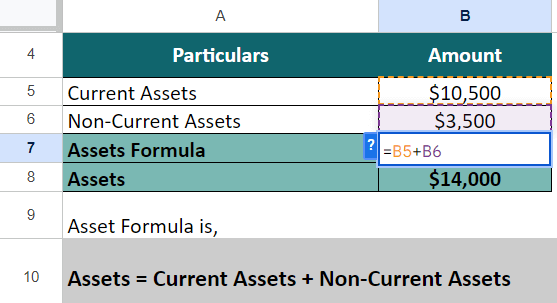
Step 3: Calculate Total Assets
Total assets = Current Assets + Non-Current Assets
= $10,500 + $3,500 = $14,000
Thus, Marcus’ business has assets worth $14,000, which he can use for his business as and when needed.
Example#2
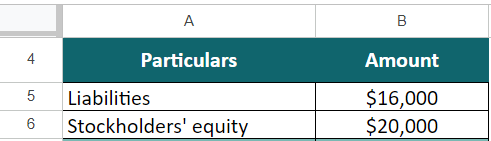
Wayne Enterprises is preparing its financial reports and wants to know its assets. They have liabilities worth $16,000 and stockholders’ equity worth $20,000. Calculate the total assets for Wayne Enterprises.
Given,
Solution:
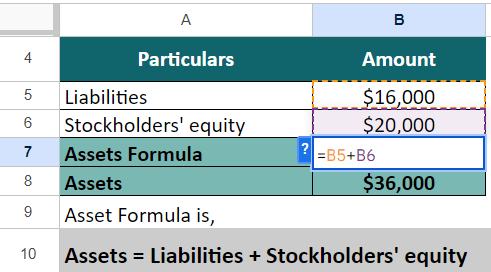
We have both the variables, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity, so let’s implement the below formula:
Total Assets = Liabilities + Stockholders’ equity
= $16,000 + $20,000
= $36,000
Thus, Wayne Enterprises has assets worth $36,000. The company may use these to grow its business or evaluate its worth.
Asset Valuation Methods
Asset valuation helps investors decide if they should buy/sell their shares, apply for loans or insurance, how to calculate taxes accurately, etc. The valuation differs based on the type of asset and valuation methods.
Below are the various valuation methods for the three common types of assets that companies and individuals own.
Tangible Asset Valuation Method
It helps businesses know the worth of their assets and their contribution to overall net worth. Following are some methods to calculate the value of these assets.
- Cost Method/Historical Cost Method: The cost method values assets at their original purchase cost. It does not consider any changes in the item’s value over time, focusing only on the initial acquisition cost for accounting purposes.
- Market Value/Current Value Method: The market value method bases the value on the item’s current market price. It takes into account the most up-to-date market value, reflecting changes in supply and demand or other factors that affect its worth.
- Value-based/Cash inflow Method: The value-based method determines an asset’s value by estimating its future cash inflows or income potential. It focuses on the asset’s ability to generate cash in the future, considering factors like revenue, profits, or rental income.
Intangible Asset Valuation Method
This valuation helps businesses and individuals understand the worth of intangible assets, making informed decisions about investments, acquisitions, and licensing agreements. Here are a few methods used to value an Intangible asset:
- Market Value Method: It helps find the current worth of a resource, considering its current market value, and is common for valuing publicly traded securities like stocks and bonds.
- Income Method: It helps find the item’s value by estimating its present value based on the income it is expected to generate in the future.
- Cost Method: It calculates the value of creating the intangible asset in today’s market and allocates the calculated cost as the value.
Stock Valuation Method
It determines how much a company’s stock is priced fairly or represents a good deal, helping investors decide whether it is a good buy. Below are the various methods companies use to value stocks:
- Discounted Dividend Model: It determines the stock value by looking at how much the company pays in dividends now (current dividend) and how fast those dividends will grow in the future (constant growth rate).
- Discounted Cash Flow Model: It calculates the value of the stock by looking at the expected cash flows (money) it can make in the future.
- Comparable Valuation: It compares ratios like the PE, PB, or price-to-cash-flow ratios of similar industry companies to determine if the stock is overvalued or undervalued.
Asset Ratios
In this section, we will be discussing the different asset ratios, their formulas, and their uses:
| Ratio | Formula | Use |
| Debt-to-Asset | Total Debt / Total Assets | Measures the portion of a company’s assets that the company has financed using debt. |
| Equity-to-Asset | Total Equity / Total Assets | Shows the proportion of a company’s assets financed by shareholders’ equity. |
| Return on Assets (ROA) | Net Income / Total Assets | Measures how effectively a company is using its assets to generate profit. |
| Asset Turnover | Sales / Total Assets | Measures the efficiency of a company to use its assets to generate sales. |
| Fixed Asset Turnover | Sales / Fixed Assets | Measures how efficiently a company uses only its fixed assets, such as property, plant, and equipment, to generate sales. |
| Working Capital | Current Assets / Current Liabilities | Measures a company’s ability if the company will be able to repay the short-term debt using only its assets. |
| Quick Ratio | (Current Assets – Inventory) / Current Liabilities | It is similar to the working capital ratio except that it does not consider inventory as it is not easily convertible into cash. |
| Asset-to-Equity | Total Assets / Total Equity | It Helps investors, analysts, and businesses determine a company’s financial leverage and risk. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are hidden assets?
Answer: Hidden assets, also called invisible or intangible assets, are valuable resources that do not have a physical or tangible form. However, they hold economic worth and play a significant role in determining the value of a company. Companies typically don’t disclose these assets in their financial statements unless they have a specific value.
Examples: Human capital, customer loyalty, brand value, etc.
Q2. Why is asset classification important?
Asset classification is helpful for many financial aspects. It makes financial reporting easier, helps businesses identify risks related to the object, correctly calculate taxes, follow regulatory rules, and more.
Q3. What are the assets that cannot depreciate?
Answer: Below is a list of assets that can’t depreciate, which means they don’t lose their value over time:
- Land: Land does not depreciate or lose value over time but rather appreciates over time due to its long useful life.
- Intangible resources with unlimited useful life: Certain intangible assets, such as goodwill, don’t have a useful life and can’t depreciate.
- Fine art and collectibles: Objects such as paintings, sculptures, antiques, and rare collectibles are generally not subject to depreciation as their value increases over time.
- Natural resources: Resources such as oil wells, mineral deposits, and timber stands can’t depreciate as they can give value even after a long time.
Q4. Define goodwill assets.
Answer: Goodwill assets represent the reputation, customer loyalty, brand recognition, and overall positive image of the company in the market. They don’t have a physical form but contribute equally to the company’s success, market standing, and ability to attract customers and investors.
Recommended Articles
This article was a guide to assets where we discussed its meaning, types, and formulas. We also mentioned Excel examples with very simplified calculations. You may also read other related articles mentioned below: