Updated July 18, 2023

Definition of Assets Example
Assets of the business are the economic resources owned by the business entities, and the use of such assets will result in the inflow of economic benefits, usually cash inflow, to the organization where these resources can be tangible as well as intangible in nature and are recorded in company’s balance sheet.
Explanation
Assets are the business-owned resources that are utilized by the business for earning profits. They are very important for any business enterprise for its growth and survival. These resources are valued in monetary terms and are reported in the company’s balance sheet at historical cost. The assets of the business are bifurcated as fixed assets (that are used for more than a year and provide economic benefits for several years) such as plant & machinery, office equipment, land & building, etc., and current assets (that are expected to be converted into cash within a one year period) such as inventory, trade receivables, cash & cash equivalents.
Examples of Assets
The various example of assets are as follows:
- Land &Building: Every business has an office workplace that requires an office building. If the building is on rent, then it is not an asset of the company, but if it is owned, then such Land &Building is the fixed asset for that business and is recorded at its construction cost/ purchase cost.
- Plant & Machinery: Plant & Machinery are the equipment, installations, or fittings used to run the business. For example, there is a business of manufacturing chairs. The owner purchased a cutting machine worth $3500. This cutting machine is required to conduct day-to-day activities while making chairs and has life for more than a year. So this is a fixed asset of the company.
- Office Furniture: office furniture includes furniture and fixtures such as tables, chairs, computer desks, electrical fittings, sofas, etc., that are fitted into the business for use in the office.
- Trade Receivables: Trade receivables are the current assets of the business. Trade receivables include business debtors, bills receivables, etc. Trade receivables are created when the sales are made to the customers on a credit basis. During credit sales, the customers have yet to pay the money against the goods they purchased from the business within the credit period. So, until customers pay off all the dues, they are recorded as Debtors in the books of accounts under the head trade receivables.
- Inventory: Inventory consists of the goods available to the company at a specific time. These goods can be finished goods ready for sale, in the process of completion (work in progress), or the raw materials used for making the finished goods. Inventories are the current assets.
- Cash & Cash Equivalent: The most liquid asset of the company is Cash and cash equivalents, which include cash balance, bank balance, checks received from debtors but not deposited in banks, coins, and currencies, etc., that are easily convertible into real cash within a period of 3 months or less from the time of reporting it in the books of accounts of the business.
- Patents: Patents are the exclusive property rights granted by the government authorities to the inventors of new designs, logos, or any other article so that others cannot use their invention to profit.
- Investments: The investments of the business are the company’s assets as they yield a return to the business in the near future. For example, ABC incorporation purchases equity shares worth $5,000 of PQR Inc. that will give dividends to the ABC incorporation. So this purchase of equity shares will be reported as investments in the books of ABC incorporation.
- Goodwill: Goodwill is an intangible asset and is recorded in the books of accounts when it is purchased i.e. if one company takes over another company by paying consideration for the same, then in such case, the goodwill arises when the cost of purchase is greater than the fair market value of the assets, and the difference of both is the amount of goodwill. Then such goodwill is reported in the company’s books which acquires the other business as purchased goodwill.
- Prepaid Expenses: the business’s expenses that are paid in advance by the business are also reported as the business’s assets. For example, a company named Web Inc. that deals in mobile phones paid an insurance premium of $500 on October 1st,2018 month. The financial year followed by Web Inc. is from April to March. At the time of initial payment i.e., on October 1, 2018, the company will pass the following entries:
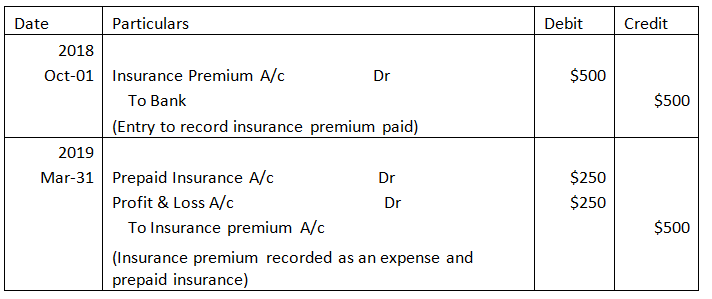
Since only half of the expense is related to the current financial year, it is booked as an expense in the current year. Half of the amount is paid for next year, so it is recorded as a prepaid expense at the year-end, and it will be shown on the balance sheet as a current asset.
- Security Deposits: Security deposits can be any deposit, such as deposits with landlords, government authorities, etc. For example, deposits with the electricity department are recorded as security deposits in the business’s financial accounts.
Conclusion
Thus, Assets are the resources owned by the business enterprises that will provide financial benefits in the future. Some assets are long-term, such as all the fixed assets like buildings, furniture, plant and & machinery, etc., that are used for more than one year and will provide an inflow of cash for several years. In contrast, some are short terms, such as trade receivables and stocks, etc., which will only provide benefits in the short run.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Assets Example. Here we also discuss the definition and example of assets and a detailed explanation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –



