Updated October 31, 2023
Difference Between Assets vs Liabilities
In Assets vs. Liabilities, assets are resources, like real estate or machinery, that we use to make money or run the business. However, liability is the money we owe others, like student loans or debt payments.
Assets refer to resources owned by an individual, entity, or country that possess economic value and can provide future benefits. Depending on the time frame of the benefit, Assets can be further classified into two groups i.e. Current Assets and Non-current Assets. Assets that provide benefits or income within one year are termed current assets, while assets that provide benefits to an organization over a long period or for more than one year are referred to as non-current assets or fixed assets. For example, Cash, Bills receivables, or Bank Overdrafts can be used for tenure within one year; hence, they are Current Assets. In contrast, land, buildings, machinery, and goodwill have a lifespan of several years, and their benefits can be utilized for more than one year.
Hence, they fall in the category of Fixed assets. Again, ‘Goodwill’, ‘ Patents’, or ‘Copyrights’ are not physical assets that cannot be seen or touched. Thus, they come under the group of ‘Intangible Assets’. On the other hand, Liabilities are the obligations, Debts, or losses a firm/individual bears during a Business. Liabilities can also be classified based on Current and non-current depending on the time frame. Obligations that typically extend beyond one year are referred to as non-current liabilities. Examples of non-current liabilities include long-term borrowings, shareholders’ reserves, deferred tax liabilities, and long-term provisions. In contrast, when a firm has outstanding short-term financial obligations, they are categorized as current liabilities. Examples of current liabilities include short-term borrowings, trade payables, other current liabilities, and short-term provisions.
The format of Assets and Liabilities: The following example shows the format of a Balance sheet where all the Assets and Liabilities are shown.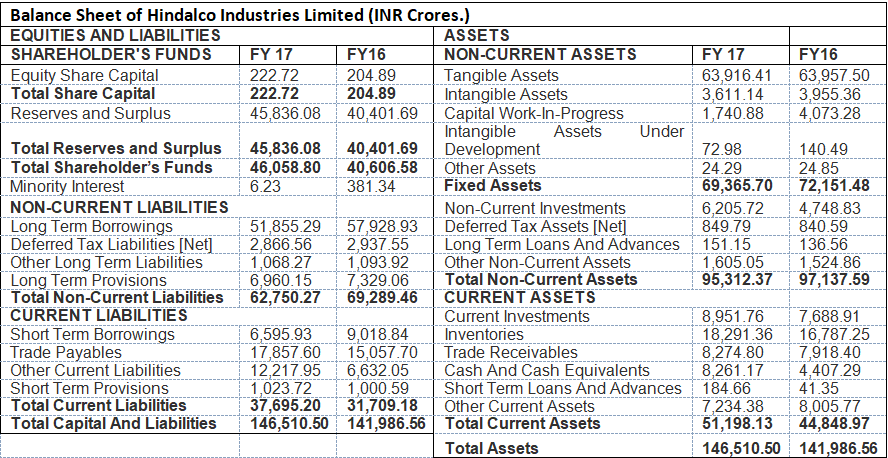
Head To Head Comparison Between Assets vs Liabilities (Infographics)
Below is the top 6 difference between Assets vs Liabilities

Key Differences Between Assets vs Liabilities
There is a major difference between Assets and Liabilities, which are demonstrated as follows:
- In Financial Accounting, liabilities represent the obligation to settle the debt or the borrowed amount in the future. On the other hand, Assets are the resources responsible for future Revenues for the company.
- Assets are associated with depreciation, meaning that assets are considered “depreciable objects” as they undergo a deduction of a certain percentage of their total value each year. Liabilities are ‘Non-depreciable.
- A balance sheet displays assets on the right side and liabilities on the left side of the format.
- Assets can be classified into two types, viz. Current Assets (Short term or less than one year) and Non-Current Assets (More than one year). Liabilities, on the other hand, can be classified as Current liability and non-current liability.
- Heavy Borrowing and fewer Shares holder’s equity are considered unhealthy for the company. On the other hand, lower borrowing and higher reserves indicate profitability and efficient usage of Assets and operational efficiency. On the other hand, one should utilize assets properly to ensure that the book value of fixed assets remains the same, and the goodwill (intangible assets) should grow, indicating operational efficiency.
Assets vs Liabilities Comparison Table
Below is the comparison Table between Assets vs Liabilities
| The Basis of Comparison | Assets | Liabilities |
| Related to | Resources owned by a Firm/Individual/Company etc. | Debt or amount owned by a Firm/Individual/Company etc. |
| Meaning |
A company owns assets, which are properties or valued objects that generate future income. Efficient utilization of these assets is typically necessary to ensure the possibility of future income. |
Borrowings or any obligations to repayment by the Company are termed Liabilities. It may be short-term or long-term, depending upon the nature of Liability. |
| Depreciation | All Fixed (non-current) assets have depreciation associated with them. Regular usage of machines, land, and buildings primarily causes erosion, leading to depreciation. We assume that the efficiency level of fixed assets erodes over time, leading to a decrease in their financial valuation each year. | Depreciation can only be applied to Assets as they generate income. Hence, Liabilities are Non-depreciable. |
| Calculations | Assets = Liabilities+ Owner’s Equity | Liabilities = Assets – Owner’s Equity. |
| Types | Non-Current Assets and Current Assets | Non-Current Liabilities and Current-liabilities |
| Interest Costs and Interest Income |
Interest income is generated through assets. For example, when an entity lends money to third parties, business organizations, firms, etc., there is an expectation of generating income in the form of interest. This interest is charged on the predetermined loan amount. |
When a firm, organization, or company takes a loan, there is an obligation to pay interest on the borrowed amount. The interest is predetermined by both parties involved. Thus, ‘Interest Costs’ is an expense for the Firm/Company. |
Assets vs Liabilities – Final Thoughts
The Assets and Liabilities are part of the balance sheet, which reflects the Company’s financial position in a certain period. The health of the Business becomes visible while doing the cross-sectional analysis of the Company.
Recommended Articles
This has guided the top 6 differences between Assets vs Liabilities. Here, we take the difference between Assets and Liabilities with examples, infographics, and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


