Introduction to Automation in Manufacturing
Modern manufacturing depends heavily on digital tools and advanced technologies. Automation in manufacturing boosts productivity, reduces waste, and ensures consistent product quality. Tools like production planning software and machine monitoring systems help manufacturers run efficiently. Machine learning, predictive maintenance, and real-time data tracking allow businesses to make smart decisions and reduce downtime. At the same time, training workers for automation has become essential to keep things running smoothly.
Key Digital Tools Driving Automation in Manufacturing
Software solutions are the driving force behind modern manufacturing operations. Two key digital tools significantly improve production efficiency and quality control.
#1. Production Planning Software
Production planning software is central to manufacturing automation because it enables faster, data-driven decisions. The software adjusts based on real-time supply chain updates, helping manufacturers quickly adapt to customer needs.
Key Factors
- Material availability
- Workforce resources
- Equipment capacity
- Delivery schedules
- Forecasted demand
The benefits of production planning software
- 30% to 50% shorter production cycles
- Optimized material and labor usage
- Lower inventory costs
- Smoother production on the plant floor
For Example
Opcenter helps businesses efficiently schedule materials, people, and machines to improve profits and customer service. It supports:
- Long-term resource planning
- Mid-term capacity adjustments
- Short-term shift scheduling
Manufacturing Execution Systems (MES)
MES also supports predictive maintenance by collecting production data without human input. This helps companies:
- Set accurate standards
- Improve work quotas
- Streamline scheduling
#2. Machine Monitoring Systems
Machine monitoring turns raw equipment data into useful information. These systems cut downtime by 30% to 50% and boost throughput by 10% to 30%. Labor productivity rises by 15% to 30%.
Core Functions
- Machine availability
- Production flow
- Output quality
- Equipment health
Real-Time Monitoring & Performance Tracking
Software like MachineMetrics analyzes this data instantly. It helps identify problems early and monitors:
- Equipment usage
- Efficiency levels
- Part performance
- Work order status
Predictive Maintenance Support
Machine monitoring also supports predictive maintenance by alerting teams before breakdowns occur. This reduces:
- Repair costs
- Sudden downtime
- Equipment damage
- Maintenance delays
Integration & System Connectivity
Integration with cloud systems enhances the benefits of automation. Platforms like Ignition allow:
- Remote machine access
- Role-based dashboards
- Maintenance scheduling
- Asset tracking
These digital solutions form the backbone of manufacturing process digitalization, driving better efficiency and visibility on the shop floor.
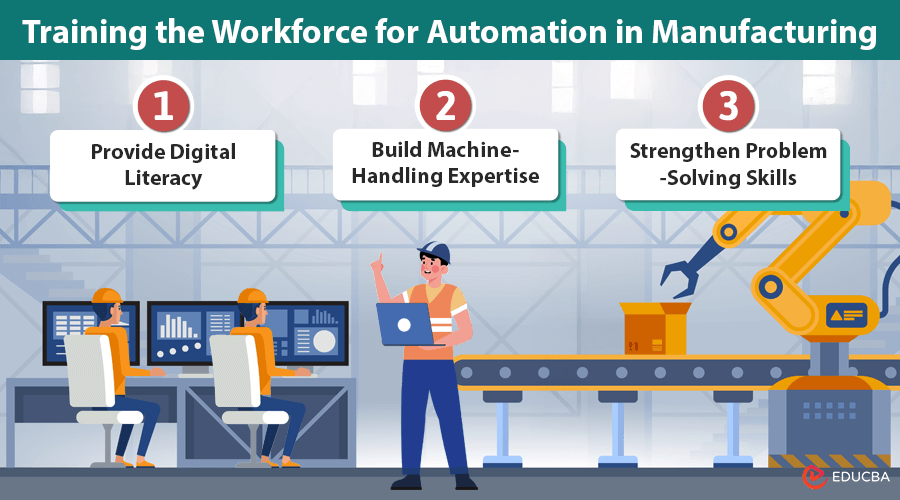
Training the Workforce for Automation in Manufacturing
Companies must train workers to use digital tools and technologies to benefit fully from automation in manufacturing. Key training areas include digital literacy, machine handling, and problem-solving.
#1. Provide Digital Literacy
Many factory workers need help with basic tech skills. Studies show that 38% are not ready for digital tasks. Training programs focus on:
- Using computers and apps
- Understanding digital dashboards
- Online communication
- Cybersecurity basics
Some companies collaborate with educational institutions. For instance, FANUC trains students in robotics and automation. Online learning makes it easier for workers to train while staying on the job.
#2. Build Machine-Handling Expertise
With automation in manufacturing, workers supervise machines more than they perform manual tasks. Training includes:
- Machine setup and controls
- Following safety rules
- Handling basic repairs
- Using data for quality checks
Hands-on practice and VR/AR tools give workers real-world experience. Programs like Rockwell Automation’s Academy of Advanced Manufacturing offer certifications in automation skills.
#3. Strengthen Problem-Solving Skills
Workers must be able to solve problems and make quick decisions. Training programs focus on:
- Finding root causes using tools like the “5 Whys”
- Making decisions with data
- Team-based problem solving
- Continuous improvement
Simulations using machine learning help workers gain confidence in handling real-time issues. Well-trained staff lead to:
- Smoother operations
- Fewer defects
- More innovation
- Higher job satisfaction
Clear communication on how automation in manufacturing supports jobs can reduce fear and resistance to change.
Measuring Automation Success Metrics in Manufacturing
Success metrics show how automation affects manufacturing operations. Precise measurements enable manufacturers to track their progress and spot areas for improvement.
#1. Production Speed Metrics
Production speed is a core indicator of automation success. These metrics reflect how well systems are performing across different areas of the manufacturing process.
Throughput Calculations
Throughput measures the units produced per unit of time (hour or day). The formula is:
This metric highlights how automation in manufacturing improves output volume across machines, lines, and entire plants.
Cycle Time Analysis
Cycle time is the total duration required to produce a product, calculated as:
Manufacturers use cycle time data to:
- Assess overall process efficiency
- Identify inefficiencies at detailed levels
- Monitor improvements after automation
Production Volume Documentation
Recording production volume provides detailed logs of items manufactured over time. A key related metric is Total Effective Equipment Performance (TEEP), which evaluates equipment effectiveness during both operational and non-operational periods by analyzing:
- Equipment availability
- Performance rates
- Quality standards
- Maintenance periods
#2. Error Rate Tracking
Even though automated systems are generally more reliable than manual ones, errors can still occur. Proper tracking ensures quick detection and resolution.
First Time Through (FTT)
FTT measures the percentage of products that meet quality standards without rework. For example, a 90% FTT rate means 9 out of 10 products pass inspection the first time. This metric provides a direct view of how automation in manufacturing improves quality.
Defect Density
Defect density compares defective items against total production. Regular monitoring helps:
- Identify quality issues early
- Guide corrective actions
- Support continuous process improvements
Scrap Rate Analysis
Scrap rate tracks unusable units in production:
Lower scrap rates indicate fewer manufacturing defects. Automation helps maintain process control and minimize product loss.
#3. Cost Savings Calculation
Understanding financial impact is critical when evaluating automation initiatives. Several cost-related metrics help manufacturers assess return on investment (ROI).
Return on Investment (ROI)
ROI evaluates the financial benefit of automation against its setup and operational costs. Key factors include:
- Lower labor expenses
- Improved productivity
- Enhanced quality control
- Reduced material waste
Labor Cost Analysis
Automation reduces manual work, resulting in direct labor savings.
- Operating Human Efficiency (OHE) averages 80%
- Operating Equipment Efficiency (OEE) reaches 90%
This comparison highlights the productivity boost offered by automated systems.
Energy Consumption per Unit
Automated systems help reduce energy costs and expose hidden inefficiencies that manual processes may overlook.
Manufacturing Cost Per Unit
This metric combines all expenses involved in production:
Automation reduces this cost by enabling:
- Faster production cycles
- Fewer quality issues
- Lower waste levels
- Reduced labor requirements
Capacity Utilization
This metric shows how effectively a team uses the equipment. Automated systems often deliver:
- 20% to 110% faster production compared to manual processes
- Higher reliability in quality control
- Improved detection rates over human inspectors, who range between 60% and 90% accuracy
Final Thoughts
Automation in manufacturing is transforming the industry by improving productivity, reducing costs, and increasing quality. Manufacturers can run smarter operations with tools like production planning software and machine monitoring systems. But technology alone is not enough—employee training is just as important. Companies that invest in both digital tools and workforce development will lead the future of manufacturing with greater innovation, cost savings, and global competitiveness.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide to automation in manufacturing helps you streamline your production processes and improve efficiency. Check out these recommended articles for insights and strategies to enhance manufacturing operations.
