Updated July 25, 2023
Definition of Average Collection Period
Average collection period (ACP), also known as the ‘ratio of days to sales outstanding,’ is the average number of days the company takes to collect its payment after it makes a credit sale. The financial ratio gives an indication of the firm’s liquidity by providing an average number of days required to convert receivables into cash.
ACP is calculated using the average balance receivable divided by the average credit sales a company makes daily.
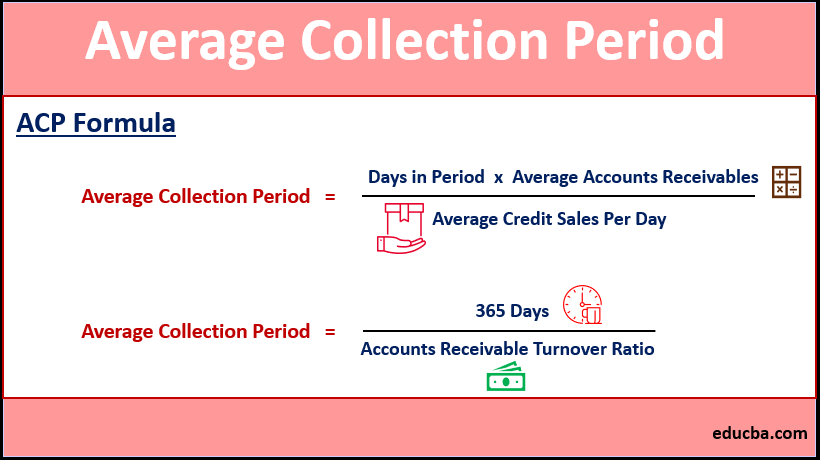
Formula of ACP
or,
There is also another formula to calculate the Average Collection Period
Where,
Examples of Average Collection Period (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of the Average Collection Period in a better manner.
Example #1
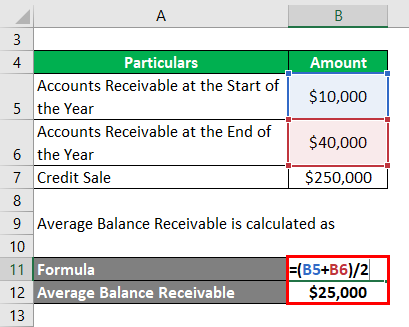
A company XYZ dealing in home décor has accounts receivable of $10,000 at the start of the year and $40,000 at the end of the year. The credit sale made for this amount is $250,000.
Solution:
Calculation of Average Balance Receivable:
- Average Balance Receivable = ($10,000 + $40,000) / 2
- Average Balance Receivable = $25,000
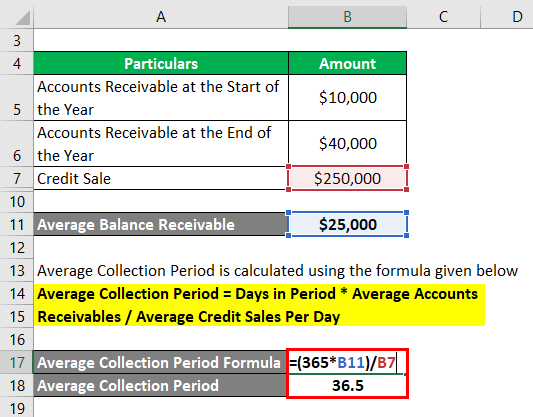
The formula to calculate ACP is as below:
Average Collection Period = Days in Period * Average Accounts Receivables / Average Credit Sales Per Day
- ACP = (365 * $25,000) / $250,000
- ACP = 36.5 days
This indicates that, on average, the company receives the amount after 36.5 days.
Example #2
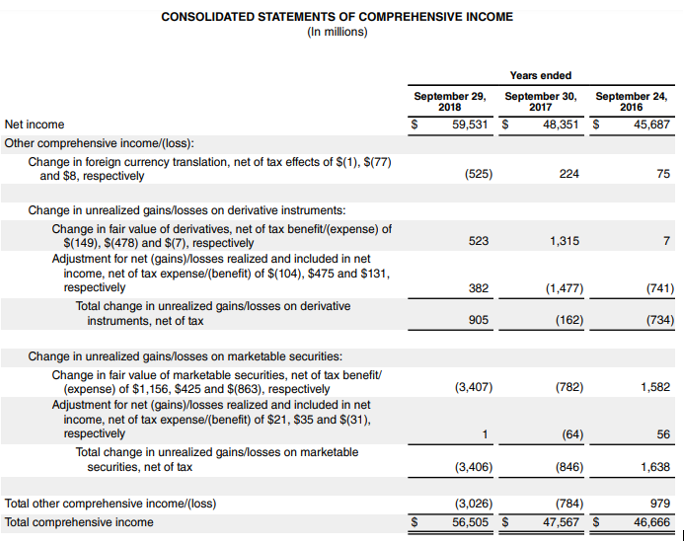
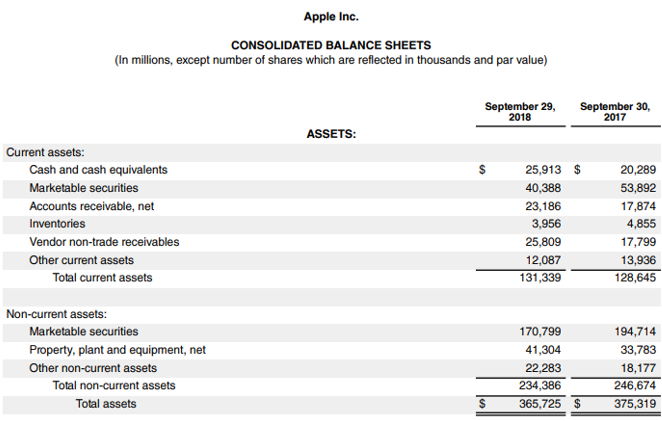
Consider the balance sheet and Income statement for Apple Inc.
Source Link: Apple Inc. Balance Sheet
Solution:
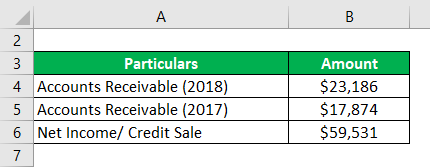
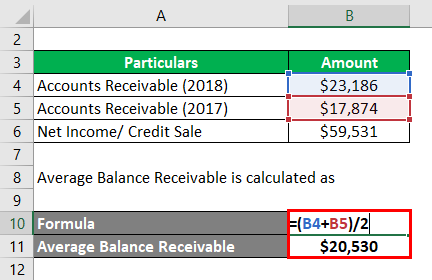
Calculation of Average Net Receivables for Apple Inc:
- Average Net Receivables = ($23,186 + $17,874) / 2
- Average Net Receivables = $20,530
Since the Company has not provided the number of credit sales, we can consider the net sales to calculate the collection period days.
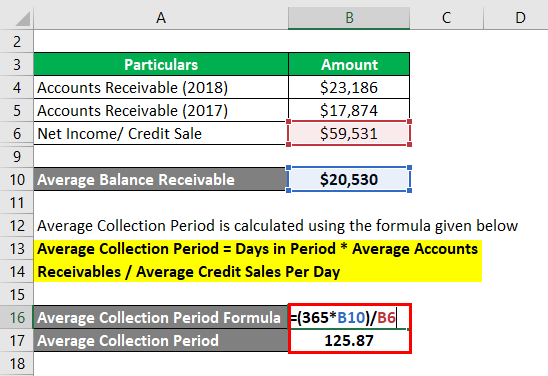
The formula to calculate ACP is as below:
Average Collection Period = Days in Period * Average Accounts Receivables / Average Credit Sales Per Day
- ACP = (365 * $20,530) / $59,531
- ACP = 125.87 days
Advantages of the Average Collection Period
The advantages of the ACP are as follows:
- The company can make a decision on how to pay its short-term debt by lowering its ACP.
- It can keep track of its ability to collect the amount of receivables.
- The company can decide how to collect the balance by knowing its ACP.
- By comparing the ACP of previous years, a company can predict whether its ability to collect receivables is increasing i.e. days taken to collect receivables are decreasing. If the ACP is increasing, it indicates that the company is losing its liquidity.
Increasing the Average Collection Period
An increase in the ACP would indicate any of the following conditions:
- Management has decided to loosen the credit conditions to customers to boost sales, or a certain category of customers is given a longer credit window- This could be true in case a small business house is trying to sell to a bigger business whose credit quality is good. The small business believes that it will not default.
- Liquidity issues in the economy could cause customers to delay payments.
- Either the company’s collections department has reduced its effort, or there is a staff shortage. In both cases, the collection for the period is less, increasing the number of outstanding receivables.
Decreasing the Average Collection Period
ACP can be decreased using the following practices:
- Management may decrease the length of credit or tweak its credit policy to reduce credit sales. This may lower the risk for the company.
- By offering discounts on early receivables than agreed and putting penalties on late receivables.
- Increase communication levels with customers and run credit checks on them.
- Increasing collection efforts by employing more employees and using technology. Incentivizing employees towards reducing the ACP.
Commonly, it is considered that the ACP aimed by a company is one-third times lower than the expressed credit terms.
Important Points to Note on Average Collection Period
- If a company is selling its products/ services seasonally, calculating the ACP for the whole year would not be just, and the formula for ACP should be adjusted likewise.
- A higher ACP indicates that the company needs to take steps to collect receivables. Otherwise, there is a risk of receivables turning into bad debt.
Conclusion
The average Collection Period is when a company collects the amount from the goods and services sold on credit. Tracking ACP helps the company to check its finances and make a credit policy. The ACP is also indicative of the Company’s short-term liquidity.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Average Collection Period. Here we discuss calculating the it with practical examples. We also provide a downloadable Excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –