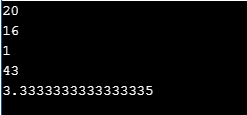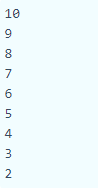Updated March 18, 2023
Introduction to Back End Programming Languages
The 2 major kinds of web development take place; frontend and backend development. The front end majorly deals with the UI part of coding where the web servers interact with the users, and backend development is the coding that happens at the server-side. The front end is visible to the audience, whereas the back end isn’t. Hence it is also responsible for the way it works internally. The websites we use in our day-to-day life are usually a combination of languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, which are all guarded by the browser we use, which deciphers the code so that it can be easily interacted with. In this topic, we are going to learn about Back End Programming Languages.
Backend code is the one that communicates with the frontend, sending and receiving messages that have to be interpreted and displayed on the web page. Further to this, there are 2 kinds of websites- static and dynamic. A static web page is the one whose contents do not change much, and a dynamic web application is the one whose contents change according to the data present in its database and can be customized. Therefore, every website needs a database that manages and stores all the information. The many databases in the market are Oracle SQL, MySQL, PostgresSQL, and SQLServer.
Some of the backend programming languages used to create dynamic websites are C, C++, Java, Ruby, PHP, .Net, and Python. And some of the examples of dynamic websites are Google, WordPress, Facebook, and Twitter.
List of Back End Programming Languages
Here let us go through some of the back end programming languages and get a basic idea of how to use them:
1. Java
Java is a general-purpose, object-oriented and concurrent programming language developed by Sun Microsystems in 1995. It uses a JVM (Java Virtual Machine) engine, which provides a runtime environment to run the Java Code and its applications. It translates Java byte code into a language that the machines can interpret. JVM forms a part of JRE (Java Runtime Environment).
Java has certain key features as follows:
- Object-oriented– This means the code is structured and modeled as a set of objects which can be manipulated, controlled, and easily extended.
- Basic– Java language is very basic and simple to master once you have understood the concept of OOP (Object Oriented Programming)
- Platform independent– Java does not depend on any specific platform because, during compilation, it is compiled to an independent bytecode format which can be distributed and translated by JVM on any platform.
- Robust– Java has good Memory management and Exception handling, which makes it minimize error-prone code.
- Multi-Threading,– Java can run multiple tasks concurrently due to this feature which helps save a lot of memory.
Example
Let us get to know how to write a basic program in Java:
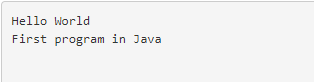
public class JavaFirstProgram {
public static void main(String []args) {
System.out.println("Hello World"); // outputs Hello World to console output
System.out.println("First program in Java");
}
}Output:
Naming Conventions in Java
Some of the basic naming conventions to be followed in Java are:
- Package: Package names are always written in lowercase ASCII letter format. A few examples are like net, org, com, etc.
- Class and interface: Nouns must be used for naming classes, and the first letter should start with a capital.
- Method: Verbs must be used for naming methods, and the first letter should be in lowercase, whereas further internal words must be in capital letters.
- Variable: It should be short and understandable. Variable names must not start with any special characters and should have more than one letter in them.
Advantages of Java
- Because of its Stack allocation system called LIFO (Last In First Out), we can do data management more efficiently.
- Various API’s have been provided, which can be used for Database connectivity, Networking, Parsing XML files, etc.
- Java language has security as an intrinsic part of its design which is developed for secure use. JVM performs a verification of the byte code through its unique identifier before running it.
Disadvantages of Java
- Linking takes place dynamically, which makes the program slow since linking is called at run-time.
- Also, the translation of bytecode to machine language takes place at run-time, which also slows down the speed.
2. Ruby
Ruby is a programming language coded by Yukihiro Matsumoto during the mid-1990s. It is an open-source, object-oriented, dynamic and reflective language. Like Java, it is platform-independent and hence can run on Windows, Mac and all Unix versions. Ruby follows a principle called POLA (Principle Of Least Astonishment), which means that the language reduces the confusion for experienced users.
Some of the features of Ruby are:
- Object-oriented– This means everything in Ruby is expressed in the form of objects. Every object will have a class, and each class will have a superclass. All the rules written for objects apply to the entire Ruby.
- Flexibility– In Ruby, we can add, remove and customize parts easily. Existing parts can be modified, and there are no such restrictions as such.
- Dynamic typing– Programs in Ruby are not compiled as such. A variable can hold all types of objects. Ruby looks up at a method name when it is called, regardless of the object type.
- Mixin– One of the unique features of Ruby is that it has a single inheritance only. It mainly operates on modules that don’t have many instances. Alternatively, a module can be united with class.
- Hashing– It is one of the collection type of key-value pairs separated by commas.
- Open– This means Ruby classes and methods can be ended with a question and exclamation marks.
- Persistence– In the case of the missing method, Ruby calls the same with its name, with which it could not locate its arguments.
Example
For the following programs, open any editor and save the file in .rb format.
1. We can output any sentence with the “puts” keyword as follows:
puts "Hello example in Ruby"Output:
2. Simple mathematics can be performed in Ruby as below:
# Arithmetic operator examples for: +, -, /, *
puts 4 * 5
# Example for finding the exponent of 4 to the power of 2
puts 4**2
# To find modulus and retrieves the remainder of 4
puts 13 % 4
# Example for the order of the given operations
puts 3 + 5 * 8
# Performing operation on integer and floating-point numbers
puts 10 / 3.0Output:
3. The variable types need not be mentioned here since Ruby identifies them automatically:
distance = 0.4
#We shall use integer and float type both
time = 8.65 / 3600
speed = distance / time
puts "The average speed of the car is #{speed} km/h"Output:
Advantages of Ruby
- Easy to understand because of simple syntax
- Ruby has a library called Gems which allows extensive functionalities for the web applications we develop.
Disadvantages of Ruby
- The number of people who choose Ruby over other programming languages is very less.
- Ruby has a slow runtime speed.
3. Python
Python is an open-source, object-oriented and interactive programming language that was named after a television show called “Monty Python’s Flying Circus” by Guido van Rossum in 1991. Python is an interpreted language which means there is no compilation required to run it. It is a high-level and simple to learn the language for beginners because of its easy syntax. It is also platform-independent.
Some of its key features are:
- Dynamic typing– The variable data types need not be declared explicitly as they are allotted in run-time.
- Extensive and integrable– Other languages like C and C++ can be unified with Python. It is hence called to be extensible.
- High-Level– This enables its users to focus on problem-solution rather than worrying about system architecture or memory management.
- Interpreted– Python code execution takes place line by line, and since there is no need for compilation, it is easy to debug.
- Extensive Standard Library– There are many build-in modules and functions in its library, reducing the coding effort. Also, a lot of libraries are present such as regular expressions, web browsers, testing, etc.
- Expressive– Python is easier to understand and read; hence, it helps to focus on the solutions rather than syntax.
- GUI Support– Graphical User Interface can be developed using Python.
Examples
Let us go through some of the basic coding examples in Python.
1. the print command is used for printing the output as follows:
print("Hello World Example for Python")Output:
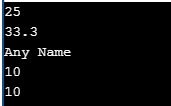
2. Assigning variables can be done as below:
number = 25 # Assigning an integer
decimal = 33.3 # Assigning a floating number
string = "Any Name" # A string
common1 = common2 = 10 # Common Assigning of values
print number, "\n"
print decimal, "\n"
print string, "\n"
print common1, "\n"
print common2, "\n"Output:
3. A simple for loop is as follows:
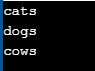
animals = ["cats", "dogs", "cows", "monkeys"]
for i in animals:
print(i)
if i == "cows":
breakOutput:
Advantages of Python
- Numerous Third-Party modules are contained by Python hence making it interactable with other platforms.
- Python supports integration with languages like C and others.
- It has huge support libraries that have internet protocols, web service tools, string operations, and operating system interfaces, which reduce the lengthy code to be written as some of them are readily available.
- Because of its integration feature, unit testing capabilities and intensified control competence, it increases one’s productivity and can be used for multiple protocol network applications.
Disadvantages of Python
- Because Python is interpreted, it makes the execution relatively slow and cannot be used where high speed is required.
- Python is not preferred for mobile development as it is considered weak because of its lack of security. One of the applications built on Python is Carbonnelle.
- Python has primitive database access compared to popular ones like JDBC and ODBC; hence, it cannot be used where complex legacy data needs to be processed.
- It imposes design restrictions because of its dynamic typing feature, which throws a lot of run-time errors hence requiring more testing time.
4. PHP
“PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor“, which previously stood for “Personal Home Page”, is another open-source scripting language used on the server-side. It is very popular being used in various big giants like WordPress and Facebook. PHP language can only be interpreted by the server having PHP installed. Its file ends with an extension “.php”. Compared to other languages, PHP is considered a stable language.
PHP has some unique features as follows:
- It can be integrated with other databases like Oracle, MySQL, Sybase, PostgreSQL, Microsoft SQL Server, and Informix.
- It has extensive libraries for using various modules and for data representation.
- It is again an interpreted language and also platform-independent
- In PHP, all the keywords, methods, classes and user-defined functions are not case-sensitive and are only case sensitive when a variable is declared.
- PHP generates dynamic content.
- It has a built-in error reporting system, thus helps to generate a warning/error notice.
- It creates a summary of the latest accesses for the user by providing real-time access logging.
- There is no need to declare data types in PHP since it shall be taken during execution based on the variable value. Hence called a loosely typed language.
Syntax: A PHP script has starting tag as “<?php” and ending tag as “?>” tags.
<?php
echo 'Hello World example of PHP';
// PHP code goes here
?>Output:
Examples
1. Below is the example for declaring and displaying variables in PHP
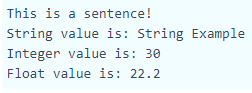
<?php
$x = "This is a sentence!"; //Assigning a sentence
echo $x;
echo "<br/>";
$str="String Example";
$x=30;
$y=22.2;
echo "String value is: $str <br/>";
echo "Integer value is: $x <br/>";
echo "Float value is: $y <br/>";
?>Output:
2. A basic for loop example can be written as follows:
<?php
for($i=10;$i>=2;$i--){
echo "$i <br/>";
}
?>Output:
Advantages of PHP
- It is low in maintenance costs with less development, giving a good performance.
- Since it is open-source, it is easy to install it fast and to use it readily. The developer can choose from one of the many frameworks available, thus reducing the development time.
- The codebase is very much organized, clean and easy to code. The syntax is also easy to learn and use.
- Connects to various databases relatively fast hence mainly used for web application development.
- It is easy to test PHP based applications as unit testing can be performed easily. It also offers automation for other tasks.
- PHP has built-in tools that provide security to web applications from outside security threats like data tampering, forgery, hacking, etc.
Disadvantages of PHP
- It is not preferred for large and complex web applications.
- It may lead to improper information to the developer because of its weak type.
- PHP does not support modification for core behavior of applications
- PHP requires additional code to be written for everything, whereas the PHP framework doesn’t.
Conclusion
In this blog, we hope you have got a better picture of some of the most popular and widely used backend programming languages. Based on the explanation shown for all, it is upto you to decide the language you choose according to your business requirements.
This does not mean that these are the only 4 languages out there. Day by day, lots of new scripting languages are emerging, which can also be included in your project. The front end must always be supported by strong server-side scripting. Thus, a backend developer should identify the goals first and integration requirements before choosing a programming language.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Back End Programming Languages. Here we discuss some of the Back End Programming Languages and basic idea on how to use them. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –