Updated July 17, 2023
Definition of Basis Points
Basis points are a unit of measurement for expressing the difference between two interest rates, for instance, between the prime rate and a variable rate loan.
One calculates it as a percentage, with one basis point equaling 0.01%. They are similar to prevailing interest rates in the market. They are denoted as a percentage, with 1% equaling 100 basis points, and are abbreviated as “bp,” “bips,” or “bps.”
Banks often use “basis points” when quoting interest rates, especially when discussing the spread between two rates. The London Interbank Offered Rate (LIBOR) is a benchmark interest rate commonly used in financial markets, and some interest rates may be quoted as a certain number of basis points above or below LIBOR. To calculate the difference in basis points between two interest rates, one multiplies the difference between the two rates by 100. For instance, if the interest rate on a stock is 10% and it increases to 10.10%, the increase is 10 basis points. Investors must understand the calculation of basis points to make informed decisions when comparing interest rates, as banks may quote interest rates in these points.
Examples
Example 1:
An investor is considering investing in a stock with an interest rate of 10.25%. After a while, the interest rate rises to 10.65%, which means the increase in basis points equals (65-25), i.e., 40 points. The bank will then quote that the interest rate is 40 basis points higher than the earlier quoted rate.
Example 2:
An investor is planning to invest in the market and is considering a bond for the same. The bank quotes that the basis points will be 50 from the LIBOR (London Inter-Bank Offer Rate). This means that the interest rate will be 0.50% higher than the LIBOR. Therefore, before investing, the investor should first know the current LIBOR rate since it serves as a base for identifying interest rates.
Which Tools Does Basis Point Apply?
The points commonly serve as a unit of measurement to indicate the difference between interest rates, helping to identify the spread between them. One calculates the difference by subtracting the decimal units of the interest rates. Nowadays, banks use these points to determine the strength of investors. Calculators for calculating the points are available online; investors and financial institutions utilize them to quote their interest rates.
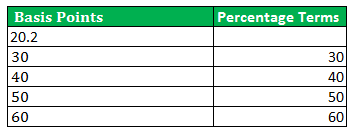
Basis Points Table
Suppose an investor has witnessed an increase in the interest rate from 10% to 20%. The new interest rate is calculated as (20% × 10%) = 22%, equal to 20 or 200 basis points. Now the table is as follows:
Calculators often come into use for calculating these points, which are a spread that helps to identify the prevailing interest rate in the market.
How to Convert Basis Points to Percentages?
To convert the points into percentages, one needs to divide them by 100. The resulting percentage value can help investors identify the interest rate associated with their investment. They often come into use for referring to interest rates in investment decisions. By understanding these points, investors can compare investment options and decide where to put their money.
Uses of Basis Points
- They often come into use to express interest rates and are helpful in identifying the value of financial instruments for investors.
- Banks often compare interest rates to the London Inter-Bank Offer Rate (LIBOR). This gives investors an idea of whether they should invest their money in a particular stock.
- Understanding these points is crucial for investors to make informed investment decisions and to comprehend the prevailing market conditions.
- The difference between two interest rates in the market is identified as basis points, and it can help investors identify better investment options.
- These points also indicate the cost of mutual funds and assist investors in evaluating different investment options.
- They are crucial in identifying the value of financial instruments and price changes, representing the spread between two interest rates in the market.
- Nowadays, financial institutions commonly use them to quote interest rates. This makes it essential for investors to understand them to effectively manage their investments.
Conclusion
Basis points are critical for investors when deciding where to invest their money. They represent the difference in interest rates and are compared to the London Inter-Bank Offer Rate (LIBOR). One also expresses them in percentages, allowing investors to make informed decisions regarding their investment options. These points aid in determining the value of stocks and analyzing price changes. The spread represented by these points helps investors calculate stock prices, which helps in understanding the benefits of investing in a particular stock.
Recommended Articles
Here are some further related articles for expanding understanding: