Meaning of Benchmarking
Benchmarking is an effective way for businesses and organizations to evaluate their performance and find opportunities for improvement. They can gain useful insights into their strengths and weaknesses and compare their performance to that of their peers or industry leaders to develop a performance improvement plan.
In simpler terms, it is looking at how well your business is doing compared to other businesses doing the same.
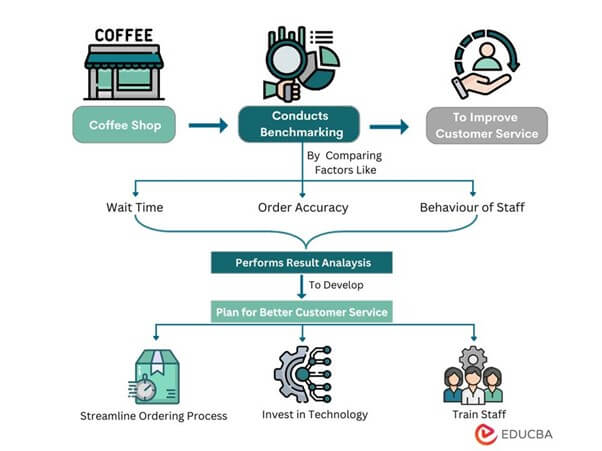
Assume you are the owner of a coffee shop and want to ensure that your customers are happy and keep coming back. You can undertake benchmarking by visiting other coffee shops in the area and observing what they’re doing differently. You may notice that one shop has quite a friendly staff, greeting customers with a smile and remembering their orders carefully. Another shop may have a high-speed service, bringing customers their coffee quickly. By comparing your coffee shop to others in the area, you can figure out what you can do better to ensure your customers are happy and return to your shop frequently.
Examples of Benchmarking
Here are some benchmarking examples from technology, finance, and education to demonstrate how it works in diverse situations, showcasing the variety of use cases of this process.
1. Technology Benchmarking
Technology benchmarking is used by businesses to compare their goods or services to those of their rivals.
Example: Apple may compare its most recent iPhone against the most recent Samsung Galaxy to establish its comparative features, capabilities, and price strategies. This might assist them in improving their products or services and remaining competitive in the market.
2. Educational Benchmarking
Schools and educational institutions use it to compare their students’ performance to other schools or institutions.
Example: A high school could compare its pupils’ academic results to those of other high schools in the district or state. This can assist them in identifying areas in which their pupils can develop and adjust their teaching techniques or curriculum accordingly.
3. Financial Benchmarking
Financial benchmarking is used by businesses to evaluate their financial performance in comparison to their rivals.
Example: A retail shop chain may compare its revenue, profitability, and market share to that of other similar-sized retail chains. This can assist them in identifying areas where their financial performance can be improved, enabling them to make educated decisions about their business plan.
Types of Benchmarking
There are four main types of benchmarking:
1. Internal Benchmarking
Internal benchmarking is comparing the performance of different departments or processes within an organization. The goal is to identify best practices and improve performance across the organization.
2. Competitive Benchmarking
Competitive benchmarking involves comparing a company’s performance against that of its competitors. The aim is to identify areas of weakness and opportunities for improvement to gain a competitive advantage.
3. Functional Benchmarking
Functional benchmarking compares a company’s procedures or methods with another business operating in a different sector. The objective is to recognize excellent practices and modify them to enhance performance.
4. External Benchmarking
The technique of comparing an organization’s performance to that of other organizations or industry standards is known as external benchmarking. This involves discovering areas where an organization’s performance might be improved by implementing best practices from other firms or industries.
Benchmarking Process
The benchmarking process typically involves the following eight steps. We have tried to give examples for each step to make the explanation understandable.
1. Define the Area to be Benchmarked
Determine the process or area of performance to be benchmarked.
Example: An e-commerce firm is aiming to improve its website’s performance.
2. Identify Benchmarking Partners
Identify companies or organizations that are performing well in the chosen area.
Example: The firm identifies several other e-commerce companies with fast-loading and user-friendly websites.
3. Collect Data
Collect data on the selected site from the benchmarking partners and the company to be benchmarked.
Example: The e-commerce firm collects data on its own website’s performance and gathers data from its benchmarking partners through website speed tests, user surveys, and site visits.
4. Analyze Data
Analyze the data to identify gaps and opportunities for improvement.
Example: The e-commerce firm analyzes the collected data to identify areas of its website that require improvement, such as page loading speed, user experience, and mobile responsiveness.
5. Identify Best Practices
Identify the best practices and processes benchmarking partners use to achieve superior performance.
Example: The e-commerce firm identifies the best practices used by its benchmarking partners, such as optimized images and videos, a simplified navigation menu, and a responsive design.
6. Implement Changes
Adopt the best practices and procedures identified in step 5 to improve the company’s performance.
Example: The e-commerce firm implements the best practices identified in step 5 by optimizing its images and videos, simplifying its navigation menu, and using a responsive design.
7. Monitor And Review
Monitor the implemented changes and performance regularly to ensure continued improvement.
Example: The e-commerce firm regularly monitors and reviews its website performance to ensure continuous improvement and adjust its strategies as per need.
8. Communicate And Celebrate Success
Communicate the results and successes of the benchmarking process to stakeholders and celebrate achievements.
Example: The e-commerce firm communicates the results of the benchmarking process and the improvements undertaken to its stakeholders and celebrates the achievements by recognizing the employees and teams involved in the process.
Benefits of Benchmarking
Benchmarking offers several benefits to businesses. Some of them are:
1. Improving Performance
It helps businesses identify areas for improvement and adopt best practices to enhance their performance. This can help them stay competitive in the marketplace, improve their functioning, and meet the changing demands of their customers.
2. Gaining a Competitive Advantage
Businesses can gain a competitive advantage by benchmarking against competitors or best-in-class companies, differentiating themselves in the marketplace, and improving profitability. This can help them stay ahead of competitors and respond effectively to changing market conditions.
3. Enhancing Customer Satisfaction
It is an effective tool for businesses to improve customer satisfaction. By identifying areas of weakness in their customer service, product quality, or other aspects of their operations, businesses can make changes to improve the customer experience. This can facilitate increased customer loyalty and retention and improved brand reputation.
4. Reducing Costs
It can help businesses identify inefficiencies and areas for cost reduction. Businesses can identify areas where they can reduce waste and streamline their operations by comparing their operations, processes, and costs to those of industry leaders or best-in-class companies. This can lead to increased profitability.
5. Enhancing Employee Engagement
Involving employees in the benchmarking process can enhance their engagement and motivation. Businesses can increase employee satisfaction and retention by giving a sense of ownership and involvement in the improvement process.
6. Driving Innovation
It can inspire businesses to develop innovative solutions to improve performance and stay ahead of the competition. By learning from industry leaders, businesses can identify new ideas and strategies to drive growth and success. This can help businesses stay innovative and adaptable in changing market conditions.
Top Benchmarking Softwares and Tools
There are several benchmarking tools and software available on the market. Here are the top four:
1. Tableau
Tableau is a robust data visualization platform that enables organizations to connect, display, and share real-time data insights. Tableau’s data visualizations let its user understand where they stand compared to their competitors with the help of advanced benchmarking. Various online courses are available to learn Tableau quickly and easily.
Features
- Data blending
- Drag-and-drop analytics
- Interactive dashboards
- Real-time data insights
- Collaborative features
2. QlikView
QlikView is a business intelligence application for creating interactive data visualizations and dashboards. It provides an interactive dashboard for tracking your progress with the help of data exploration and collaboration tools to help with benchmarking. There are various comprehensive online courses available to learn QlikView.
Features
- Data exploration
- Collaboration tools
- Interactive dashboards
- Mobile support
3. IBM Cognos
IBM Cognos is a business intelligence and performance management product that enables companies to analyze data, generate reports, and track performance in real time. It has features, like data visualization and collaborative tools make it a great choice for people to assist with benchmarking for its business.
Features
- Data modeling
- Data visualization
- Collaboration tools
- Real-time monitoring
4. SAP Business Objects
SAP Business Objects is a business intelligence and analytics platform that enables organizations to analyze data, generate reports, and communicate insights with stakeholders. This software hosts an array of features for various benchmarking fulfillments, such as predictive analytics.
Features
- Data integration
- Data visualization
- Real-time data insights
- Mobile support
These tools and software assist firms in gathering and analyzing data, identifying areas for development, and implementing best practices to improve performance.
Final Thoughts
Benchmarking is a potent instrument that may aid businesses in enhancing their performance. Organizations may get insights that boost efficiency, production, and profitability by carefully choosing the benchmarking approach and thoroughly examining the findings.
Yet, it’s critical to remember that it is not a universally applicable approach, and the procedure must be modified to match the organization’s objectives, available resources, and market conditions. Moreover, because the competitive landscape is ever-changing, it should be seen as an ongoing activity rather than a one-time event.
FAQs
Q1. Why is benchmarking important?
Ans. Benchmarking helps you find areas for development to bring your firm up to speed with the growth and success of other businesses in your industry or specialty.
Q2. What are the challenges of benchmarking?
Ans. There are different challenges to benchmarking, for example, selecting proper benchmarks, finding reliable and relevant data, ensuring the data is accurate, and implementing changes based on its results.
Q3. Is benchmarking the same as KPIs (Key Performance Indicators)?
Ans. Benchmarks and KPIs are not the same concepts. Benchmarks serve as a point of comparison for performance levels, whereas KPIs assess how well a process or activity is doing.
For example, a company can use benchmarking to compare sales revenue with competitors, whereas it can use KPIs like lead conversion rates to evaluate the effectiveness of its sales process.
Recommended Articles
The above Article is a summary of Benchmarking. Here we discuss its Meaning, Examples, Types, Process, Benefits, benchmarking tools, etc. To learn more, please read recommended articles,