Updated July 12, 2023

What is Beta in Finance?
Beta is a measure of the non-diversifiable risk of a stock. We can say that the Beta of a stock measures the sensitivity of the stock concerning a broad-based market index. Generally, in a rising market, it is good to have high beta stocks; in a falling market, it is advisable to hold on to low beta stocks.
Formula
There are two-three ways by which Beat can calculate, and it also depends upon the data given:
Explanation
The beta of a stock represents the level of risk associated with it. The risk cuts across industries and affects all the companies operating in the market. It is the parameters of risk that an entity’s cash flows may affect by factors beyond the control of the entity’s management. The changes in interest rates, inflation, taxation, political uncertainty, the break of war, etc., affect all companies. The non-diversification risk reflects the sensitivity of an entity’s revenue to changes in macroeconomic factors and depends on the degree of sensitivity of costs to total revenue. An entity with low revenue sensitivity, i.e., where the revenues are relatively stable, will carry a low-risk relative to another with high revenue sensitivity. Diversification in the market can reduce the beta of the stock. Investors can consider the risk by reviewing the risk of the stock.
Examples of Beta in Finance (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation in a better manner.
Example #1
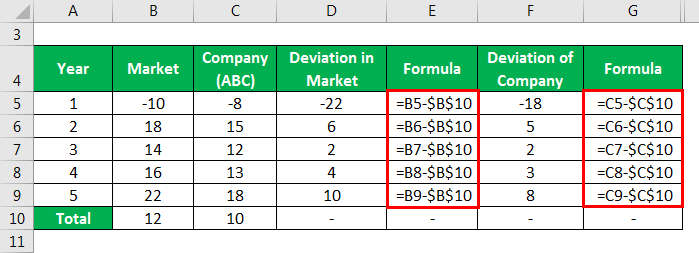
The annual Rates of return of ABC Ltd and the market rates of return are given below. Calculate the Beta coefficient value of the stocks of ABC.
Solution:
Deviation in Market and Company calculates as
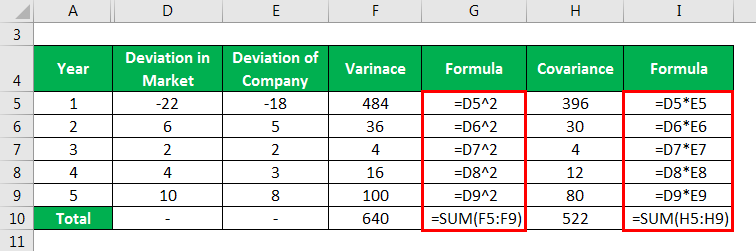
Variance and Covariance calculates as
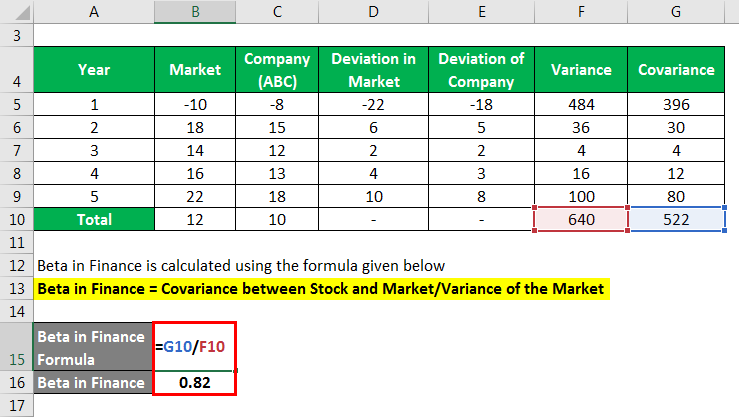
Beta in Finance calculate using the formula given below
Beta in Finance = Covariance between Stock and Market/Variance of the Market
- Beta in Finance = 522/640
- Beta in Finance = 0.82
The beta of the stock of ABC= 0.82.
Interpretation of Beta in Finance
- A beta is a risk-measuring tool by which an investor can decide whether they are required to invest in a company’s stock or not.
- The interpretation of the beta value is that if a stock’s beta is greater than 1, we call it a high beta stock. Such stocks are riskier than the stock market. They move faster than the movement in the stock market. If the market goes up, this stock goes up faster. If the market falls, this stock falls faster.
- If the stock’s beta is less than 1, we call it a low beta stock. Such stocks are less risky than the stock market. They move slower than the movement in the stock market. If the market goes up, this stock goes up slower. If the market falls down, this stock falls slower.
- Stocks with a beta of 1 are called unity stocks. Such stock mimics the market. They move in tandem with the market. If the market increases by a certain percentage, this stock increases by the same percentage. If the market falls by a certain percentage, this stock falls by the same percentage.
Uses and Importance of Beta in Finance
- Beta helps measure the risk associated with the stock if investors plan to buy or sell them.
- The beta value is an interpretation of the stock prices affected by market conditions.
- Beta can help investors draw a line between a risky and risk-free asset.
- The investors can decide between the two risky assets and the premium for one risky asset concerning another.
- With the help of the beta value, investors can seek a higher return for a risky asset.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Below are the points that explain the Advantages and Disadvantages:
Advantages
- Beta measures the degree of responsiveness of expected return on a given security relative to changes in the market movement.
- Beta helps to make the decision very smooth for the investors.
- Beta value can easily interpret the finance for the investors.
- Beta value not only helps the investors but also helps the company’s management check its stock prices, and measures can be taken to minimize the same.
Disadvantages
- Beta cannot be considered the best tool.
- Beta has limited predictive value in ascertaining future share price movements vis-a-vis market movements.
- Beta is based on past trends and data.
- Investors should not rely on past data because the stock doesn’t depend on past data.
- Falling back on the beta based on the price movement of the controlled price era will hence be unhelpful.
Conclusion
Beta measures only one portion of the return volatility caused by systematic risk. It doesn’t measure the entire element that causes the variability in the return on an asset, i.e., total risk. In practice, this is determined with the help of regression analysis relating returns on security to market returns. Beta depends on the past trend and which is not feasible.
Beta measures the stock’s volatility concerning the market index. Beta is also an indicator for investors who want to invest in the company’s stock. Beta can easily differentiate between the risk-free asset and the risky asset. The investors will define the premium for one risky asset concerning another. Investors can get an extra reward for taking the risk. The risk can be easily measured and considered by the investors and the market, and the company can take measures to control the stock prices.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Beta in Finance. Here we discuss how to calculate, along with practical examples. We also provide a downloadable Excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –