Introduction to Big Data vs Traditional Data
In today’s data-driven world, understanding the differences and benefits of Big Data and Traditional Data is necessary for businesses seeking to harness the power of information. While Big Data is characterized by its immense volume, velocity, and variety, Traditional Data offers structured and consistent datasets that have long supported decision-making. This article digs into the distinctive features of these data paradigms, highlighting their unique advantages and guiding your understanding of their applications.
Table of Content
What is Big Data?
Big data refers to immense and intricate datasets marked by three key aspects: volume, velocity, and variety. With data pouring in at an unprecedented speed from diverse sources, traditional methods falter in processing. Specialized tools like distributed computing and advanced analytics are used to unlock its potential. Amidst data accuracy and value extraction challenges, big data empowers industries to uncover hidden patterns, optimize processes, and make informed decisions for competitive advantage.
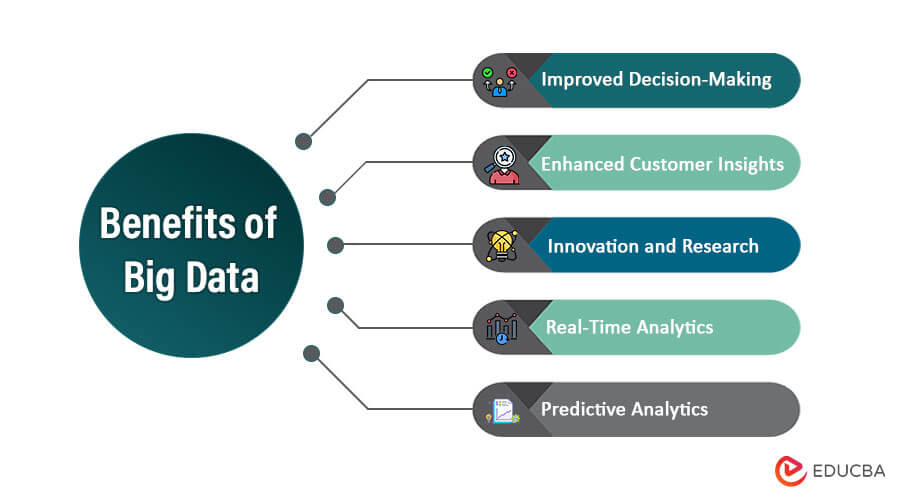
Benefits of Big Data
- Improved Decision-Making: Big data empowers improved decision-making by providing valuable insights and patterns from vast and diverse datasets. Businesses can identify trends, opportunities, and potential risks, enabling data-driven strategies that increase efficiency, competitive advantages, and overall performance.
- Enhanced Customer Insights: Big data enables enhanced customer insights by analyzing vast amounts of customer data. This allows businesses to better understand customer preferences, behaviors, and needs, leading to personalized services, targeted marketing, improved customer experiences, and increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Innovation and Research: Big data fosters innovation and research by providing access to vast amounts of information. Researchers can analyze and derive valuable insights from diverse datasets, leading to scientific discoveries, advancements in various fields, and technological innovations that benefit society and drive progress.
- Real-Time Analytics: Real-time analytics is a significant benefit of big data. It allows organizations to analyze data as it is generated, providing immediate insights and actionable information. This capability enables businesses to respond promptly to changing conditions, make timely decisions, and gain a competitive advantage in dynamic markets.
- Predictive Analytics: Predictive analytics is another valuable benefit of big data. Organizations can build models that predict future trends, events, and outcomes by analyzing historical and real-time data. This foresight enables proactive decision-making, risk mitigation, and strategic planning, improving performance and business outcomes.
What is Traditional Data?
Traditional data refers to structured and relatively manageable sets of information that can be easily stored, processed, and analyzed using conventional database management systems and data processing tools. This data type is organized into well-defined tables with rows and columns, making it suitable for straightforward querying and analysis. Unlike big data’s complex and massive datasets, traditional data typically involves smaller volumes, simpler formats, and lower processing speeds.
Each data field has a clear meaning in traditional data, and data types (e.g., numbers, text, dates) are explicitly specified. The relationships between different data elements are well-defined through primary keys, foreign keys, and join operations.
Examples of traditional data include financial records, customer information, inventory data, and sales transactions. This data is typically processed and analyzed using SQL (Structured Query Language) and traditional database management systems.
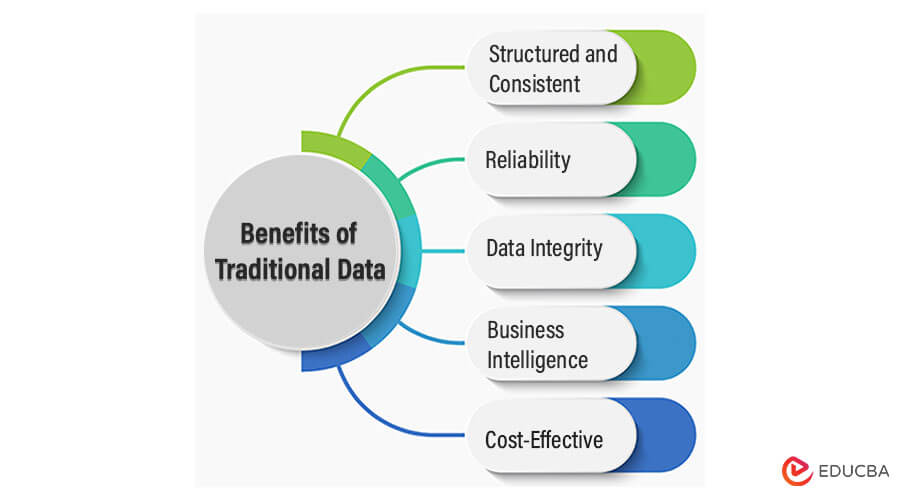
Benefits of Traditional Data
- Structured and Consistent: The structured and consistent nature of traditional data offers benefits such as streamlined processing, efficient analysis, enhanced accuracy, predictable relationships, easy integration with existing systems, and reduced potential for errors. This organized format enables straightforward querying, reporting, and historical analysis, ultimately supporting informed decision-making and seamless data management.
- Reliability: Since traditional data is stored in relational databases with ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, and durability) properties, it is highly reliable and ensures data accuracy and consistency. Reliability specifies the consistency and dependability of data. Reliable data is accurate, consistent, and free from errors or inconsistencies.
- Data Integrity: Traditional data systems implement data integrity constraints to maintain data quality and prevent data corruption, enhancing the overall reliability of the information. Data integrity ensures data accuracy and reliability by preventing unauthorized modifications, errors, or corruption. It maintains the data’s unaltered, complete, and trustworthy state throughout its lifecycle, supporting accurate analysis, informed decision-making, and overall data quality.
- Business Intelligence: Traditional data serves as the foundation for business intelligence tools and reporting systems, enabling businesses to gain valuable insights and make informed decisions based on structured data analysis.
- Cost-Effective: Managing and processing traditional data is generally more cost-effective than handling big data. Traditional databases and infrastructure require less complex technology, making it a cost-efficient option for many businesses.
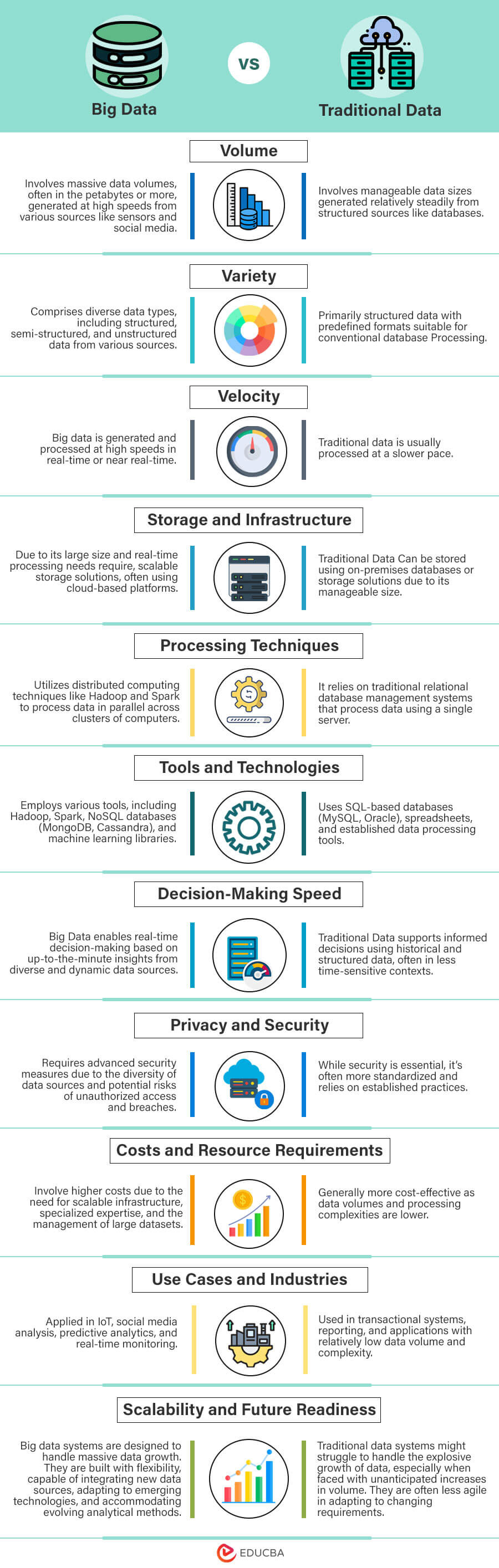
Differences Between Big Data and Traditional Data
Key Similarities for Big Data vs Traditional Data
- Data Processing: Big and traditional data require processing to derive valuable insights and support decision-making. While big data processing involves distributed computing and complex algorithms, traditional data processing typically uses SQL-based operations.
- Data Quality: Big and Traditional Data rely on maintaining high data quality. Ensuring accurate, complete, and reliable data is essential for meaningful analysis and informed decision-making. Regardless of the data’s volume or type, efforts to validate, clean, and enhance data quality are crucial to ensure integrity and value across big and traditional data environments.
- Data Storage: Big and Traditional Data require effective data storage solutions. While the scale and technologies used might differ, the fundamental need to securely store and manage data remains consistent. Both environments seek optimized storage mechanisms to efficiently handle data volumes, ensuring accessibility, reliability, and adherence to data retention policies.
- Data Security: Big and Traditional Data require robust data security measures. Protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access, breaches, and cyber threats is paramount regardless of the data’s volume or source. Implementing encryption, access controls, authentication, and compliance with data protection regulations are essential practices in both environments to maintain data confidentiality and integrity.
- Data Integration: Big and Traditional Data require combining information from diverse sources. Effective integration enhances decision-making by providing a comprehensive view. Regardless of the data’s size or complexity, integrating internal and external data optimizes insights, supporting informed strategies and improved business processes.
- Data Source: Big and Traditional Data rely on internal and external data sources for insights. Accurate, diverse, and relevant data fuels informed decision-making. Whether harnessing vast streams of real-time data or utilizing structured datasets, understanding and leveraging data sources contribute to successful analysis and meaningful business outcomes in both contexts.
Conclusion
In the realm of data, one size doesn’t fit all. The choice between Big and Traditional Data hinges on your organization’s needs and goals. Big Data opens doors to real-time insights, predictive analytics, and innovation, while Traditional Data provides reliability, structure, and cost-effectiveness. Remember, both have their place in the modern business landscape. Whether you’re harnessing the dynamic potential of Big Data or relying on the stability of Traditional Data, the key lies in aligning your data strategy with your business objectives to pave the way for success.
FAQ’s
Q1. Are Big Data processing techniques complex?
Ans: Yes, Big Data employs distributed computing and machine learning, compared to traditional SQL queries used for structured data.
Q2. How can I choose between Big Data and Traditional Data for my business?
Ans: Consider factors like data volume, types, processing speed needs, and industry requirements. Tailor your choice to match your organization’s goals and challenges.
Q3. Is data quality equally important for both Big Data and Traditional Data?
Ans: Absolutely, maintaining high data quality is crucial for meaningful analysis and informed decisions, regardless of data type or volume.
Q4. Do both data types require secure storage solutions?
Ans: Yes, both Big Data and Traditional Data demand effective data storage to ensure accessibility, reliability, and adherence to retention policies.
Q5. How do these data types integrate data from various sources?
Ans: Both require integrating diverse data sources for comprehensive insights. Internal and external data integration optimizes decision-making in both contexts.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Big Data vs Traditional Data” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.