What is Bill of Lading?
The Bill of Lading (BOL or B/L) is a legal transportation document signed when a seller wants to send goods to a buyer from another country. But the seller and the buyer don’t sign it. Instead, the shipping agent who helps the seller transport the goods to another location/country and the master of the ship that carries the goods sign it. This document goes on a little journey itself while the goods are on their way to the other country — from the seller’s shipping agent to the seller, then to the buyer, and finally to the buyer’s shipping agent.
The term “Bill of Lading” has two important words: “bill” and “lading.” “Bill” refers to the document that shows how much the goods cost. “Lading” means loading the goods onto a ship or plane for transporting them from one place to another.
BOL includes the following details:
- Shipper’s name (shipping agent who handles transportation)
- Carrier’s name (ship or trucking company that actually transports goods)
- Consignee’s name (buyer or the person who receives the goods)
- Date of shipment
- Description of goods (quantity, price, etc.)
- Freight charges
- Destination
Table of Contents
Process: How BOL Works?
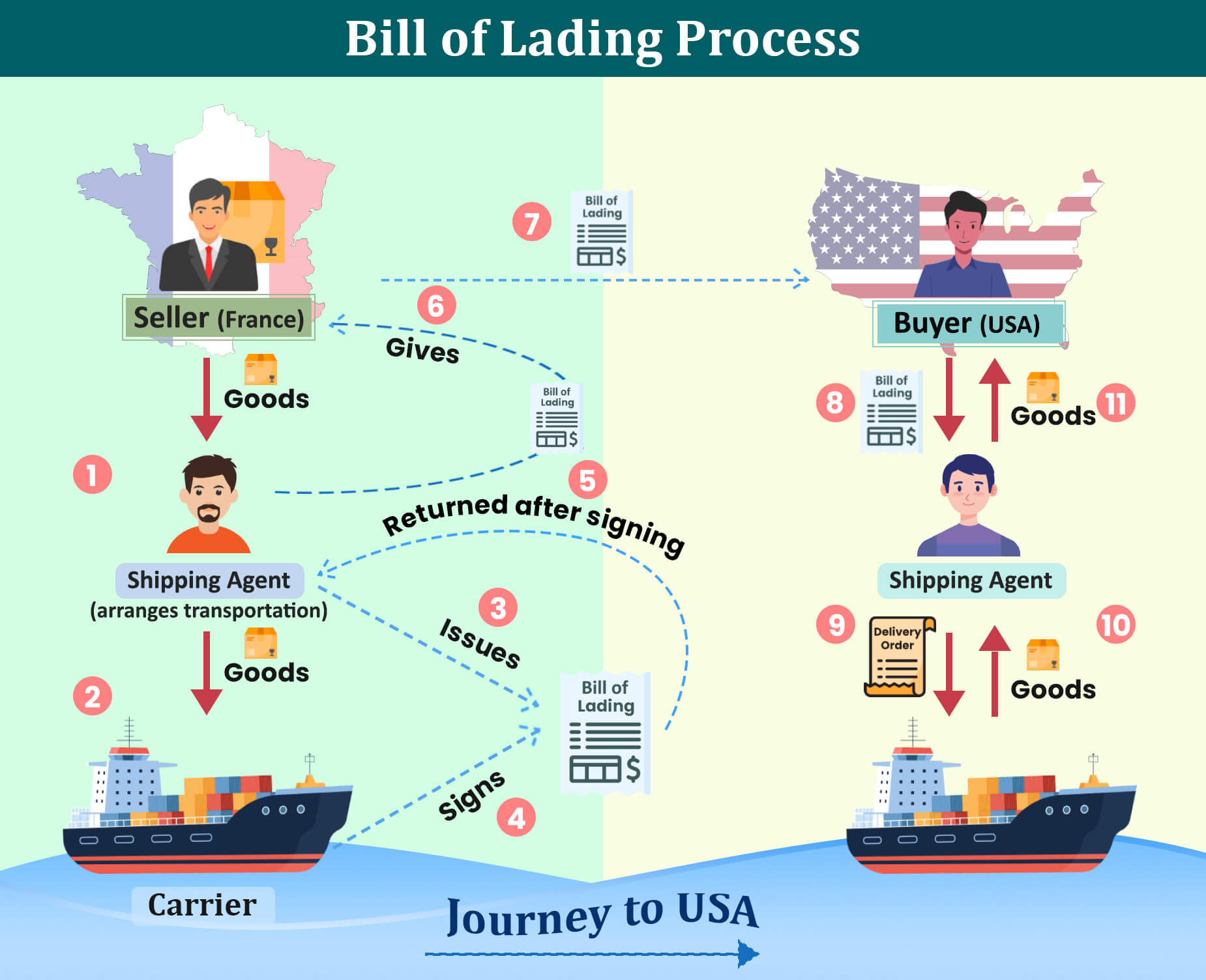
Let us now see a simple example explaining the process.
Suppose a winery based in France wants to ship a large consignment of wine to a buyer in the USA. The process will be as follows:
- Seller finds a Shipping Agent: The seller (winery) identifies a shipping agent who can arrange the transportation of the wine to the USA. The seller then gives the wine to the shipping agent.
- Start of Documentation: Once the shipping agent receives the wine from the seller, he/she begins the paperwork, which includes creating the (BOL).
- Two versions of BOL are Created: The shipping agent makes two versions of the BOL – the Original Negotiable BOL (signed one) and the Non-negotiable BOL (basically a copy).
- Shipping Agent Chooses a Carrier: The shipping agent then finds a carrier who can transport the wine from France to the USA via a ship (sea route). The carrier can be a transport carrier like a ship or a truck company if it involves both sea and land transport.
- Signing of BOL: The shipping agent and the captain of the ship (the carrier) sign the BOL. Once the carrier signs, it means that the wine is officially loaded onto the ship. The carrier then returns the signed BOL to the shipping agent.
- Sea Journey: The ship sails across the sea to reach the USA port.
- BOL Handover: The shipping agent gives the signed BOL to the seller, who then sends it to the buyer. The buyer hands the BOL over to their own shipping agent (this agent is different from the seller’s shipping agent).
- Issue of Delivery Order (DO): After receiving the original BOL, the buyer’s shipping agent issues the delivery order (DO). He then collects the goods/cargo (wine) once it arrives at the port in the USA.
- Delivery of Goods: The shipping agent then delivers the goods to the buyer.
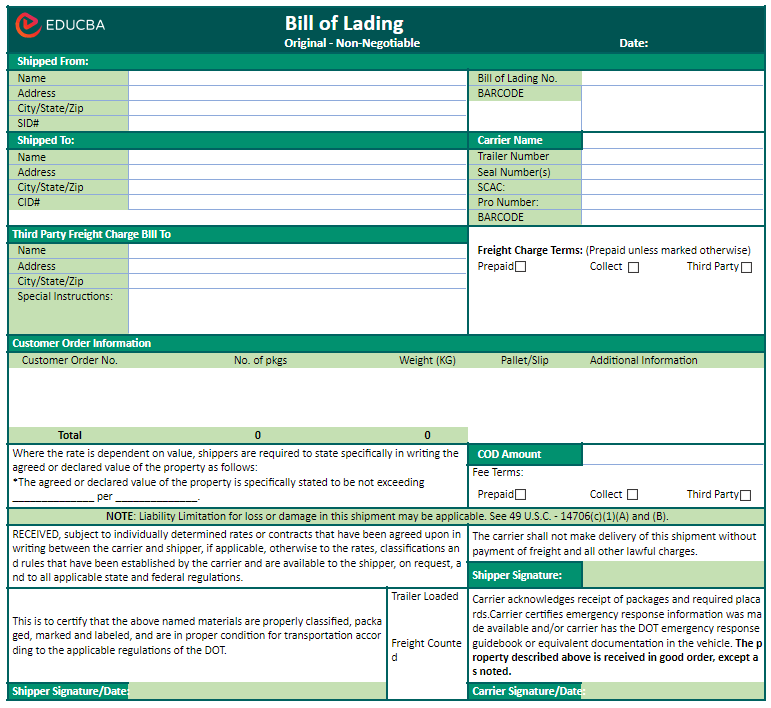
BOL Format
Given below is a basic format of BOL. However, a BOL can include additional details based on the shipment.
| Detail on BOL | What it means? |
| Shipper’s Name | Name of the entity sending the goods. |
| Carrier’s Name | Name of the transportation company or carrier. |
| Consignee’s Name | Name of the entity receiving the goods. |
| Bill of Lading Number | Unique identification number for the document. |
| Date | Date the Bill of Lading is issued. |
| Description of Goods | A clear description of the shipped goods. |
| Quantity | Number of packages or weight of goods. |
| Unit Price | Cost per unit of the shipped goods. |
| Total Cost | Total cost of the goods. |
| Freight Charges | Cost of transportation services. |
| Special Instructions | Any specific instructions for handling or delivery. |
| Shipper Signature | Signature of the shipping agent. |
| Carrier Signature | Signature of the carrier. |
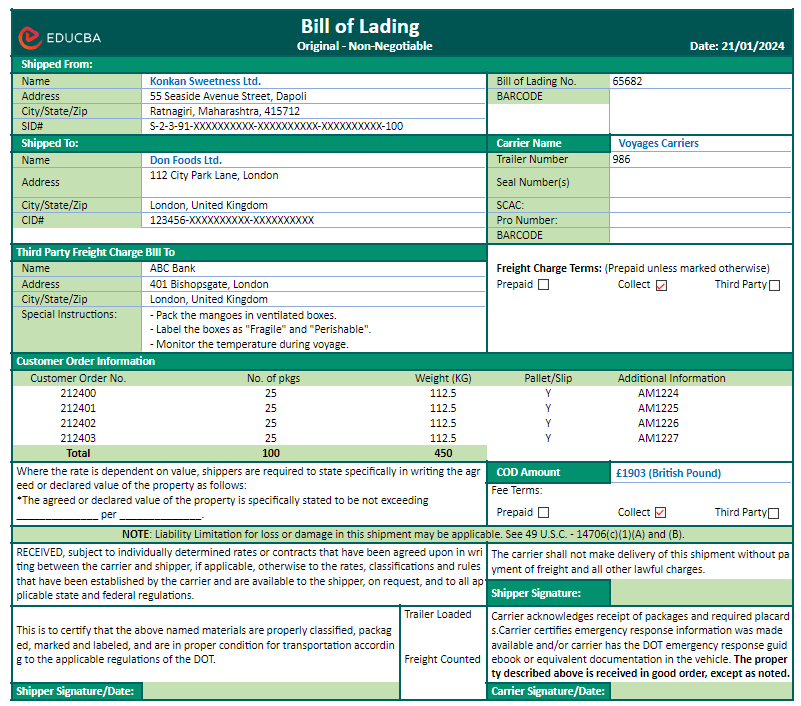
Example of Bill of Lading (with Excel Template)
Konkan Sweetness Ltd., a commercial mango orchard in Ratnagiri, India, is charged with delivering a batch of Alphonso mangoes to the food and beverages company “Don Foods” in London. They have ordered the delivery of 100 boxes of Alphonso mangoes. The delivery process involves utilizing the services of a carrier company known as “Voyage Carriers,” which specializes in transporting goods via the sea route.
The sample Bill of Lading will be as follows:
The above Bill of Lading (BOL) holds essential information, including details about the sender (Konkan Sweetness Ltd.) and the recipient (Don Foods), addresses, and a comprehensive description of the mango boxes. It also records transportation terms, charges, and fees associated with the shipment.
As the Alphonso mangoes are loaded onto the carrier by Konkan Sweetness Ltd. for their journey from Ratnagiri, India, to London, the BOL accompanies the shipment. Upon arrival in London, when Don Foods is ready to receive the mangoes, they must present the BOL to the carrier, in this case, Voyage Carriers. The carrier carefully checks the document to ensure that all information is accurate and in order. Once satisfied with the verification process, Voyage Carriers releases the Alphonso mangoes to Don Foods, effectively completing the transaction and ensuring a seamless delivery process. The BOL, in this context, serves as a crucial receipt for the mango shipment, documenting the details of the transaction and facilitating a transparent and secure exchange between the parties involved.
Types of Bill of Lading
The Shipping and transportation industry has different types of BOL. They serve different purposes, and here are some of the most common ones:
1. Straight Bill of Lading
It is a receipt for shipped goods, which is non-negotiable. This document clearly states the name of the person who should get the goods. So, the delivery should be made only to the person mentioned on the BOL and not to anyone else.
ABC Inc.(seller) is sending some products to XYZ Inc. using a Straight Bill of Lading. The receipt says only XYZ Inc. (the buyer) can get the products. Nobody else can take over the document while the products are on their way. It is to ensure the right person gets the delivery.
2. Order Bill of Lading
An Order Bill of Lading is a negotiable document that allows the transfer of goods from the shipper to another party through endorsement and delivery. This type of BOL can be used as collateral for financial transactions, providing flexibility in the transfer of ownership.
ABC Inc. (sender) sends products to XYZ Inc. (buyer) without immediate payment, and they create an Order Bill of Lading. Instead of waiting for XYZ Inc. to pay, ABC Inc. hands over the document to a bank. By doing this, the bank gains control of the document and can use it as a guarantee to give XYZ Inc. a loan. This helps ABC Inc. have more financial flexibility while the goods are on their way.
3. Bearer Bill of Lading
It is a negotiable document that facilitates the transfer of goods by the physical possession of the document itself. Unlike an order Bill of Lading requiring endorsement (formal approval), this type allows the holder to claim the goods simply by having the document in hand.
ABC Courier Company holds a Bearer Bill of Lading for a shipment. ABC physically hands the document to XYZ Courier Company to transfer responsibility for delivery to XYZ. It ensures a secure and smooth transfer of the shipment’s control and responsibility without formal endorsement.
4. Sea Waybill
A Sea Waybill is used in sea freight to acknowledge goods receipt, acting as proof of the carriage contract. It doesn’t transfer ownership of the transported goods.
If ABC Inc. is shipping goods from China to the US, they can use a Sea Waybill to acknowledge the receipt of the goods and establish the terms of the transportation contract. But, this document doesn’t mean they own the goods and can’t be passed to someone else when the shipping deal needs a fixed agreement.
5. Clean Bill of Lading
It is a document issued in shipping to confirm that the received carrier is in proper order and condition without any damage or discrepancies. It indicates that the cargo conforms to the terms and conditions of the transportation contract.
ABC Inc. (shipper) ships a consignment to XYZ Inc. (carrier) Upon inspecting the goods and finding everything in good condition, XYZ Inc. issues a Clean Bill of Lading to prove that they received the shipment under the agreed-upon terms, with no damage or issues noted.
6. Claused Bill of Lading
Shipping companies use a Claused Bill of Lading when discrepancies, shortages, or damages occur to the goods received during shipping. This document contains notations or clauses that specify issues observed during the loading or unloading.
If ABC Inc. (shipper) sends a shipment to XYZ Inc. (carrier), and some products are damaged upon receipt, a Claused Bill of Lading can be issued. This document will specifically mention the damages or discrepancies observed during shipping.
7. Inland Bill of Lading
This document serves exclusively for transporting goods within the boundaries of a country. It is specifically designed for land transport shipments and excludes ocean or international elements.
If ABC Inc. in the United States needs to transport products to XYZ Inc. within the same country, they can employ an inland Bill of Lading. This document is for land shipments in the U.S. It is a contract saying we will take your goods from one place to another and prove that you own them while they are moving.
8. Ocean Bill of Lading
It is a shipping document specifically designed for goods transported by sea. It is a receipt, carriage contract, and title document between the shipper and the carrier. This document outlines crucial details such as the nature of the goods, the destination, and the agreement terms.
ABC Inc. (seller) uses an Ocean Bill of Lading when shipping products from China to the US. This document specifies key information, including the type and quantity of goods, the vessel details, and the agreed-upon terms for the sea transport. It is a vital record facilitating the smooth and organized shipment of goods across the oceanic route.
9. Through Bill of Lading
It’s a transport document covering the entire journey of goods from origin to destination, utilizing various modes like land and sea transport. It makes things smooth and organized for the entire process of moving and delivering goods.
If ABC Inc. plans to transport goods from China to the US using both sea and land transport, they can use a Through Bill of Lading. This will provide all the info about the entire journey, from shipping across the ocean to moving on a train in the United States afterward. It simplifies a multi-modal shipment’s documentation and contractual aspects.
10. Negotiable Bill of Lading
This type of shipping document allows the transfer of ownership of goods from one party to another through endorsement and delivery. It functions as a negotiable instrument, meaning that whoever possesses the document has the right to claim the goods.
ABC Inc. is shipping electronic products to XYZ Inc. on credit. To secure a bank loan, XYZ Inc. uses a negotiable Bill of Lading, transferring ownership of the goods to the bank as collateral. In case of default, the bank can take possession of the goods, ensuring security for the loan.
11. Non-negotiable Bill of Lading
It is a shipping document that signifies the receipt of goods by the carrier and outlines the terms of transportation. Unlike negotiable bills, ownership of the goods is not intended to be transferred through endorsement.
ABC Inc. is shipping products to XYZ Inc., so the transfer of ownership is unnecessary. In this case, a non-negotiable Bill of Lading would be used to acknowledge the receipt of goods by the carrier and establish the terms of the shipment without facilitating the transfer of ownership.
12. Uniform Bill of Lading
A Uniform or Straight Bill of Lading (SBL) is a document companies use to keep things consistent when they are sending and receiving goods. It ensures that all the information about shipments looks the same, no matter how they are transported. This helps make paperwork easier and ensures both parties have the same information.
ABC Inc., a company shipping products through different carriers and transportation methods, adopts a Uniform Bill of Lading. ABC Inc. can use a standardized format for all its shipments, making managing and tracking goods consistently easier. This applies regardless of the specific carrier or mode of transportation involved. Uniformity reduces the likelihood of errors, improves efficiency, and facilitates smoother logistics operations for ABC Inc.
Final Thoughts
A Bill of Lading holds crucial importance in the import/export business, particularly in international trade, as it comprehensively outlines shipment details.
It acts as a safety net for the shipper and consignee because it provides all the details of the shipment, reducing the chances of fraud and ensuring the safe and timely delivery of the goods.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Who issues the Bill of Lading?
Answer: The carrier or the shipping company issues the BOL. It outlines the terms of the transportation agreement between the shipper and the carrier.
Q2. What is the purpose of the Bill of Lading?
Answer: The BOL is a proof of receipt for the shipping company, showing that the goods were received and delivered in good shape. It also acts as a kind of agreement between the shipping company, the carrier (who transports the goods), and the person who is getting the goods.
Q3. What information does a Bill of Lading typically include?
Answer: A Bill of Lading typically includes the shipper’s name and consignee, their signatures, description of the goods, the shipping route, the mode of transport, the freight rate, and any special instructions.
Q4. What is the significance of the “clean” and “dirty” Bill of Lading?
Answer: A “clean” Bill of Lading indicates that the goods were received in good condition, while a “dirty” or “foul” Bill of Lading notes discrepancies, damages, or irregularities in the received goods.
Q5. What is the role of the “Notify Party” on a Bill of Lading?
Answer: The Notify Party is an entity or person designated on the Bill of Lading to receive notifications about the arrival of the goods at the destination port. It is often different from the consignee and helps in timely communication.
Q6. Can a Bill of Lading be used for multimodal transport?
Answer: Yes, a Multimodal Bill of Lading covers transporting goods using different modes (e.g., sea, air, rail, and road). It provides a comprehensive document for the entire transportation process.
Q7. Can a Bill of Lading be transferred to another party during shipment?
Answer: Yes, depending on the type of Bill of Lading. An Order Bill of Lading is negotiable and allows transfer to another party through endorsement and delivery. At the same time, a “Straight Bill of Lading” is non-negotiable and can only be claimed by the original consignee.
Q8. Can a Bill of Lading be electronic?
Answer: Yes, electronic Bills of Lading (e-B/L) are increasingly common. The legal standing is the same as traditional paper B/Ls but provides faster and more efficient processing.
Q9. Can the information on a Bill of Lading be amended after issuance?
Answer: Yes, changes to a Bill of Lading are possible, but all parties’ consent is necessary. Any modifications should be formally recorded through an amendment or rider appended (additional document for changes made) to the original document.
Q10. What is a “Telex Release” in relation to the Bill of Lading?
Answer: A Telex Release is a method of transferring cargo without requiring the physical surrender of the original Bill of Lading. It is used when the cargo reaches its destination, and the consignee wants to take possession without the original document.
Recommended Articles
We hope this article on “Bill of Lading” was beneficial to you. To learn more about related topics, refer to the articles below.