Updated March 21, 2023
Introduction to Bitwise Operations in C#
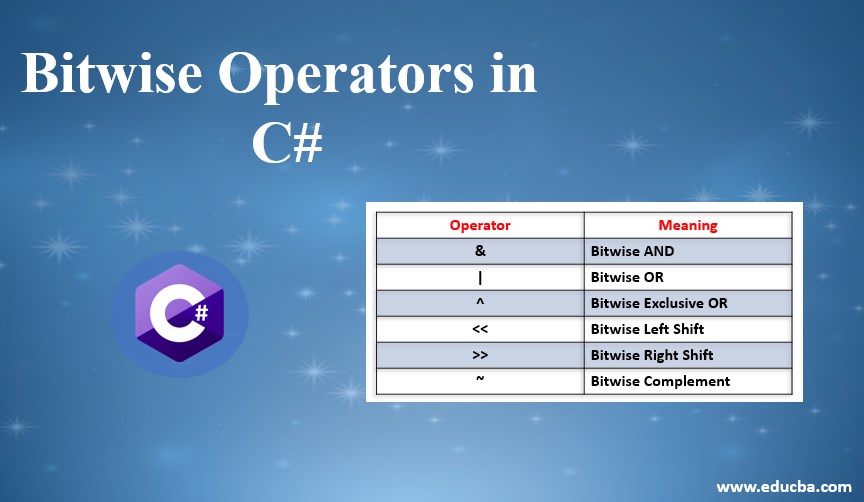
Bitwise Operators are nothing but the operations performed on the bit levels, and C# allows a variety of bitwise operations using the operators AND, OR, NOT, etc. The operators generally used for bitwise operation are AND (&) which returns true when both operands are true, OR (|) which returns true only when operands are true, Exclusive OR (XOR or ^) which returns a comparable result depending on the input, Left Shift (<<) which is used to move the bit to left, Right Shift (>>) which is used to move the bit to right, and Complement (~) which is used on single operand and it returns the complement bit value based on the input.
Types of Bitwise Operators in C#
Following are various types of Bitwise operators defined in C#:
- Bitwise AND (&): Each bit from the first operand is associated with that of its second operand. When both bits are 1 then the result bit is 1 if not 0.
- Bitwise OR(|): Each bit from the first operand is associated with that of its second operand. If either of the bit is 1 then the result bit is 1 if not 0.
- Bitwise Exclusive OR (XOR – ^): Every bit from the first operand is comparable to its second operand’s subsequent bit. When one bit is 0 and the other is 1 the result bit is 1 if not the result bit is 0.
- Bitwise Left Shift (<<): It moves the number to the left, depending on the number of bits defined. The zeroes are appended to the smallest bits.
- Bitwise Right Shift (>>): It moves the number to the right, depending on the number of bits defined. The zeroes are appended to the smallest bits.
- Bitwise Complement (~): Bitwise complement operator is a unary operator that operates on one operand only. The ~ operator switches from 1 to 0 and from 0 to 1.
Examples of Bitwise Operators in C#
The following article explains how bitwise operators work below mentioned are the examples of bitwise operators in C#:
1. Bitwise AND
It only gives True while using AND operation if both values are True. This operator can be implemented by using ‘&’ operator.
Example:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
byte myvarA = 10;// This binary is equivalent for 10 is 01010
byte myvarB = 20;// This binary is equivalent for 20 is 10100
long myresult = myvarA & myvarB; // The result of AND operation result is: 00000
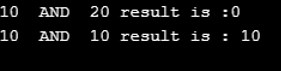
Console.WriteLine("{0} AND {1} result is :{2}",myvarA,myvarB,myresult);
myvarA = 10;// This binary is equivalent for 10 is 01010
myvarB = 10;// This binary is equivalent for 10 is 01010
myresult = myvarA & myvarB; // The result of AND operation result is: 01010
Console.WriteLine("{0} AND {1} result is : {2}",myvarA,myvarB,myresult);
}
}Output:
Open the text editor and save the file with .cs extension with the name of your choice. Execute the program by using suitable c# compiler and you will be getting below output:
2. Bitwise OR
It only provides FALSE while using the OR method if both the values are FALSE. OR operation is true in all other cases. This operator can be implemented by using the ‘|’ operator.
Example:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
byte myvarA = 10;// This binary is equivalent for 10 is 01010
byte myvarB = 20;// This binary is equivalent for 20 is 10100
long myresult = myvarA | myvarB; // The result of OR operation result is: 11110
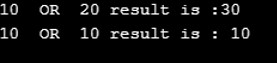
Console.WriteLine("{0} OR {1} result is :{2}",myvarA,myvarB,myresult);
myvarA = 10;// This binary is equivalent for 10 is 01010
myvarB = 10;// This binary is equivalent for 10 is 01010
myresult = myvarA | myvarB; // The result of OR operation result is: 01010
Console.WriteLine("{0} OR {1} result is : {2}",myvarA,myvarB,myresult);
}
}Output:
Compile and execute the above code, you will get the following output:
3. Bitwise EXOR
If the related bits are unique, then this gives 1, otherwise 0. This operator can be implemented by using the ‘^’ operator.
Example:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
int num1 = 14, num2 = 11, myresult;
myresult = num1^num2;
Console.WriteLine("{0} ^ {1} = {2}", num1, num2, myresult);
}
}Output:
Compile and execute the above code, you will get the following output:
4. Bitwise RightShift
If RightShift operations are performed with a binary value, the bits will be shifted to one location on the right side. This operator can be implemented by using ‘>>’ operator.
Example:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
byte myvarA = 10;// This binary is equivalent for 10 is 01010
long myresult = myvarA >> 1; // The right shift operation result is : 0101
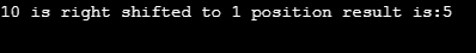
Console.WriteLine("{0} is right shifted to 1 position result is:{1}",myvarA,myresult);
}
}Output:
Compile and execute the above code, you will get the following output:
5. Bitwise LeftShift
If LeftShift operations are performed with a binary value, the bits will be shifted to one location on the left side. This operator can be implemented by using the ‘<<’ operator.
Example:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
byte myvarA = 10;// This binary is equivalent for 10 is 01010
long myresult = myvarA << 1; // The left shift operation result is : 10100
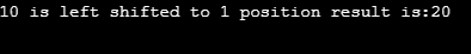
Console.WriteLine("{0} is left shifted to 1 position result is:{1}",myvarA,myresult);
}
}Output:
Compile and execute the above code, you will get the following output:
6. Bitwise Complement
Bitwise complement operator is specified by the ‘~’ which is a unary operator that operates on one operand only. The ~ operator inverts a bit, i.e. switches from 1 to 0 and from 0 to 1.
Example:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
int num = 22, num_result;
num_result = ~num;
Console.WriteLine("~{0} = {1}", num, num_result);
}
}Output:
Compile and execute the above code, you will get the following output:
Conclusion
In this article, we have seen how bitwise operators can be used in C# along with their functionality. These operators are used to perform bit by bit operations on operands, also called binary numerals. The bitwise operator analyses the binary interpretation of the functions of the two inputs on a cell-by-cell base. These operators are mainly used in communication stacks in which vital information is symbolized by the individual bits in the header connected to data.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Bitwise Operators in C#. Here we discuss the Introduction and the types of bitwise operators in C# along with different examples and its code implementation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –