Introduction to Bolts and Nuts
Bolts and nuts are among the most commonly used fasteners in various industries. From construction to automotive household repairs to complex machinery, they play a crucial role in holding structures together. Despite their simplicity, these fasteners are integral to countless applications’ safety, durability, and efficiency.
From this article, we will learn the different types of bolts and nuts, explain how they work, and discuss their uses in various industries. By the end of this post, you will have a thorough understanding of these crucial components and their roles in various applications.
What Are Bolts?
Bolts are a type of fastener characterized by a threaded shaft. They are designed to pair with a nut to hold two or more components together. Bolts are commonly used with pre-drilled holes, creating a secure and detachable connection.
Components of a Bolt
- Head: The head is the top part of the bolt, which provides a surface for tools like wrenches or sockets to grip and apply torque. Common shapes include hexagonal, square, and round heads.
- Shaft: The shaft is the elongated, threaded portion of the bolt that passes through the components being fastened.
- Thread: The thread is the helical ridge wrapped around the shaft, allowing the bolt to screw into a nut or tapped hole.
Types of Bolts
- Hex Bolts: These are commonly used in construction and repair and have hexagonal heads.
- Carriage Bolts: They have a rounded head and square neck, commonly used in woodworking applications.
- Anchor Bolts: Designed to secure objects to concrete surfaces.
- Eye Bolts: Have a looped head for attaching ropes or cables.
- Flange Bolts: Incorporate a washer-like flange to distribute the load evenly.
Materials Used for Bolts
- Steel: The most common material, available in different grades for varying strength levels.
- Stainless Steel: Provides corrosion resistance, making it perfect for outdoor or humid environments.
- Brass: Used for decorative applications or where conductivity is needed.
- Titanium: Lightweight and strong, often used in aerospace or medical applications.
What Are Nuts?
Nuts are small, flat, typically hexagonal components with a threaded hole in the center. They are designed to mate with bolts, threading together to create a secure fastening.
Components of a Nut
- Shape: Most nuts are hexagonal for ease of use with tools, but other shapes, such as square or winged nuts, exist.
- Threads: The internal threading lets the nut grip the bolt shaft securely.
Types of Nuts
- Hex Nuts: The most commonly used type, with a hexagonal shape.
- Lock Nuts: Include additional features like nylon inserts to prevent loosening due to vibration.
- Wing Nuts: Have protruding “wings” for manual tightening without tools.
- Cap Nuts: Feature a domed top to cover the exposed end of the bolt, providing a finished look.
- Flange Nuts: Incorporate a built-in washer to distribute pressure.
Materials Used for Nuts
- Steel: The most common material for general use.
- Stainless Steel: Resists rust and corrosion.
- Brass: Often used for aesthetics or specific electrical properties.
- Nylon: Lightweight and used in applications where conductivity is undesirable.
How Bolts and Nuts Work Together
Bolts and nuts work in tandem to create secure connections. The bolt passes through the joined components, and the nut threads onto the bolt’s shaft. As the nut is tightened, it applies clamping force, holding the components together.
The threads on the bolt and nut interlock, ensuring a secure grip capable of withstanding considerable forces. Proper torque during tightening ensures the joint is neither too loose nor too tight, maintaining its integrity.
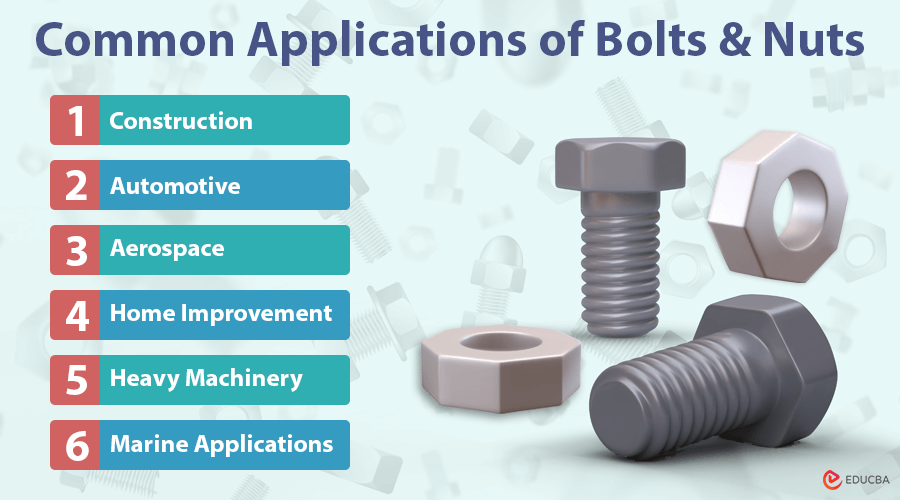
Common Applications of Bolts and Nuts
Bolt and nut is used in many industries and applications. Here are some of the most common:
- Construction: Used to assemble steel frameworks and secure wood or concrete structures.
- Automotive: Secure parts like engines, wheels, and suspension systems in vehicles.
- Aerospace: Lightweight bolts and nuts are used in aircraft and spacecraft for safety and efficiency.
- Home Improvement: Essential for DIY projects, furniture assembly, and appliance repairs.
- Heavy Machinery: Used in industrial equipment to handle heavy loads.
- Marine Applications: Stainless steel fasteners resist corrosion in boats and ships.
Maintaining Bolts and Nuts
Proper maintenance ensures they last longer and work effectively. Here are some tips for maintenance:
- Inspection: Regularly inspect bolts and nuts for wear signs, such as cracks, rust, or deformation. In high-stress areas, inspect more frequently to avoid failure.
- Lubrication: Use lubricants like anti-seize compounds to prevent seizing and wear. This also makes future disassembly easier.
- Storage: Store in a dry, well-ventilated place to prevent rust. Organize them by type and size to easily find what you need.
Final Thoughts
Bolts and nuts may seem simple, but they are indispensable components in countless applications. Their ability to securely join materials makes them essential in construction, automotive, aerospace, and many other industries. Understanding their types, materials, and proper usage ensures you can select the right fasteners.
Whether you are a professional engineer or a DIY enthusiast, basic knowledge will go a long way in helping you complete your projects effectively and safely. Next time you tighten a bolt or screw on a nut, you will appreciate the incredible design and functionality packed into these small but mighty components.
Recommended Articles
We hope this guide to bolts and nuts helps you understand their various types and applications for your projects. Check out these recommended articles for more such topics.

