Updated July 17, 2023
What is Bond Fund?
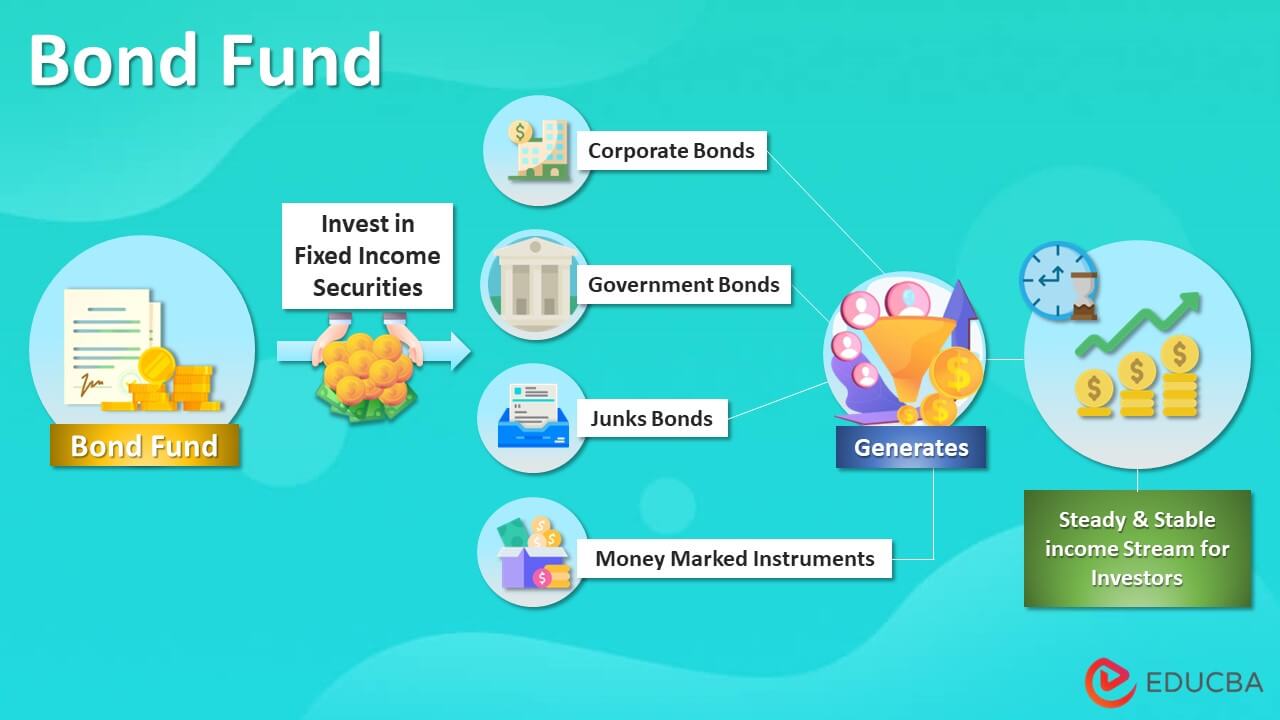
The term “bond fund” refers to the investment pool usually traded as an exchange-traded fund (ETF) or mutual fund. This fund typically invests in fixed-income securities, such as corporate bonds, government bonds, junk bonds, money market instruments, etc.
The primary objective of this type of fund is to generate a steady and stable income stream for investors. A bond fund is also popularly known as a debt fund.
Explanation
From an investor’s perspective, a bond fund is a better way of investing in bonds without buying the underlying individual bond securities. The investors can generate a steady income stream by indirectly participating in the underlying bond securities’ interest payments. Further, a bond fund manager rarely holds any securities until maturity as they usually purchase and sell bond securities in the fund as per the market conditions. So the bond fund has no maturity date, unlike the underlying individual bonds.
How Does Bond Fund Work?
In this case, the fund manager pools investors’ funds into a portfolio of fixed-income securities and bonds. The investments are usually made in established institutions with high credit ratings. The main focus of such a fund is to optimize income opportunities while maintaining the risk of credit default (both principal repayment and interest payment) to the minimum.
There are two significant sources of income for a bond fund investor –1) capital appreciation due to an increase in the Net Asset Value (NAV) over some time and 2) dividend paid by the underlying bonds at specific intervals.
Examples
Now, let us have a look at some of the best-known bond funds available across the globe:
- Vanguard Total Intl Bd Idx Investor (VTIBX): This fund has a below-average risk rating with an average return profile per Morningstar. During the last three years/5 years, as of August 31, 2020, the fund has generated a return of 4.66%/4.27%, indicating stable returns. The fund’s expense ratio is 0.13%, which is below average.
- DFA Five-Year Global Fixed-Income I (DFGBX): This fund has a below-average risk rating and a below-average return profile per Morningstar. In the last 3 years/5 years/10 years, as of August 31, 2020, the fund has generated a return of 2.13%/2.20 %/which 2.25%indicating low but very steady returns across the period. The fund’s expense ratio is 0.26%, which is relatively higher.
- PIMCO Global Bond Opps (Unhedged) Instl (PIGLX): This fund has an average risk rating with an above-average return profile per Morningstar. In the last three years/ 5 years/ 10 years, as of August 31, 2020, the fund has generated a return of 2.40%/ 3.87%/ 3.09%indicating relatively volatile returns. The fund’s expense ratio is 0.67%, which is higher.
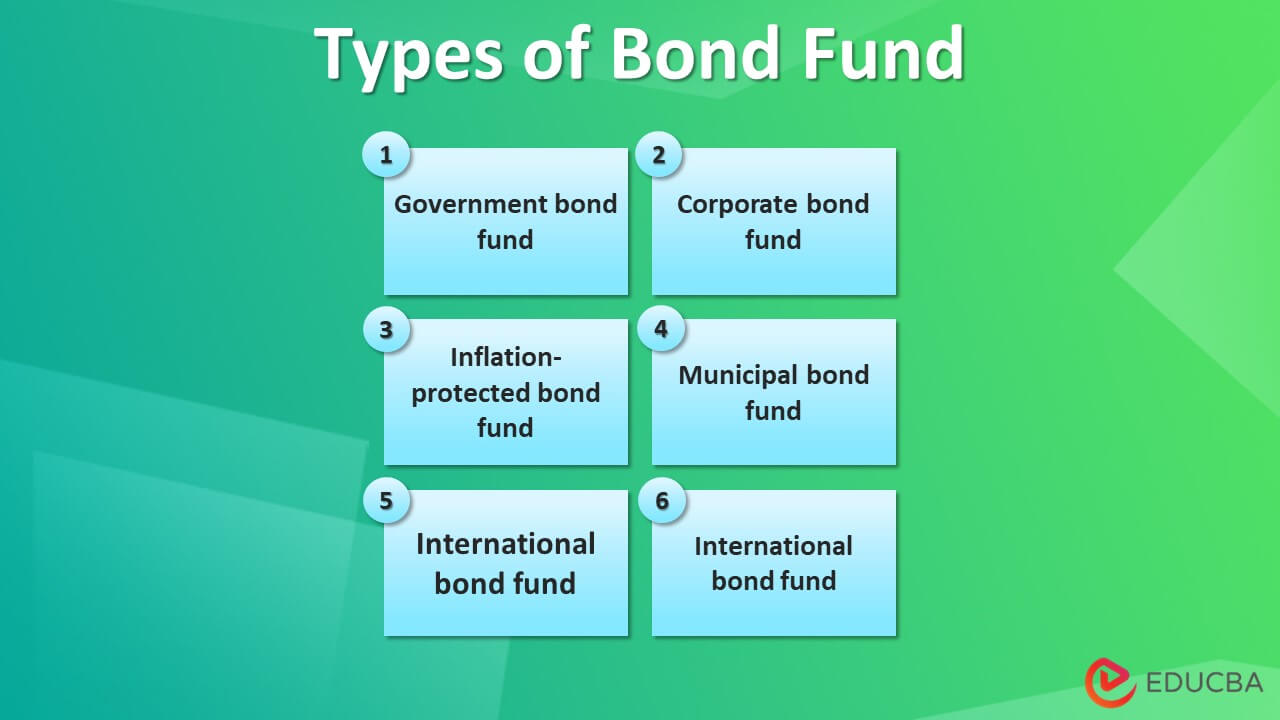
Types of Bond Funds
- Government bond fund: These types of funds invest in US government-backed bonds, such as T-bills, treasury notes, and mortgage-backed securities. The yield on these funds is usually on the lower side as the risk of default risk is almost zero.
- Corporate bond fund: High-quality corporate bonds, which offer a higher yield than government bond funds due to their relatively higher risk perception, invest these funds.
- Inflation-protected bond fund: These types of funds invest in Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS) mapped to the overall inflation rate in the US, usually Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation. As the name suggests, these funds help in hedging against inflation.
- Municipal bond fund: These funds are invested in local and state governments’ bonds. These are good investment options for people in higher income tax brackets as the bonds are free of all taxes (local, state, and federal taxes) if issued in the investors’ home state.
- International bond fund: In these types of bond funds, investments are made in bonds issued by foreign governments or corporations. As such, these funds help the investors reduce the interest rate and economic risk, given the exposure to various sovereign nations.
- Multisector bond fund: These types of funds invest in a wide range of taxable bonds, such as US Treasuries, high-yield bonds, corporate bonds, etc., and provide the highest degree of diversification to the investors.
Advantages
Some of the significant advantages are as follows:
- Investors can partake in bond funds much more quickly than individual bonds.
- The transaction costs are relatively less than what would be paid for buying the underlying individual bonds.
- Given that it is a pool of several bonds, the impact of a default in any one bond is hardly felt at the portfolio level. This is the benefit of diversification.
- The investors can withdraw or liquidate their investments at any point by selling the bond funds at the NAV.
- Professional fund managers with sufficient experience manage these funds.
Disadvantages
Some of the major disadvantages are as follows:
- The value of these funds fluctuates based on the prevailing interest rates in the market.
- These funds may not always be open to all investors as the fund managers may close the fund to new investors based on specific criteria.
- Unlike the interest payments of the underlying individual bonds, the dividend payments of the bond funds may be variable.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Bond Funds. We also discuss the introduction and how bond funds work with advantages and disadvantages. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –